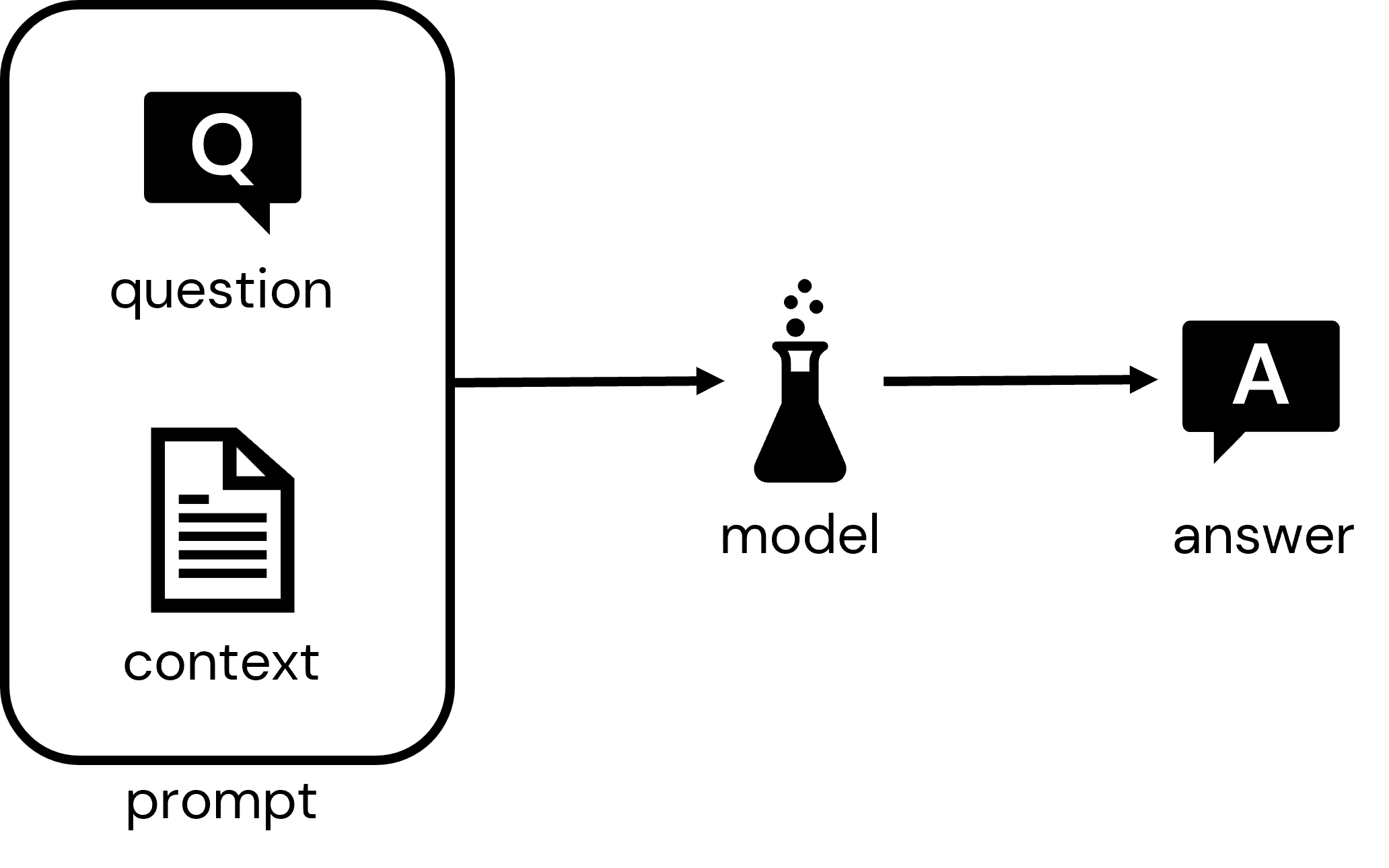
The goal of this solution accelerator is to show how we can leverage a large language model in combination with our own data to create an interactive application capable of answering questions specific to a particular domain or subject area. The core pattern behind this is the delivery of a question along with a document or document fragment that provides relevant context for answering that question to the model. The model will then respond with an answer that takes into consideration both the question and the context.
To aseemble this application, *i.e.* the Q&A Bot, we will need to assemble a series of documents that are relevant to the domain we wish to serve. We will need to index these to enable rapid search given a user question. We will then need to assemble the core application which combines a question with a document to form a prompt and submits that prompt to a model in order to generate a response. Finally, we'll need to package both the indexed documents and the core application component as a microservice to enable a wide range of deployment options.We will tackle these three steps across the following three notebooks:
- 01: Build Document Index
- 02: Assemble Application
- 03: Deploy Application
© 2023 Databricks, Inc. All rights reserved. The source in this notebook is provided subject to the Databricks License [https://databricks.com/db-license-source]. All included or referenced third party libraries are subject to the licenses set forth below.
| library | description | license | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| langchain | Building applications with LLMs through composability | MIT | https://pypi.org/project/langchain/ |
| tiktoken | Fast BPE tokeniser for use with OpenAI's models | MIT | https://pypi.org/project/tiktoken/ |
| faiss-cpu | Library for efficient similarity search and clustering of dense vectors | MIT | https://pypi.org/project/faiss-cpu/ |
| openai | Building applications with LLMs through composability | MIT | https://pypi.org/project/openai/ |
Although specific solutions can be downloaded as .dbc archives from our websites, we recommend cloning these repositories onto your databricks environment. Not only will you get access to latest code, but you will be part of a community of experts driving industry best practices and re-usable solutions, influencing our respective industries.
To start using a solution accelerator in Databricks simply follow these steps:
- Clone solution accelerator repository in Databricks using Databricks Repos
- Attach the
RUNMEnotebook to any cluster and execute the notebook via Run-All. A multi-step-job describing the accelerator pipeline will be created, and the link will be provided. The job configuration is written in the RUNME notebook in json format. - Execute the multi-step-job to see how the pipeline runs.
- You might want to modify the samples in the solution accelerator to your need, collaborate with other users and run the code samples against your own data. To do so start by changing the Git remote of your repository to your organization’s repository vs using our samples repository (learn more). You can now commit and push code, collaborate with other user’s via Git and follow your organization’s processes for code development.
The cost associated with running the accelerator is the user's responsibility.
Please note the code in this project is provided for your exploration only, and are not formally supported by Databricks with Service Level Agreements (SLAs). They are provided AS-IS and we do not make any guarantees of any kind. Please do not submit a support ticket relating to any issues arising from the use of these projects. The source in this project is provided subject to the Databricks License. All included or referenced third party libraries are subject to the licenses set forth below.
Any issues discovered through the use of this project should be filed as GitHub Issues on the Repo. They will be reviewed as time permits, but there are no formal SLAs for support.