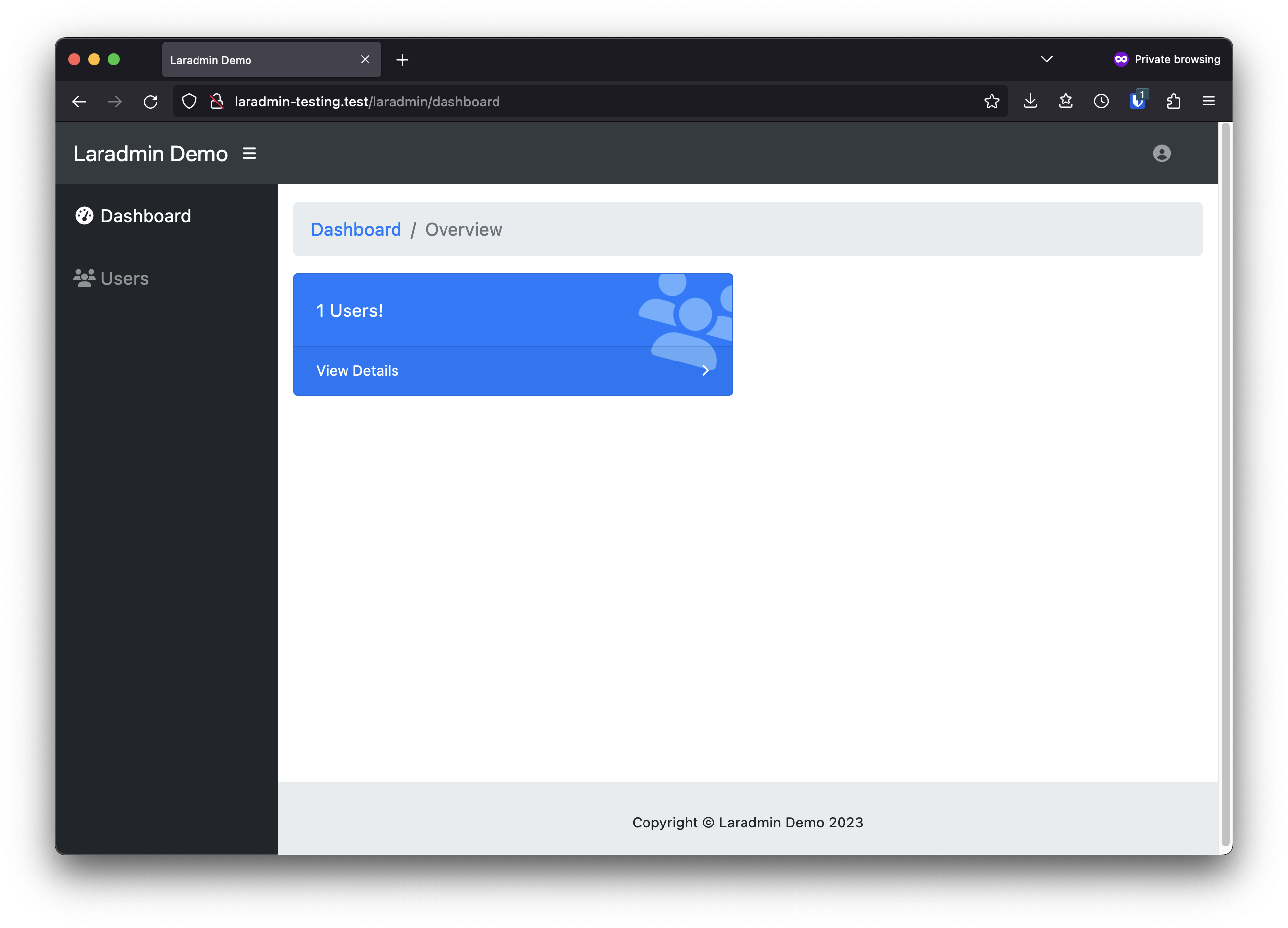
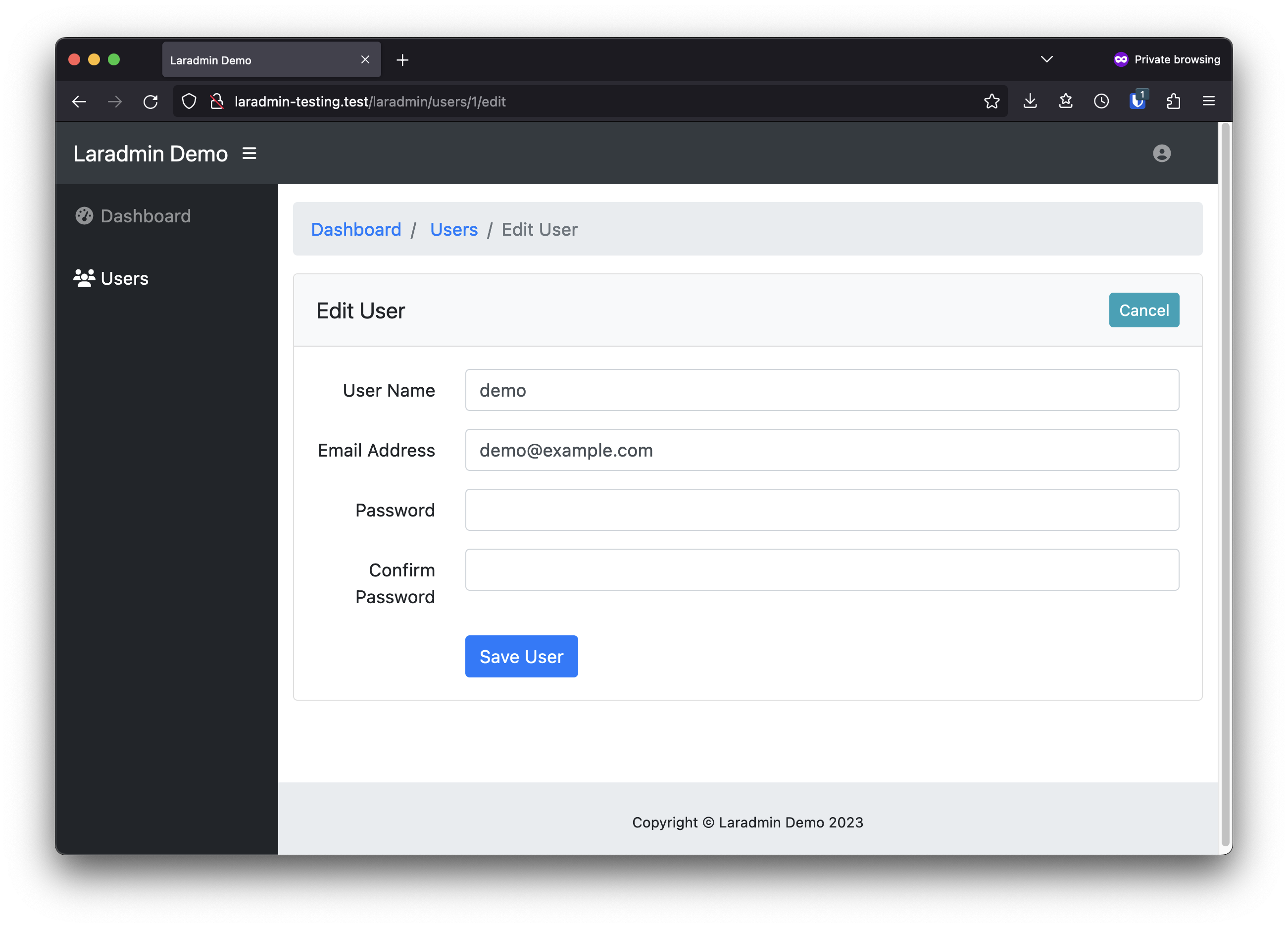
A simple, powerful, drop-in administrative interface for Laravel.
This project came about from a desire to have a simple administrative interface that could be dropped into a new or existing Laravel based site to manage any/all editable content.
IMPORTANT WARNING! This package is a work in progress. Over time, things may change. We will do our best not to break things, but please use it at your own risk.
- Installation
- Configuration Options
- Field Configuration
- Project Objectives & Goals
- Architecture Ideas
With composer, simply run the following on the commandline:
$ composer require warkensoft/laradmin:^2.0
$ php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Warkensoft\Laradmin\Provider" --tag=config --tag=public
This will install the package on your laravel application and publish a laradmin.php config file to your configuration
folder. You will use this file to configure how Laradmin will run on the application. It will also publish several
jQuery plugins needed by Laradmin to a /public/vendor/laradmin/ folder.
All the views used by the interface can be overridden as needed. To publish all customizable assets, use
$ php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Warkensoft\Laradmin\Provider"
A step by step example of how to install the package on a new Laravel installation is described here.
Out of the box Laradmin is very insecure, requiring only a logged in user to access the interface. Further security customization via middleware is highly recommended. Read more about securing Laradmin.
The following options are able to be customized in the laradmin.php configuration file.
Defines what middleware is required in order to see the Laradmin interface. Out of the box, it simply requires a logged-in user.
