- General info
- Supported Refactoring Types
- Contributors
- Current precision and recall
- How to build RefactoringMiner
- How to test RefactoringMiner
- How to use RefactoringMiner as a maven dependency
- How to use RefactoringMiner as a docker image
- How to use RefactoringMiner as a Chrome extension
- How to run RefactoringMiner from the command line
- Research
- Support for other programming languages
- Refactoring detection API usage guidelines
- AST Diff API usage guidelines
- Purity Checker
- Location information for the detected refactorings
- Statement matching information for the detected refactorings
RefactoringMiner is a library/API written in Java that can detect refactorings applied in the history of a Java project. Since version 3.0, RefactoringMiner can also generate Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) diff at commit and pull request level.
Currently, it supports the detection of the following refactorings:
supported by RefactoringMiner 1.0 and newer versions
- Extract Method
- Inline Method
- Rename Method
- Move Method
- Move Attribute
- Pull Up Method
- Pull Up Attribute
- Push Down Method
- Push Down Attribute
- Extract Superclass
- Extract Interface
- Move Class
- Rename Class
- Extract and Move Method
- Rename Package
Change Package (Move, Rename, Split, Merge)
supported by RefactoringMiner 2.0 and newer versions
- Move and Rename Class
- Extract Class
- Extract Subclass
- Extract Variable
- Inline Variable
- Parameterize Variable
- Rename Variable
- Rename Parameter
- Rename Attribute
- Move and Rename Attribute
- Replace Variable with Attribute
- Replace Attribute (with Attribute)
- Merge Variable
- Merge Parameter
- Merge Attribute
- Split Variable
- Split Parameter
- Split Attribute
- Change Variable Type
- Change Parameter Type
- Change Return Type
- Change Attribute Type
- Extract Attribute
- Move and Rename Method
- Move and Inline Method
supported by RefactoringMiner 2.1 and newer versions
- Add Method Annotation
- Remove Method Annotation
- Modify Method Annotation
- Add Attribute Annotation
- Remove Attribute Annotation
- Modify Attribute Annotation
- Add Class Annotation
- Remove Class Annotation
- Modify Class Annotation
- Add Parameter Annotation
- Remove Parameter Annotation
- Modify Parameter Annotation
- Add Variable Annotation
- Remove Variable Annotation
- Modify Variable Annotation
- Add Parameter
- Remove Parameter
- Reorder Parameter
- Add Thrown Exception Type
- Remove Thrown Exception Type
- Change Thrown Exception Type
- Change Method Access Modifier
supported by RefactoringMiner 2.2 and newer versions
- Change Attribute Access Modifier
- Encapsulate Attribute
- Parameterize Attribute
- Replace Attribute with Variable
- Add Method Modifier (
final,static,abstract,synchronized) - Remove Method Modifier (
final,static,abstract,synchronized) - Add Attribute Modifier (
final,static,transient,volatile) - Remove Attribute Modifier (
final,static,transient,volatile) - Add Variable Modifier (
final) - Add Parameter Modifier (
final) - Remove Variable Modifier (
final) - Remove Parameter Modifier (
final) - Change Class Access Modifier
- Add Class Modifier (
final,static,abstract) - Remove Class Modifier (
final,static,abstract) - Move Package
- Split Package
- Merge Package
- Localize Parameter
- Change Type Declaration Kind (
class,interface,enum,annotation,record) - Collapse Hierarchy
- Replace Loop with Pipeline
- Replace Anonymous with Lambda
supported by RefactoringMiner 2.3 and newer versions
- Merge Class
- Inline Attribute
- Replace Pipeline with Loop
supported by RefactoringMiner 2.4 and newer versions
- Split Class
- Split Conditional
- Invert Condition
- Merge Conditional
- Merge Catch
- Merge Method
- Split Method
supported by RefactoringMiner 3.0 and newer versions
- Move Code (between methods)
- Replace Anonymous with Class
- Parameterize Test (JUnit 5 @ParameterizedTest with @ValueSource)
- Assert Throws
- Replace Generic With Diamond
- Try With Resources
- Replace Conditional With Ternary
From Fowler's book (40)
1. Extract Method
2. Inline Method
3. Rename Method
4. Move Method
5. Move Attribute
6. Pull Up Method
7. Pull Up Attribute
8. Push Down Method
9. Push Down Attribute
10. Extract Superclass
11. Extract Interface
12. Move Class
13. Rename Class
14. Extract and Move Method
15. Rename Package
16. Move and Rename Class
17. Extract Class
18. Extract Subclass
19. Extract Variable
20. Inline Variable
21. Parameterize Variable
22. Extract Attribute
23. Move and Rename Method
24. Move and Inline Method
25. Encapsulate Attribute
26. Parameterize Attribute
27. Move Package
28. Split Package
29. Merge Package
30. Localize Parameter
31. Collapse Hierarchy
32. Merge Class
33. Inline Attribute
34. Split Class
35. Split Conditional
36. Invert Condition
37. Merge Conditional
38. Merge Method
39. Split Method
40. Move Code (between methods)
API changes (52)
1. Rename Variable
2. Rename Parameter
3. Rename Attribute
4. Move and Rename Attribute
5. Replace Variable with Attribute
6. Replace Attribute (with Attribute)
7. Merge Variable
8. Merge Parameter
9. Merge Attribute
10. Split Variable
11. Split Parameter
12. Split Attribute
13. Change Variable Type
14. Change Parameter Type
15. Change Return Type
16. Change Attribute Type
17. Add Method Annotation
18. Remove Method Annotation
19. Modify Method Annotation
20. Add Attribute Annotation
21. Remove Attribute Annotation
22. Modify Attribute Annotation
23. Add Class Annotation
24. Remove Class Annotation
25. Modify Class Annotation
26. Add Parameter Annotation
27. Remove Parameter Annotation
28. Modify Parameter Annotation
29. Add Variable Annotation
30. Remove Variable Annotation
31. Modify Variable Annotation
32. Add Parameter
33. Remove Parameter
34. Reorder Parameter
35. Add Thrown Exception Type
36. Remove Thrown Exception Type
37. Change Thrown Exception Type
38. Change Method Access Modifier
39. Change Attribute Access Modifier
40. Replace Attribute with Variable
41. Add Method Modifier (final, static, abstract, synchronized)
42. Remove Method Modifier (final, static, abstract, synchronized)
43. Add Attribute Modifier (final, static, transient, volatile)
44. Remove Attribute Modifier (final, static, transient, volatile)
45. Add Variable Modifier (final)
46. Add Parameter Modifier (final)
47. Remove Variable Modifier (final)
48. Remove Parameter Modifier (final)
49. Change Class Access Modifier
50. Add Class Modifier (final, static, abstract)
51. Remove Class Modifier (final, static, abstract)
52. Change Type Declaration Kind (class, interface, enum, annotation, record)
Migrations (8)
1. Replace Loop with Pipeline
2. Replace Anonymous with Lambda
3. Replace Pipeline with Loop
4. Merge Catch
5. Replace Anonymous with Class
6. Replace Generic With Diamond
7. Try With Resources
8. Replace Conditional With Ternary
Test-specific (2)
1. Parameterize Test (JUnit 5 @ParameterizedTest with @ValueSource)
2. Assert Throws
- Nikolaos Tsantalis: Core + APIs
- Danilo Ferreira e Silva: Git repository mining infrastructure + APIs
- Pouria Alikhani Fard: AST diff + AST diff benchmark
- Victor Veloso: Test-specific refactoring detection
- Pedram Nouri: Refactoring purity checker
- Tayeeb Hasan: CodeTracker - block tracking + CodeTracker Chrome extension
- Mehran Jodavi: CodeTracker - method & variable tracking
- Sadegh Aalizadeh: Refactoring motivation detection
- Hassan Mansour: Refactoring Aware Commit Review Chrome extension
- Ameya Ketkar: Refactoring oracle 2.0 validation
- Davood Mazinanian: Refactoring oracle web application + Refactoring oracle 1.0 validation
- Matin Mansouri: Rename Variable detection + Refactoring oracle 1.0 validation
- Laleh M. Eshkevari: Refactoring oracle 1.0 validation
As of January 4, 2025 the precision and recall of the tool on an oracle consisting of 547 commits from 188 open-source projects is:
| Refactoring Type | TP | FP | FN | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 12401 | 20 | 226 | 0.998 | 0.982 |
| Extract Method | 1007 | 1 | 22 | 0.999 | 0.979 |
| Rename Class | 56 | 0 | 2 | 1.000 | 0.966 |
| Move Attribute | 255 | 2 | 8 | 0.992 | 0.970 |
| Move And Rename Attribute | 16 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Attribute | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Rename Method | 388 | 4 | 21 | 0.990 | 0.949 |
| Inline Method | 118 | 0 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.992 |
| Move Method | 386 | 3 | 6 | 0.992 | 0.985 |
| Move And Rename Method | 128 | 0 | 4 | 1.000 | 0.970 |
| Pull Up Method | 288 | 0 | 5 | 1.000 | 0.983 |
| Move Class | 1095 | 0 | 4 | 1.000 | 0.996 |
| Move And Rename Class | 38 | 0 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.974 |
| Move Source Folder | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Pull Up Attribute | 139 | 0 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.993 |
| Push Down Attribute | 35 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Push Down Method | 45 | 0 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.978 |
