A simple framework for experimenting with Reinforcement Learning in Python.
There are loads of other great libraries out there for RL. The aim of this one is twofold:
- Simplicity.
- Reproducibility of results.
A brief tutorial for a slightly earlier version is available here. As of version 0.77, the library should work with both Python 2 and Python 3. Please let me know if you find that is not the case!
simple_rl requires numpy and matplotlib. Some MDPs have visuals, too, which requires pygame. Also includes support for hooking into any of the Open AI Gym environments. The library comes along with basic test script, contained in the tests directory. I suggest running it and making sure all tests pass when you install the library.
The easiest way to install is with pip. Just run:
pip install simple_rl
Alternatively, you can download simple_rl here.
If you use simple_rl in your research, please cite the workshop paper as follows:
@article{abel2019simple_rl,
title={simple_rl: Reproducible Reinforcement Learning in Python},
author={David Abel},
booktitle={ICLR Workshop on Reproducibility in Machine Learning},
year={2019}
}
I just added a new feature I'm quite excited about: easy reproduction of results. Every experiment run now outputs a file "full_experiment.txt" in the results/exp_name/ directory. The new function reproduce_from_exp_file(file_name), when pointed at an experiment directory, will reassemble and rerun an entire experiment based on this file. The goal here is to encourage simple tracking of experiments and enable quick result-reproduction. It only works with MDPs though -- it does not yet work with OOMDPs, POMDPs, or MarkovGames (I'd be delighted if someone wants to make it work, though!).