'middleware' => [ 'auth' ]
The base path for the Laradmin area. For example, the default would allow you to access the Laradmin interface at: https://yourdomain.com/laradmin/dashboard
'adminpath' => 'laradmin',
The base template used to display the Laradmin interface. You may replace this with your own if needed, however it would likely be better to use the view overrides instead by publishing the views and modifying them as needed.
'layout' => 'laradmin::layouts.admin',
Allows you to define how many entries are listed per page on model indexes.
'index-length' => 10,
Here is where you define what models will be editable in the Laradmin interface. The following example defines the \App\User model to be editable in Laradmin, what the path and routes will be, and the fields that will be displayed in order to edit the records. See Field Configuration for more details on the fields themselves.
'crudable' => [
// Sample entry for a standard laravel user record.
'\\App\\User' => [
'path' => 'users', // The path to the model under /laradmin/
'route' => 'users', // The route name used for the model
'nav_title' => 'Users', // The title used in the navigation sidebar
'plural' => 'Users', // The plural form of the model
'singular' => 'User', // The singular form of the model
'nav_icon' => 'fa-users', // The font-awesome icon for admin nav elements
// Fields used for model data
'fields' => [
[
'type' => \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Input::class,
'name' => 'name',
'label' => 'User Name',
'placeholder' => 'Somebody Smith',
'default' => '',
'rules' => 'required',
],
[
'type' => \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Input::class,
'name' => 'email',
'label' => 'Email Address',
'placeholder' => '[email protected]',
'default' => '',
'rules' => 'required',
],
[
'type' => \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Password::class,
'name' => 'password',
'label' => 'Password',
'placeholder' => 'Enter password here...',
'default' => '',
'rules' => 'confirmed',
'searchable' => false,
],
[
'type' => \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Password::class,
'name' => 'password_confirmation',
'label' => 'Confirm Password',
'placeholder' => 'Repeat password here...',
'default' => '',
'rules' => '',
'searchable' => false,
],
],
// Define what columns should appear on the model index. field=>label pairs
'index' => [
'id' => 'ID',
'name' => 'Name',
'email' => 'Email Address',
],
// Show a widget on the dashboard for this model.
'dashboard-widget' => [
'name',
'email',
'created_at',
],
// Define the default sort order for the model index and dashboard widget.
'sort' => [
'key' => 'name', // Sort field name
'dir' => 'asc', // Sort field direction
],
], // End of User definition
],
Each field that you want to allow to be modified by Laradmin must be defined as a field declaration in the fields array. These generally follow a pattern such as the following:
'type' => \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Input::class,
'name' => 'name',
'label' => 'User Name',
'placeholder' => 'Somebody Smith',
'default' => '',
'rules' => 'required',
The type variable defines a Field class in the Laradmin interface. The following classes currently exist.
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Input::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Password::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Textarea::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Select::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Checkbox::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\DateTime::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\ImageUpload::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\Summernote::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\SelectFromMany::class
- \Warkensoft\Laradmin\Fields\SelectManyFromMany::class
You may define additional classes in your own application as needed, so long as they conform to the FieldContract
interface. In this way you can extend the Laradmin platform with any additional types of fields you might need.
The purpose of the Field classes is two-fold. First, they should define the view to be used in displaying the field.
This is done through a simple view() method on the class which returns a string with the view name.
Second, they have the ability to filter and modify the submitted model data before it is saved, in order to make any necessary changes.
See the Laradmin Field Types & Configuration for specific details on how to configure each of these types of fields.
Laradmin security is controlled via middleware defined in the laradmin.php configuration file. Out of the box, it only
requires a logged in user by using the auth middleware. You may define additional middleware requirements by modifying
the value of the middleware parameter in the config. For example, you may wish to create a new middleware file that
requires logged in users to have an 'is_admin' parameter on there account, and only allow them access if it is set to
true.
Building middleware for Laravel is beyond the scope of this document, but may be researched further here in the Laravel documentation. https://laravel.com/docs/10.x/middleware
- Works with standard Laravel user authentication.
- Drops in as a simple dependency via composer.
- Fully overriddable by custom scripting in order to extend as needed.
- Clean & simple interface.
- Extensible to support any type of content data.
- Support common model relationships.
- Community driven.
- Entirely controlled through a config file.
- Config file defines list of models to support admin CRUD.
- Model config describes:
- validation rules
- text labels (plural, singular, ...)
- controller classname (if overridden)
- route name
- path
- displayed index fields (for use in the view)
- Config file defines each field on each model as to the following:
- Label
- Name
- Type (input, textarea, checkbox, radio, select, image upload, relationship, tags list, ...)
- Placeholder
- Default value
- Relationship details (if any)
- Field types are tied directly to view partials.