| Extract Interface | 22 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Extract Superclass | 74 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Extract Subclass | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Extract Class | 106 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Extract And Move Method | 119 | 0 | 61 | 1.000 | 0.661 |
| Move And Inline Method | 13 | 0 | 4 | 1.000 | 0.765 |
| Replace Anonymous With Class | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Rename Package | 16 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Move Package | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Extract Variable | 304 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Extract Attribute | 23 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Inline Variable | 110 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Inline Attribute | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Rename Variable | 333 | 3 | 11 | 0.991 | 0.968 |
| Rename Parameter | 493 | 2 | 24 | 0.996 | 0.954 |
| Rename Attribute | 146 | 0 | 9 | 1.000 | 0.942 |
| Merge Variable | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Merge Parameter | 28 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Merge Attribute | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Split Variable | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Split Parameter | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Split Attribute | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Variable With Attribute | 123 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Attribute With Variable | 28 | 0 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.966 |
| Parameterize Variable | 111 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Localize Parameter | 26 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Parameterize Attribute | 23 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Change Return Type | 433 | 0 | 12 | 1.000 | 0.973 |
| Change Variable Type | 807 | 2 | 7 | 0.998 | 0.991 |
| Change Parameter Type | 653 | 1 | 10 | 0.998 | 0.985 |
| Change Attribute Type | 244 | 0 | 8 | 1.000 | 0.968 |
| Add Method Annotation | 332 | 0 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.997 |
| Remove Method Annotation | 100 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Modify Method Annotation | 29 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Attribute Annotation | 62 | 0 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.984 |
| Remove Attribute Annotation | 18 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Modify Attribute Annotation | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Class Annotation | 52 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Class Annotation | 20 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Modify Class Annotation | 35 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Parameter Annotation | 34 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Parameter Annotation | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Modify Parameter Annotation | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Parameter | 849 | 2 | 1 | 0.998 | 0.999 |
| Remove Parameter | 311 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Reorder Parameter | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Variable Annotation | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Variable Annotation | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Thrown Exception Type | 41 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Thrown Exception Type | 270 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Change Thrown Exception Type | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Change Method Access Modifier | 332 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Change Attribute Access Modifier | 231 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Encapsulate Attribute | 49 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Method Modifier | 89 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Method Modifier | 111 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Attribute Modifier | 142 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Attribute Modifier | 143 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Variable Modifier | 135 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Parameter Modifier | 133 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Variable Modifier | 62 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Parameter Modifier | 39 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Change Class Access Modifier | 78 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Add Class Modifier | 37 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Remove Class Modifier | 45 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Split Package | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Merge Package | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Change Type Declaration Kind | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Collapse Hierarchy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Loop With Pipeline | 35 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Pipeline With Loop | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Anonymous With Lambda | 45 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Merge Class | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Split Class | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Split Conditional | 19 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Invert Condition | 33 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Merge Conditional | 14 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Merge Catch | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Merge Method | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Split Method | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Move Code | 19 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Assert Throws | 14 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Try With Resources | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Generic With Diamond | 77 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Replace Conditional With Ternary | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
Since release 3.0.0, RefactoringMiner requires Java 17 or newer and Gradle 7.4 or newer.
In order to build the project, run ./gradlew jar (or gradlew jar, in Windows) in the project's root directory.
Alternatively, you can generate a complete distribution zip including all runtime dependencies running ./gradlew distZip.
You can also work with the project with Eclipse IDE. First, run ./gradlew eclipse to generate Eclipse project metadata files. Then, import it into Eclipse using the Import Existing Project feature.
As of release 3.0, all RefactoringMiner tests have been migrated to JUnit 5 and do not require any more to clone repositories.
Moreover, all unit tests can be executed in parallel. The more CPU cores, the faster the test suites will execute.
You can run gradle test to execute all tests.
The available test suites are:
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/test/TestAllRefactorings : Tests the overall precision and recall of RefactoringMiner on the Refactoring Oracle (547 commits)
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/test/TestAllRefactoringsByCommit : Tests the number of True Positives, False Positives and False Negatives, separately for each commit of the Refactoring Oracle (547 commits)
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/test/TestStatementMappings: Tests the statement mapping accuracy of RefactoringMiner (125 commits)
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/test/TestJavadocDiff: Tests the comment and Javadoc mapping accuracy of RefactoringMiner
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/test/TestCommandLine: Tests the command-line functionality of RefactoringMiner
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/test/TestParameterizeTestRefactoring: Tests the Parameterize Test Refactoring detection
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/astDiff/tests/Defects4JPerfectDiffTest: Tests the AST node mapping accuracy of RefactoringMiner on the Defects4J dataset
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/astDiff/tests/RefactoringOraclePerfectDiffTest: Tests the AST node mapping accuracy of RefactoringMiner on the Refactoring Oracle dataset
- src/test/java/org/refactoringminer/astDiff/tests/SpecificCasesTest: Tests the AST node mapping accuracy of RefactoringMiner on some specific cases
Since version 2.0, RefactoringMiner is available in the Maven Central Repository. In order to use RefactoringMiner as a maven dependency in your project, add the following snippet to your project's build configuration file:
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.tsantalis</groupId>
<artifactId>refactoring-miner</artifactId>
<version>3.0.10</version>
</dependency>
build.gradle
implementation 'com.github.tsantalis:refactoring-miner:3.0.10'
Since version 3.0, RefactoringMiner is available in DockerHub. A new image is created automatically on every Monday midnight. You can find detailed instructions on how to install and use the image at Docker README.