See the second example below for a quick sense of how to use this feature.
Some examples showcasing basic functionality are included in the examples directory.
To run a simple experiment, import the run_agents_on_mdp(agent_list, mdp) method from simple_rl.run_experiments and call it with some agents for a given MDP. For example:
# Imports
from simple_rl.run_experiments import run_agents_on_mdp
from simple_rl.tasks import GridWorldMDP
from simple_rl.agents import QLearningAgent
# Run Experiment
mdp = GridWorldMDP()
agent = QLearningAgent(mdp.get_actions())
run_agents_on_mdp([agent], mdp)
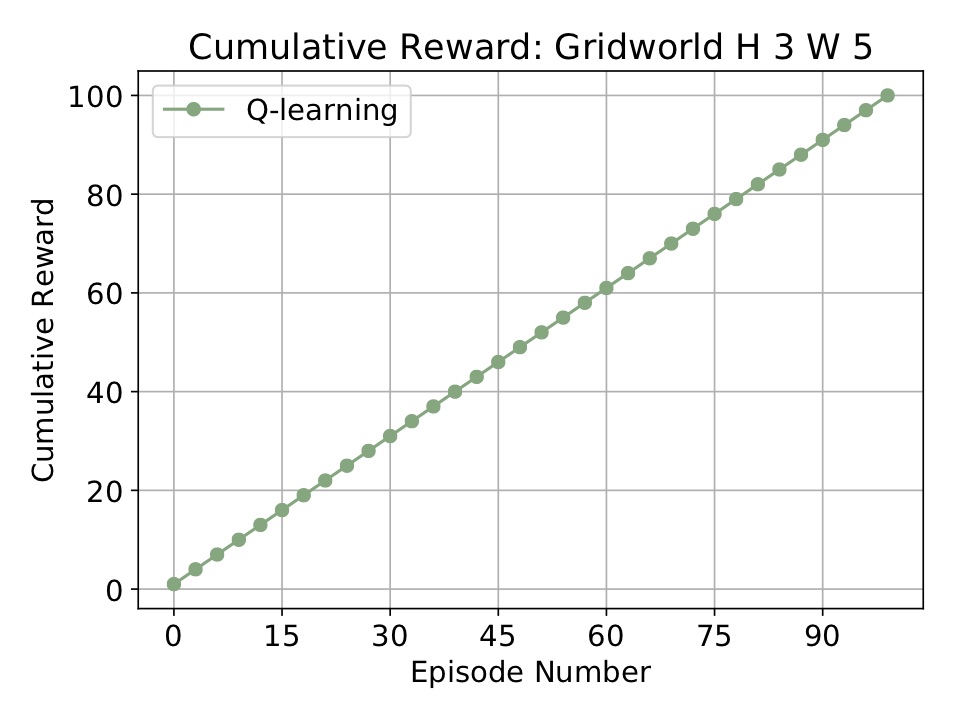
Running the above code will run Q-learning on a simple GridWorld. When it finishes it stores the results in cur_dir/results/* and makes and opens the following plot:
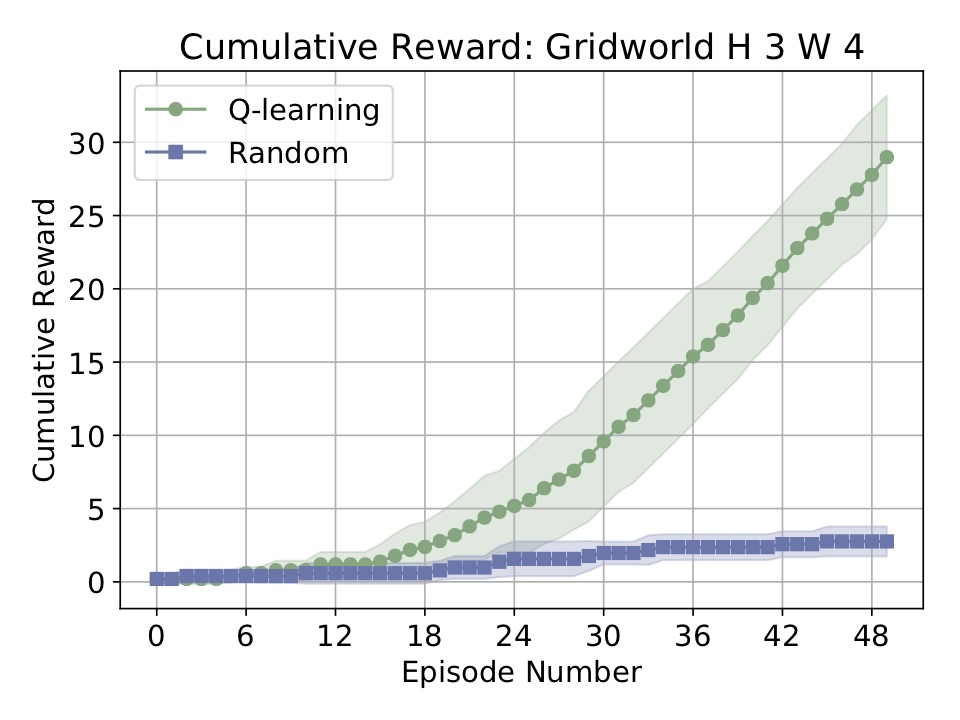
For a slightly more complicated example, take a look at the code of simple_example.py. Here we run two agents on the grid world from the Russell-Norvig AI textbook:
from simple_rl.agents import QLearningAgent, RandomAgent, RMaxAgent
from simple_rl.tasks import GridWorldMDP
from simple_rl.run_experiments import run_agents_on_mdp
# Setup MDP.
mdp = GridWorldMDP(width=4, height=3, init_loc=(1, 1), goal_locs=[(4, 3)], lava_locs=[(4, 2)], gamma=0.95, walls=[(2, 2)], slip_prob=0.05)
# Setup Agents.
ql_agent = QLearningAgent(actions=mdp.get_actions())
rmax_agent = RMaxAgent(actions=mdp.get_actions())
rand_agent = RandomAgent(actions=mdp.get_actions())