If you want to get refactoring information when inspecting a commit on GitHub, you can install our Refactoring Aware Commit Review Chrome extension.
The Chrome extension can detect refactorings for public projects and commits matching the following URL patterns:
https://github.com/user/project/commit/idhttps://github.com/user/project/pull/id/commits/id
When you build a distributable application with ./gradlew distZip, you can run Refactoring Miner as a command line application. Extract the file under build/distribution/RefactoringMiner-version.zip in the desired location, and cd into the bin folder (or include it in your path). Then, run RefactoringMiner -h to show its usage:
> ./RefactoringMiner -h
-h Show options
-a <git-repo-folder> <branch> -json <path-to-json-file> Detect all refactorings at <branch> for <git-repo-folder>. If <branch> is not specified, commits from all branches are analyzed.
-bc <git-repo-folder> <start-commit-sha1> <end-commit-sha1> -json <path-to-json-file> Detect refactorings between <start-commit-sha1> and <end-commit-sha1> for project <git-repo-folder>
-bt <git-repo-folder> <start-tag> <end-tag> -json <path-to-json-file> Detect refactorings between <start-tag> and <end-tag> for project <git-repo-folder>
-c <git-repo-folder> <commit-sha1> -json <path-to-json-file> Detect refactorings at specified commit <commit-sha1> for project <git-repo-folder>
-gc <git-URL> <commit-sha1> <timeout> -json <path-to-json-file> Detect refactorings at specified commit <commit-sha1> for project <git-URL> within the given <timeout> in seconds. All required information is obtained directly from GitHub using the OAuth token in github-oauth.properties
-gp <git-URL> <pull-request> <timeout> -json <path-to-json-file> Detect refactorings at specified pull request <pull-request> for project <git-URL> within the given <timeout> in seconds for each commit in the pull request. All required information is obtained directly from GitHub using the OAuth token in github-oauth.properties
With a locally cloned repository, run:
> git clone https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git refactoring-toy-example
> ./RefactoringMiner -c refactoring-toy-example 36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd
If you don't want to clone locally the repository, run:
> ./RefactoringMiner -gc https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git 36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd 10
For all options you can add the -json <path-to-json-file> command arguments to save the JSON output in a file. The results are appended to the file after each processed commit.
For the -gc and -gp options you must provide a valid OAuth token in the github-oauth.properties file stored in the bin folder.
You can generate an OAuth token in GitHub Settings -> Developer settings -> Personal access tokens.
In both cases, you will get the output in JSON format:
{
"commits": [{
"repository": "https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git",
"sha1": "36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd",
"url": "https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example/commit/36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd",
"refactorings": [{
"type": "Pull Up Attribute",
"description": "Pull Up Attribute private age : int from class org.animals.Labrador to class org.animals.Dog",
"leftSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Labrador.java",
"startLine": 5,
"endLine": 5,
"startColumn": 14,
"endColumn": 21,
"codeElementType": "FIELD_DECLARATION",
"description": "original attribute declaration",
"codeElement": "age : int"
}],
"rightSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Dog.java",
"startLine": 5,
"endLine": 5,
"startColumn": 14,
"endColumn": 21,
"codeElementType": "FIELD_DECLARATION",
"description": "pulled up attribute declaration",
"codeElement": "age : int"
}]
},
{
"type": "Pull Up Attribute",
"description": "Pull Up Attribute private age : int from class org.animals.Poodle to class org.animals.Dog",
"leftSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Poodle.java",
"startLine": 5,
"endLine": 5,
"startColumn": 14,
"endColumn": 21,
"codeElementType": "FIELD_DECLARATION",
"description": "original attribute declaration",
"codeElement": "age : int"
}],
"rightSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Dog.java",
"startLine": 5,
"endLine": 5,
"startColumn": 14,
"endColumn": 21,
"codeElementType": "FIELD_DECLARATION",
"description": "pulled up attribute declaration",
"codeElement": "age : int"
}]
},
{
"type": "Pull Up Method",
"description": "Pull Up Method public getAge() : int from class org.animals.Labrador to public getAge() : int from class org.animals.Dog",
"leftSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Labrador.java",
"startLine": 7,
"endLine": 9,
"startColumn": 2,
"endColumn": 3,
"codeElementType": "METHOD_DECLARATION",
"description": "original method declaration",
"codeElement": "public getAge() : int"
}],
"rightSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Dog.java",
"startLine": 7,
"endLine": 9,
"startColumn": 2,
"endColumn": 3,
"codeElementType": "METHOD_DECLARATION",
"description": "pulled up method declaration",
"codeElement": "public getAge() : int"
}]
},
{
"type": "Pull Up Method",
"description": "Pull Up Method public getAge() : int from class org.animals.Poodle to public getAge() : int from class org.animals.Dog",
"leftSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Poodle.java",
"startLine": 7,
"endLine": 9,
"startColumn": 2,
"endColumn": 3,
"codeElementType": "METHOD_DECLARATION",
"description": "original method declaration",
"codeElement": "public getAge() : int"
}],
"rightSideLocations": [{
"filePath": "src/org/animals/Dog.java",
"startLine": 7,
"endLine": 9,
"startColumn": 2,
"endColumn": 3,
"codeElementType": "METHOD_DECLARATION",
"description": "pulled up method declaration",
"codeElement": "public getAge() : int"
}]
}
]
}]
}
When you build a distributable application with ./gradlew distZip, you can run Refactoring Miner as a command line application. Extract the file under build/distribution/RefactoringMiner-version.zip in the desired location, and cd into the bin folder (or include it in your path). Then, run RefactoringMiner diff -h to show its usage:
> ./RefactoringMiner diff -h
--url <commit-url> Run the diff with a GitHub commit url
--url <pr-url> Run the diff with a GitHub PullRequest url
--src <folder1> --dst <folder2> Run the diff with two local directories
--repo <repo-folder-path> --commit <commitID> Run the diff with a locally cloned GitHub repository
Each command creates a jetty server instance to visualize the AST diff in your web browser http://127.0.0.1:6789
To export the mappings/actions, add --export to the end of the command. The files are saved by default in the RefactoringMiner bin directory.
For example, to visualize the diff of a GitHub Pull Request, run
> ./RefactoringMiner diff --url https://github.com/JabRef/jabref/pull/11180
To visualize the diff of a GitHub commit, run
> ./RefactoringMiner diff --url https://github.com/JetBrains/intellij-community/commit/7ed3f273ab0caf0337c22f0b721d51829bb0c877
For the --url option you must provide a valid OAuth token in the github-oauth.properties file stored in the bin folder.
You can generate an OAuth token in GitHub Settings -> Developer settings -> Personal access tokens.
If you are using RefactoringMiner in your research, please cite the following papers:
Nikolaos Tsantalis, Matin Mansouri, Laleh Eshkevari, Davood Mazinanian, and Danny Dig, "Accurate and Efficient Refactoring Detection in Commit History," 40th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2018), Gothenburg, Sweden, May 27 - June 3, 2018.
@inproceedings{Tsantalis:ICSE:2018:RefactoringMiner,
author = {Tsantalis, Nikolaos and Mansouri, Matin and Eshkevari, Laleh M. and Mazinanian, Davood and Dig, Danny},
title = {Accurate and Efficient Refactoring Detection in Commit History},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Software Engineering},
series = {ICSE '18},
year = {2018},
isbn = {978-1-4503-5638-1},
location = {Gothenburg, Sweden},
pages = {483--494},
numpages = {12},
url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3180155.3180206},
doi = {10.1145/3180155.3180206},
acmid = {3180206},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
keywords = {Git, Oracle, abstract syntax tree, accuracy, commit, refactoring},
}
Nikolaos Tsantalis, Ameya Ketkar, and Danny Dig, "RefactoringMiner 2.0," IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, vol. 48, no. 3, pp. 930-950, March 2022.
@article{Tsantalis:TSE:2020:RefactoringMiner2.0,
author = {Tsantalis, Nikolaos and Ketkar, Ameya and Dig, Danny},
title = {RefactoringMiner 2.0},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering},
year = {2022},
volume = {48},
number = {3},
pages = {930-950},
doi = {10.1109/TSE.2020.3007722}
}
Pouria Alikhanifard and Nikolaos Tsantalis, "A Novel Refactoring and Semantic Aware Abstract Syntax Tree Differencing Tool and a Benchmark for Evaluating the Accuracy of Diff Tools," ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, 2024. (accepted)
@article{Alikhanifard:TOSEM:2024:RefactoringMiner3.0,
author = {Alikhanifard, Pouria and Tsantalis, Nikolaos},
title = {A Novel Refactoring and Semantic Aware Abstract Syntax Tree Differencing Tool and a Benchmark for Evaluating the Accuracy of Diff Tools},
year = {2024},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
issn = {1049-331X},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3696002},
doi = {10.1145/3696002},
note = {Just Accepted},
journal = {ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology},
month = {sep},
keywords = {Source code differencing, Abstract Syntax Trees, Benchmark}
}
Keynote at the Fifth International Workshop on Refactoring (IWoR 2021)
RefactoringMiner has been used in the following studies:
- Danilo Silva, Nikolaos Tsantalis, and Marco Tulio Valente, "Why We Refactor? Confessions of GitHub Contributors," 24th ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering (FSE 2016), Seattle, WA, USA, November 13-18, 2016.
- Davood Mazinanian, Ameya Ketkar, Nikolaos Tsantalis, and Danny Dig, "Understanding the use of lambda expressions in Java", Proceedings of the ACM on Programming Languages, vol. 1, issue OOPSLA, Article 85, 31 pages, October 2017.
- Diego Cedrim, Alessandro Garcia, Melina Mongiovi, Rohit Gheyi, Leonardo Sousa, Rafael de Mello, Baldoino Fonseca, Márcio Ribeiro, and Alexander Chávez, "Understanding the impact of refactoring on smells: a longitudinal study of 23 software projects," 11th Joint Meeting on Foundations of Software Engineering (ESEC/FSE 2017), Paderborn, Germany, September 4-8, 2017.
- Alexander Chávez, Isabella Ferreira, Eduardo Fernandes, Diego Cedrim, and Alessandro Garcia, "How does refactoring affect internal quality attributes?: A multi-project study," 31st Brazilian Symposium on Software Engineering (SBES 2017), Fortaleza, CE, Brazil, September 20-22, 2017.
- Navdeep Singh, and Paramvir Singh, "How Do Code Refactoring Activities Impact Software Developers' Sentiments? - An Empirical Investigation Into GitHub Commits," 24th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC 2017), Nanjing, Jiangsu, China, December 4-8, 2017.
- Mehran Mahmoudi, and Sarah Nadi, "The Android Update Problem: An Empirical Study," 15th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories (MSR 2018), Gothenburg, Sweden, May 28-29, 2018.
- Anthony Peruma, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, Michael J. Decker, and Christian D. Newman, "An empirical investigation of how and why developers rename identifiers," 2nd International Workshop on Refactoring (IWoR 2018), Montpellier, France, September 4, 2018.
- Patanamon Thongtanunam, Weiyi Shang, and Ahmed E. Hassan, "Will this clone be short-lived? Towards a better understanding of the characteristics of short-lived clones," Empirical Software Engineering, Volume 24, Issue 2, pp. 937–972, April 2019.
- Isabella Ferreira, Eduardo Fernandes, Diego Cedrim, Anderson Uchôa, Ana Carla Bibiano, Alessandro Garcia, João Lucas Correia, Filipe Santos, Gabriel Nunes, Caio Barbosa, Baldoino Fonseca, and Rafael de Mello, "The buggy side of code refactoring: understanding the relationship between refactorings and bugs," 40th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings (ICSE 2018), Gothenburg, Sweden, May 27-June 3, 2018.
- Matheus Paixao, "Software Restructuring: Understanding Longitudinal Architectural Changes and Refactoring," Ph.D. thesis, Computer Science Department, University College London, July 2018.
- Mehran Mahmoudi, Sarah Nadi, and Nikolaos Tsantalis, "Are Refactorings to Blame? An Empirical Study of Refactorings in Merge Conflicts," 26th IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER 2019), Hangzhou, China, February 24-27, 2019.
- Bin Lin, Csaba Nagy, Gabriele Bavota and Michele Lanza, "On the Impact of Refactoring Operations on Code Naturalness," 26th IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER 2019), Hangzhou, China, February 24-27, 2019.
- Sarah Fakhoury, Devjeet Roy, Sk. Adnan Hassan, and Venera Arnaoudova, "Improving Source Code Readability: Theory and Practice," 27th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC 2019), Montreal, QC, Canada, May 25-26, 2019.
- Carmine Vassallo, Giovanni Grano, Fabio Palomba, Harald C. Gall, and Alberto Bacchelli, "A large-scale empirical exploration on refactoring activities in open source software projects," Science of Computer Programming, Volume 180, Pages 1-15, July 2019.
- Eman Abdullah AlOmar, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, and Ali Ouni, "Can refactoring be self-affirmed?: An exploratory study on how developers document their refactoring activities in commit messages," 3rd International Workshop on Refactoring (IWOR 2019), Montreal, QC, Canada, May 28, 2019.
- Ana Carla Bibiano, Eduardo Fernandes, Daniel Oliveira, Alessandro Garcia, Marcos Kalinowski, Baldoino Fonseca, Roberto Oliveira, Anderson Oliveira, and Diego Cedrim, "A Quantitative Study on Characteristics and Effect of Batch Refactoring on Code Smells," 13th ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (ESEM 2019), Porto de Galinhas, Brazil, September 16-20, 2019.
- Eman Abdullah AlOmar, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, Ali Ouni, and Marouane Kessentini, "On the Impact of Refactoring on the Relationship between Quality Attributes and Design Metrics," 13th ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (ESEM 2019), Porto de Galinhas, Brazil, September 16-20, 2019.
- Edmilson Campos Neto, Daniel Alencar da Costa, and Uirá Kulesza, "Revisiting and Improving SZZ Implementations," 13th ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (ESEM 2019), Porto de Galinhas, Brazil, September 16-20, 2019.