# Run experiment and make plot.
run_agents_on_mdp([ql_agent, rmax_agent, rand_agent], mdp, instances=5, episodes=50, steps=10)
The above code will generate the following plot:
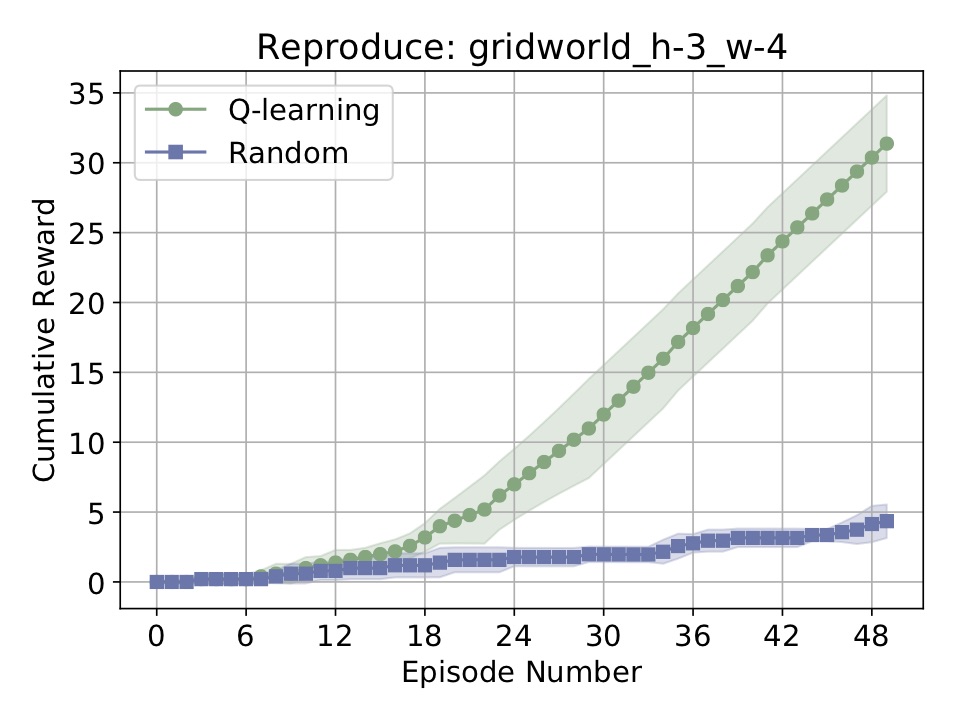
To showcase the new reproducibility feature, suppose we now wanted to reproduce the above experiment. We just do the following:
from simple_rl.run_experiments import reproduce_from_exp_file
reproduce_from_exp_file("gridworld_h-3_w-4")
Which will rerun the entire experiment, based on a file created and populated behind the scenes. Then, we should get the following plot:
Easy! This is a new feature, so there may be bugs -- just let me know as things come up. It's only supposed to work for MDPs, not POMDPs/OOMDPs/MarkovGameMDPs (so far). Take a look at reproduce_example.py for a bit more detail.
-
(agents): Code for some basic agents (a random actor, Q-learning, [R-Max], Q-learning with a Linear Approximator, and so on).
-
(experiments): Code for an Experiment class to track parameters and reproduce results.
-
(mdp): Code for a basic MDP and MDPState class, and an MDPDistribution class (for lifelong learning). Also contains OO-MDP implementation [Diuk et al. 2008].
-
(planning): Implementations for planning algorithms, includes ValueIteration and MCTS [Couloum 2006], the latter being still in development.
-
(tasks): Implementations for a few standard MDPs (grid world, N-chain, Taxi [Dietterich 2000], and the OpenAI Gym).
-
(utils): Code for charting and other utilities.
If you'd like to contribute: that's great! Take a look at some of the needed improvements below: I'd love for folks to work on those items. Please see the contribution guidelines. Email me with any questions.
Make an MDP subclass, which needs:
-
A static variable, ACTIONS, which is a list of strings denoting each action.
-
Implement a reward and transition function and pass them to MDP constructor (along with ACTIONS).
-
I also suggest overwriting the "__str__" method of the class, and adding a "__init__.py" file to the directory.
-
Create a State subclass for your MDP (if necessary). I suggest overwriting the "__hash__", "__eq__", and "__str__" for the class to play along well with the agents.
Make an Agent subclass, which requires:
-
A method, act(self, state, reward), that returns an action.
-
A method, reset(), that puts the agent back to its tabula rasa state.
I'm hoping to add the following features:
- Planning: Finish MCTS [Coloum 2006], implement RTDP [Barto et al. 1995]
- Deep RL: Write a DQN [Mnih et al. 2015] in PyTorch, possibly others (some kind of policy gradient).
- Efficiency: Convert most defaultdict/dict uses to numpy.
- Reproducibility: The new reproduce feature is limited in scope -- I'd love for someone to extend it to work with OO-MDPs, Planning, MarkovGames, POMDPs, and beyond.
- Docs: Tutorial and documentation.
- Visuals: Unify MDP visualization.
- Misc: Additional testing.
Cheers,
-Dave