- Valentina Lenarduzzi, Nyyti Saarimäki, and Davide Taibi, "The Technical Debt Dataset," 15th International Conference on Predictive Models and Data Analytics in Software Engineering (PROMISE 2019), Porto de Galinhas, Brazil, September 18, 2019.
- Anthony Peruma, "A preliminary study of Android refactorings," 6th International Conference on Mobile Software Engineering and Systems (MOBILESoft 2019), Montreal, Quebec, Canada, May 25-26, 2019.
- Anthony Peruma, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, Michael J. Decker, and Christian D. Newman, "Contextualizing Rename Decisions using Refactorings and Commit Messages," 19th IEEE International Working Conference on Source Code Analysis and Manipulation (SCAM 2019), Cleveland, OH, USA, September 30-October 1, 2019.
- Soumaya Rebai, Oussama Ben Sghaier, Vahid Alizadeh, Marouane Kessentini, and Meriem Chater, "Interactive Refactoring Documentation Bot," 19th IEEE International Working Conference on Source Code Analysis and Manipulation (SCAM 2019), Cleveland, OH, USA, September 30-October 1, 2019.
- Matheus Paixao, and Paulo Henrique Maia, "Rebasing in Code Review Considered Harmful: A Large-Scale Empirical Investigation," 19th IEEE International Working Conference on Source Code Analysis and Manipulation (SCAM 2019), Cleveland, OH, USA, September 30-October 1, 2019.
- Willian Oizumi, Leonardo Da Silva Sousa, Anderson Oliveira, Luiz Matheus Alencar, Alessandro Garcia, Thelma E. Colanzi and Roberto Oliveira, "On the density and diversity of degradation symptoms in refactored classes: A multi-case study," 30th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE 2019), Berlin, Germany, October 28-31, 2019.
- Marcos César de Oliveira, Davi Freitas, Rodrigo Bonifácio, Gustavo Pinto, and David Lo, "Finding Needles in a Haystack: Leveraging Co-change Dependencies to Recommend Refactorings," Journal of Systems and Software, Volume 158, December 2019.
- Walter Lucas, Rodrigo Bonifácio, Edna Dias Canedo, Diego Marcílio, and Fernanda Lima, "Does the Introduction of Lambda Expressions Improve the Comprehension of Java Programs?," XXXIII Brazilian Symposium on Software Engineering (SBES 2019), Salvador, Brazil, September 23-27, 2019.
- Bo Shen, Wei Zhang, Haiyan Zhao, Guangtai Liang, Zhi Jin, and Qianxiang Wang, "IntelliMerge: A Refactoring-Aware Software Merging Technique," Proceedings of the ACM on Programming Languages, vol. 3, OOPSLA, Article 170, October 2019.
- Martina Iammarino, Fiorella Zampetti, Lerina Aversano, and Massimiliano Di Penta, "Self-Admitted Technical Debt Removal and Refactoring Actions: Co-Occurrence or More?," 35th IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME 2019), Cleveland, OH, USA, September 29-October 4, 2019.
- Ally S. Nyamawe, Hui Liu, Nan Niu, Qasim Umer, and Zhendong Niu, "Automated Recommendation of Software Refactorings based on Feature Requests," 27th IEEE International Requirements Engineering Conference (RE 2019), Jeju Island, South Korea, September 23-27, 2019.
- Maurício Aniche, Erick Maziero, Rafael Durelli, and Vinicius Durelli, "The Effectiveness of Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Software Refactoring," IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2020.
- Ana Bibiano, Vinicius Soares, Daniel Coutinho, Eduardo Fernandes, João Correia, Kleber Tarcísio, Anderson Oliveira, Alessandro Garcia, Rohit Gheyi, Marcio Ribeiro, Baldoino Fonseca, Caio Barbosa, and Daniel Oliveira, "How Does Incomplete Composite Refactoring Affect Internal Quality Attributes?," 28th IEEE International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Leonardo Sousa, Willian Oizumi, Alessandro Garcia, Anderson Oliveira, Diego Cedrim, and Carlos Lucena, "When Are Smells Indicators of Architectural Refactoring Opportunities? A Study of 50 Software Projects," 28th IEEE International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Devjeet Roy, Sarah Fakhoury, John Lee, and Venera Arnaoudova, "A Model to Detect Readability Improvements in Incremental Changes," 28th IEEE International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Akira Fujimoto, Yoshiki Higo, Junnosuke Matsumoto, and Shinji Kusumoto, "Staged Tree Matching for Detecting Code Move across Files," 28th IEEE International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Matheus Paixão, Anderson Uchôa, Ana Carla Bibiano, Daniel Oliveira, Alessandro Garcia, Jens Krinke, and Emilio Arvonio, "Behind the Intents: An In-depth Empirical Study on Software Refactoring in Modern Code Review," 17th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories (MSR 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Leonardo da Silva Sousa, Diego Cedrim, Alessandro Garcia, Willian Oizumi, Ana Carla Bibiano, Daniel Oliveira, Miryung Kim, and Anderson Oliveira, "Characterizing and Identifying Composite Refactorings: Concepts, Heuristics and Patterns," 17th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories (MSR 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Anthony Peruma, Christian D. Newman, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, Ali Ouni, and Fabio Palomba, "An Exploratory Study on the Refactoring of Unit Test Files in Android Applications," 4th International Workshop on Refactoring (IWoR 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Eman Abdullah AlOmar, Anthony Peruma, Christian D. Newman, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, and Ali Ouni, "On the Relationship Between Developer Experience and Refactoring: An Exploratory Study and Preliminary Results," 4th International Workshop on Refactoring (IWoR 2020), Seoul, South Korea, 2020.
- Yoshiki Higo, Shinpei Hayashi, and Shinji Kusumoto, "On Tracking Java Methods with Git Mechanisms," Journal of Systems and Software, Volume 165, July 2020.
- Eduardo Fernandes, Alexander Chávez, Alessandro Garcia, Isabella Ferreira, Diego Cedrim, Leonardo Sousa, and Willian Oizumi, "Refactoring Effect on Internal Quality Attributes: What Haven't They Told You Yet?," Information and Software Technology, 2020.
- Rrezarta Krasniqi, and Jane Cleland-Huang, "Enhancing Source Code Refactoring Detection with Explanations from Commit Messages," IEEE 27th International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER 2020), London, ON, Canada, February 18-21, 2020.
- Anthony Peruma, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, Michael J.Decker, and Christian D.Newman, "Contextualizing rename decisions using refactorings, commit messages, and data types," Journal of Systems and Software, Volume 169, November 2020.
- Lerina Aversano, Umberto Carpenito, and Martina Iammarino, "An Empirical Study on the Evolution of Design Smells," Information, vol. 11, no. 7:348, 2020.
- Jevgenija Pantiuchina, Fiorella Zampetti, Simone Scalabrino, Valentina Piantadosi, Rocco Oliveto, Gabriele Bavota, and Massimiliano Di Penta, "Why Developers Refactor Source Code: A Mining-based Study," ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, Volume 29, Issue 4, Article 29, September 2020.
- Ally S. Nyamawe, Hui Liu, Nan Niu, Qasim Umer, and Zhendong Niu, "Feature requests-based recommendation of software refactorings," Empirical Software Engineering, Volume 25, pp. 4315–4347, 2020.
- Eman Abdullah AlOmar, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, and Ali Ouni, "Toward the automatic classification of Self-Affirmed Refactoring," Journal of Systems and Software, Volume 171, January 2021.
- Vinícius Soares, Anderson Oliveira, Juliana Alves Pereira, Ana Carla Bibano, Alessandro Garcia, Paulo Roberto Farah, Silvia Regina Vergilio, Marcelo Schots, Caio Silva, Daniel Coutinho, Daniel Oliveira, and Anderson Uchôa, "On the Relation between Complexity, Explicitness, Effectiveness of Refactorings and Non-Functional Concerns," 34th Brazilian Symposium on Software Engineering (SBES 2020), October 19–23, 2020.
- Willian Oizumi, Diego Cedrim, Leonardo Sousa, Ana Carla Bibiano, Anderson Oliveira, Alessandro Garcia, and Daniel Oliveira, "Recommending Composite Refactorings for Smell Removal: Heuristics and Evaluation," 34th Brazilian Symposium on Software Engineering (SBES 2020), October 19–23, 2020.
- Massimiliano Di Penta, Gabriele Bavota, and Fiorella Zampetti, "On the Relationship between Refactoring Actions and Bugs: A Differentiated Replication," ACM Joint European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering (ESEC/FSE 2020), Sacramento, California, United States, November 8-13, 2020.
- Ameya Ketkar, Nikolaos Tsantalis, and Danny Dig, "Understanding Type Changes in Java," ACM Joint European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering (ESEC/FSE 2020), Sacramento, California, United States, November 8-13, 2020.
- Zhongxin Liu, Xin Xia, Meng Yan, and Shanping Li, "Automating Just-In-Time Comment Updating," 35th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE 2020), September 21–25, 2020.
- Zadia Codabux and Christopher Dutchyn, "Profiling Developers Through the Lens of Technical Debt," ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (ESEM 2020), October 8–9, 2020, Bari, Italy.
- Yiming Tang, Raffi Khatchadourian, Mehdi Bagherzadeh, Rhia Singh, Ajani Stewart, and Anita Raja, "An Empirical Study of Refactorings and Technical Debt in Machine Learning Systems," 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2021), Madrid, Spain, May 25-28, 2021.
- Dong Jae Kim, Nikolaos Tsantalis, Tse-Hsun (Peter) Chen, and Jinqiu Yang, "Studying Test Annotation Maintenance in the Wild," 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2021), Madrid, Spain, May 25-28, 2021.
- Yanjie Jiang, Hui Liu, Nan Niu, Lu Zhang, and Yamin Hu, "Extracting Concise Bug-Fixing Patches from Human-Written Patches in Version Control Systems," 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2021), Madrid, Spain, May 25-28, 2021.
- Giovanni Rosa, Luca Pascarella, Simone Scalabrino, Rosalia Tufano, Gabriele Bavota, Michele Lanza, and Rocco Oliveto, "Evaluating SZZ Implementations Through a Developer-informed Oracle," 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2021), Madrid, Spain, May 25-28, 2021.
- Bo Shen, Wei Zhang, Christian Kästner, Haiyan Zhao, Zhao Wei, Guangtai Liang, and Zhi Jin, "SmartCommit: a graph-based interactive assistant for activity-oriented commits," 29th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering (ESEC/FSE 2021), Athens, Greece, August 23-28, 2021.
- Dimitrios Tsoukalas, Nikolaos Mittas, Alexander Chatzigeorgiou, Dionysios Kehagias, Apostolos Ampatzoglou, Theodoros Amanatidis, and Lefteris Angelis, "Machine Learning for Technical Debt Identification," IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2021.
- Luca Traini, Daniele Di Pompeo, Michele Tucci, Bin Lin, Simone Scalabrino, Gabriele Bavota, Michele Lanza, Rocco Oliveto, and Vittorio Cortellessa, "How Software Refactoring Impacts Execution Time," ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, Volume 31, Issue 2, Article 25, pp. 1-23, April 2022.
- Jarosław Pokropiński, Jakub Gąsiorek, Patryk Kramarczyk, and Lech Madeyski, "SZZ Unleashed-RA-C: An Improved Implementation of the SZZ Algorithm and Empirical Comparison with Existing Open Source Solutions," Developments in Information & Knowledge Management for Business Applications : Volume 3, Springer International Publishing, pp. 181-199, 2022.
- Eman Abdullah AlOmar, Jiaqian Liu, Kenneth Addo, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, Christian Newman, Ali Ouni, and Zhe Yu, "On the documentation of refactoring types," Automated Software Engineering, Volume 29, Article 9, 2022.
- Giulia Sellitto, Emanuele Iannone, Zadia Codabux, Valentina Lenarduzzi, Andrea De Lucia, Fabio Palomba, and Filomena Ferrucci, "Toward Understanding the Impact of Refactoring on Program Comprehension," 29th IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER 2022), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, March 15-18, 2022.
- Eman Abdullah AlOmar, Tianjia Wang, Vaibhavi Raut, Mohamed Wiem Mkaouer, Christian Newman, and Ali Ouni, "Refactoring for Reuse: An Empirical Study," arXiv:2111.07002v1, 13 Nov 2021.
- Anton Ivanov, Zarina Kurbatova, Yaroslav Golubev, Andrey Kirilenko, and Timofey Bryksin, "AntiCopyPaster: Extracting Code Duplicates As Soon As They Are Introduced in the IDE," arXiv:2112.15230v1, 30 Dec 2021.
- Max Ellis, Sarah Nadi, and Danny Dig, "A Systematic Comparison of Two Refactoring-aware Merging Techniques," arXiv:2112.10370v1, 20 Dec 2021.
- KotlinRMiner has been developed by JetBrains Research. The project is led and maintained by Zarina Kurbatova.
- PyRef has been developed by Hassan Atwi and Bin Lin from the Software Institute at USI - Università della Svizzera Italiana, Switzerland.
- Py-RefactoringMiner has been developed by Malinda Dilhara, a Ph.D. student in the department of Computer Science at University of Colorado Boulder under the suprevision of Danny Dig.
RefactoringMiner can automatically detect refactorings in the entire history of git repositories, between specified commits or tags, or at specified commits.
In the code snippet below we demonstrate how to print all refactorings performed in the toy project https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git.
GitService gitService = new GitServiceImpl();
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
Repository repo = gitService.cloneIfNotExists(
"tmp/refactoring-toy-example",
"https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git");
miner.detectAll(repo, "master", new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
});You can also analyze between commits using detectBetweenCommits or between tags using detectBetweenTags. RefactoringMiner will iterate through all non-merge commits from start commit/tag to end commit/tag.
// start commit: 819b202bfb09d4142dece04d4039f1708735019b
// end commit: d4bce13a443cf12da40a77c16c1e591f4f985b47
miner.detectBetweenCommits(repo,
"819b202bfb09d4142dece04d4039f1708735019b", "d4bce13a443cf12da40a77c16c1e591f4f985b47",
new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
});// start tag: 1.0
// end tag: 1.1
miner.detectBetweenTags(repo, "1.0", "1.1", new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
});It is possible to analyze a specific commit using detectAtCommit instead of detectAll. The commit
is identified by its SHA key, such as in the example below:
miner.detectAtCommit(repo, "05c1e773878bbacae64112f70964f4f2f7944398", new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
});It is possible to detect refactorings between the Java files in two directories containing the code before and after some changes. This feature supports the detection of renamed and moved classes, and automatically excludes from the analysis any files with identical contents:
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
// You must provide absolute paths to the directories. Relative paths will cause exceptions.
File dir1 = new File("/home/user/tmp/v1");
File dir2 = new File("/home/user/tmp/v2");
miner.detectAtDirectories(dir1, dir2, new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
});GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
// You must provide absolute paths to the directories. Relative paths will cause exceptions.
Path dir1 = Paths.get("/home/user/tmp/v1");
Path dir1 = Paths.get("/home/user/tmp/v2");
miner.detectAtDirectories(dir1, dir2, new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
});You can provide two maps (before and after the changes) where the keys are file paths, and the values are the corresponding file contents.
Each key should correspond to a file path starting from the root of the repository. For example, src/main/java/org/refactoringminer/api/GitHistoryRefactoringMiner.java.
After populating the maps, you can use the following code snippet:
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
// Each key should correspond to a file path starting from the root of the repository
Map<String, String> fileContentsBefore;
Map<String, String> fileContentsAfter;
// populate the maps
miner.detectAtFileContents(fileContentsBefore, fileContentsAfter, new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
});To use this API, please provide a valid OAuth token in the github-oauth.properties file.
You can generate an OAuth token in GitHub Settings -> Developer settings -> Personal access tokens.
If you don't want to clone locally the repository, you can use the following code snippet:
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
miner.detectAtCommit("https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git",
"36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd", new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
}, 10);To use this API, please provide a valid OAuth token in the github-oauth.properties file.
You can generate an OAuth token in GitHub Settings -> Developer settings -> Personal access tokens.
If you want to analyze all commits of a pull request, you can use the following code snippet:
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
String repo = "https://github.com/apache/drill.git";
miner.detectAtPullRequest(repo, 1807, new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
}
}
}, 100);RefactoringMiner is actually the only tool that generates AST diff at commit level, supports multi-mappings (one-to-many, many-to-one, many-to-many mappings), matches AST nodes of different AST types, and supports semantic diff in a fully refactoring-aware fashion. You can explore its advanced AST diff capabilities in our AST Diff Gallery.
All AST Diff APIs return a ProjectASTDiff object. By calling getDiffSet() on it, you can obtain a
Set<ASTDiff>, where each ASTDiff object corresponds to a pair of Java Compilation Units.
ASTDiff extends com.github.gumtreediff.actions.Diff and thus it is compatible with the GumTree core APIs.
More detailed documentation can be found in GitHistoryRefactoringMiner JavaDoc.
// With a locally cloned git repository
GitService gitService = new GitServiceImpl();
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
Repository repo = gitService.cloneIfNotExists(
"tmp/refactoring-toy-example",
"https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git");
ProjectASTDiff projectASTDiff = miner.diffAtCommit(repo,
"36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd");
Set<ASTDiff> diffs = projectASTDiff.getDiffSet();
// To visualize the diff add the following line
new WebDiff(projectASTDiff).run();To use the following API, please provide a valid OAuth token in the github-oauth.properties file.
You can generate an OAuth token in GitHub Settings -> Developer settings -> Personal access tokens.
// With all information fetched directly from GitHub
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
String repo = "https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git";
ProjectASTDiff projectASTDiff = miner.diffAtCommit(repo,
"36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd", 10);
Set<ASTDiff> diffs = projectASTDiff.getDiffSet();
// To visualize the diff add the following line
new WebDiff(projectASTDiff).run();To use the following API, please provide a valid OAuth token in the github-oauth.properties file.
You can generate an OAuth token in GitHub Settings -> Developer settings -> Personal access tokens.
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
String repo = "https://github.com/JabRef/jabref.git";
int PR = 10847;
ProjectASTDiff projectASTDiff = miner.diffAtPullRequest(repo, PR, 100);
Set<ASTDiff> diffs = projectASTDiff.getDiffSet();
// To visualize the diff add the following line
new WebDiff(projectASTDiff).run();// With two directories containing Java source code (File API)
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
// You must provide absolute paths to the directories. Relative paths will cause exceptions.
File dir1 = new File("/home/user/tmp/v1");
File dir2 = new File("/home/user/tmp/v2");
ProjectASTDiff projectASTDiff = miner.diffAtDirectories(dir1, dir2);
Set<ASTDiff> diffs = projectASTDiff.getDiffSet();
// To visualize the diff add the following line
new WebDiff(projectASTDiff).run();// With two directories containing Java source code (Path API)
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
// You must provide absolute paths to the directories. Relative paths will cause exceptions.
Path dir1 = Paths.get("/home/user/tmp/v1");
Path dir1 = Paths.get("/home/user/tmp/v2");
ProjectASTDiff projectASTDiff = miner.diffAtDirectories(dir1, dir2);
Set<ASTDiff> diffs = projectASTDiff.getDiffSet();
// To visualize the diff add the following line
new WebDiff(projectASTDiff).run();To check whether a refactoring detected in a commit is pure (i.e., it does not include overlapping behavior-changing edits) or impure, you can use the following APIs:
For the moment, PurityChecker supports 9 refactoring types, namely Extract Method, Inline Method, Move Method, Pull Up Method, Push Down Method, Split Method, Extract and Move Method, Move and Inline Method, Move and Rename Method.
With commit of a locally cloned git repository
GitService gitService = new GitServiceImpl();
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
Repository repo = gitService.cloneIfNotExists(
"tmp/refactoring-toy-example",
"https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git");
miner.detectAtCommit(repo, "05c1e773878bbacae64112f70964f4f2f7944398", new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handleModelDiff(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings, UMLModelDiff modelDiff) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
PurityCheckResult result = PurityChecker.check(ref, refactorings, modelDiff);
if (result != null) {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
});With commit fetched directly from GitHub
To use the following API, please provide a valid OAuth token in the github-oauth.properties file.
You can generate an OAuth token in GitHub Settings -> Developer settings -> Personal access tokens.
GitHistoryRefactoringMiner miner = new GitHistoryRefactoringMinerImpl();
miner.detectAtCommit("https://github.com/danilofes/refactoring-toy-example.git",
"36287f7c3b09eff78395267a3ac0d7da067863fd", new RefactoringHandler() {
@Override
public void handleModelDiff(String commitId, List<Refactoring> refactorings, UMLModelDiff modelDiff) {
System.out.println("Refactorings at " + commitId);
for (Refactoring ref : refactorings) {
System.out.println(ref.toString());
PurityCheckResult result = PurityChecker.check(ref, refactorings, modelDiff);
if (result != null) {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
}, 10);All classes implementing the Refactoring interface include refactoring-specific location information.
For example, ExtractOperationRefactoring offers the following methods:
getSourceOperationCodeRangeBeforeExtraction(): Returns the code range of the source method in the parent commitgetSourceOperationCodeRangeAfterExtraction(): Returns the code range of the source method in the child commitgetExtractedOperationCodeRange(): Returns the code range of the extracted method in the child commitgetExtractedCodeRangeFromSourceOperation(): Returns the code range of the extracted code fragment from the source method in the parent commitgetExtractedCodeRangeToExtractedOperation(): Returns the code range of the extracted code fragment to the extracted method in the child commitgetExtractedOperationInvocationCodeRange(): Returns the code range of the invocation to the extracted method inside the source method in the child commit
Each method returns a CodeRange object including the following properties:
String filePath
int startLine
int endLine
int startColumn
int endColumnAlternatively, you can use the methods List<CodeRange> leftSide() and List<CodeRange> rightSide() to get a list of CodeRange objects for the left side (i.e., parent commit) and right side (i.e., child commit) of the refactoring, respectively.
All method-related refactoring (Extract/Inline/Move/Rename/ExtractAndMove Operation) objects come with a UMLOperationBodyMapper object, which can be obtained by calling method getBodyMapper() on the refactoring object.
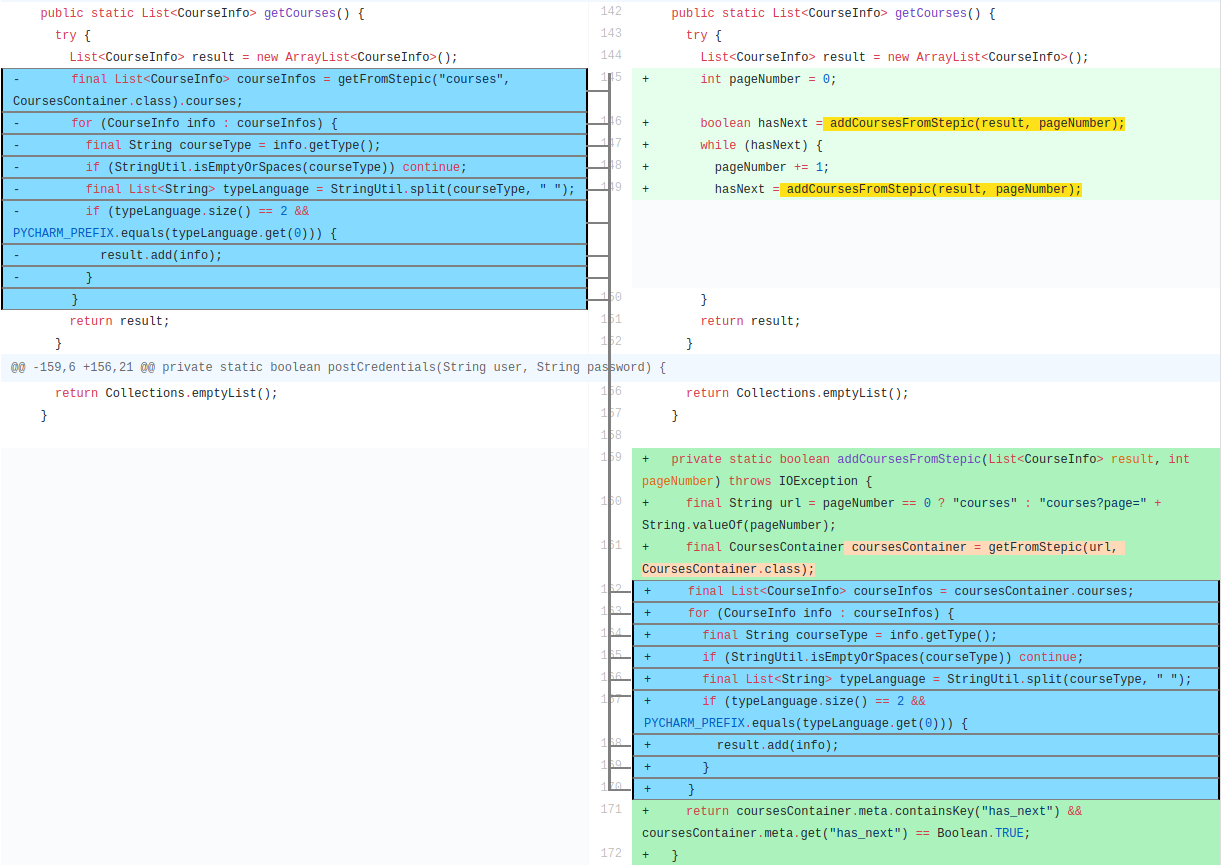
Let's consider the Extract Method refactoring in commit JetBrains/intellij-community@7ed3f27
#1. You can use the following code snippet to obtain the newly added statements in the extracted method:
ExtractOperationRefactoring refactoring = ...;
UMLOperationBodyMapper mapper = refactoring.getBodyMapper();
List<StatementObject> newLeaves = mapper.getNonMappedLeavesT2(); //newly added leaf statements
List<CompositeStatementObject> newComposites = mapper.getNonMappedInnerNodesT2(); //newly added composite statements
List<StatementObject> deletedLeaves = mapper.getNonMappedLeavesT1(); //deleted leaf statements
List<CompositeStatementObject> deletedComposites = mapper.getNonMappedInnerNodesT1(); //deleted composite statementsFor the Extract Method Refactoring example shown above mapper.getNonMappedLeavesT2() returns the following statements:
final String url = pageNumber == 0 ? "courses" : "courses?page=" + String.valueOf(pageNumber);
final CoursesContainer coursesContainer = getFromStepic(url,CoursesContainer.class);
return coursesContainer.meta.containsKey("has_next") && coursesContainer.meta.get("has_next") == Boolean.TRUE;#2. You can use the following code snippet to obtain the matched statements between the original and the extracted methods:
ExtractOperationRefactoring refactoring = ...;
UMLOperationBodyMapper mapper = refactoring.getBodyMapper();
for(AbstractCodeMapping mapping : mapper.getMappings()) {
AbstractCodeFragment fragment1 = mapping.getFragment1();
AbstractCodeFragment fragment2 = mapping.getFragment2();
Set<Replacement> replacements = mapping.getReplacements();
for(Replacement replacement : replacements) {
String valueBefore = replacement.getBefore();
String valueAfter = replacement.getAfter();
ReplacementType type = replacement.getType();
}
}For the Extract Method Refactoring example shown above mapping.getReplacements() returns the following AST node replacement for the pair of matched statements:
final List<CourseInfo> courseInfos = getFromStepic("courses",CoursesContainer.class).courses;
final List<CourseInfo> courseInfos = coursesContainer.courses;Replacement: getFromStepic("courses",CoursesContainer.class) -> coursesContainer
ReplacementType: VARIABLE_REPLACED_WITH_METHOD_INVOCATION
#3. You can use the following code snippet to obtain the overlapping refactorings in the extracted method:
ExtractOperationRefactoring refactoring = ...;
UMLOperationBodyMapper mapper = refactoring.getBodyMapper();
Set<Refactoring> overlappingRefactorings = mapper.getRefactorings();For the Extract Method Refactoring example shown above mapper.getRefactorings() returns the following refactoring:
Extract Variable coursesContainer : CoursesContainer in method
private addCoursesFromStepic(result List<CourseInfo>, pageNumber int) : boolean
from class com.jetbrains.edu.stepic.EduStepicConnector
because variable coursesContainer = getFromStepic(url,CoursesContainer.class) has been extracted from the following statement of the original method by replacing string literal "courses" with variable url:
final List<CourseInfo> courseInfos = getFromStepic("courses",CoursesContainer.class).courses;