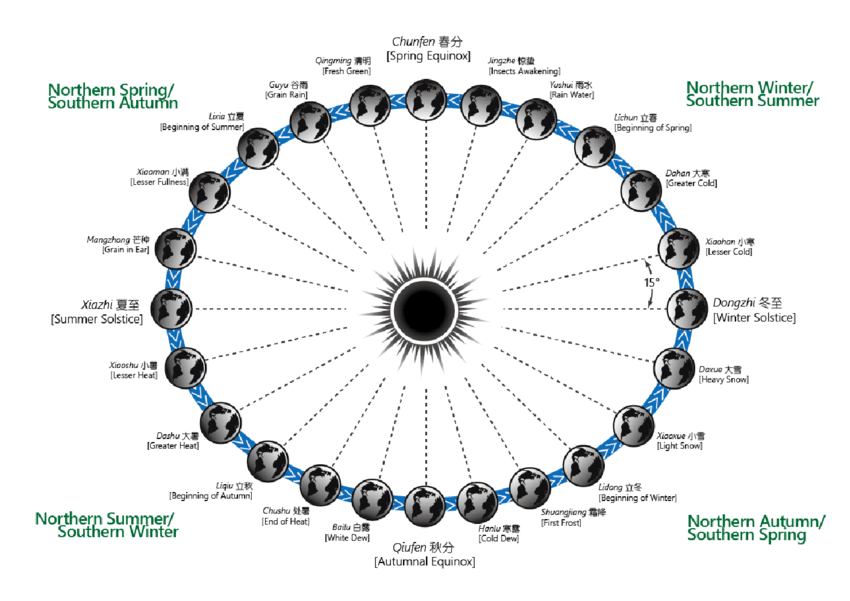
solar_terms_24 calculates and collects 24 solar terms times of each year. It utilizes NASA's JPL Horizons System API to calculate the longitude of ecliptic data. Those solar terms’ times can be translated into different timezone or languages. This gem is inspired by a Python package, solarterms
Solar term(節氣, 節気, 节气, 절기, Tiết khí) play an important role in calendars. Some examples are,
- For lunisolar calendars like Chinese calendar, it is used to decide the intercalary months
- Easter Day's date depends on a solar term. The definition of Easter day, the first Sunday after the full Moon that occurs on or after the spring equinox, the spring equinox is a solar term.
- 12 Zodiacs like, Leo, Cancer, etc. are also decided by solar terms(ref: [wiki])
This gem aims to solve 2 main problems while finding those solar terms times of each year:
The times of solar terms are decided by the longitude of the earth on the ecliptic, which changes every year. NASA's JPL Horizons System API provides accurate ecliptic data so this gem can precisely calculate the solar terms time. This gem already caches 1900-2100's data. It should be enough in normal cases; however, you can try to search any year and it will call API to do the calculation.
The time of solar terms is different in different countries because of different timezones. You can specify the timezones and languages to address this internationalization issue.
Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
gem 'solar_terms_24'And then execute:
$ bundle install
Or install it yourself as:
$ gem install solar_terms_24
The simplest way to use is through the command line:
$ solar_terms_24 list 2022
# Minor Cold: 2022-01-05 09:14
# Major Cold: 2022-01-20 02:39
# Start Of Spring: 2022-02-03 20:50
# Spring Showers: 2022-02-18 16:43
# Awakening Of Insects: 2022-03-05 14:43
# Spring Equinox: 2022-03-20 15:33
# Pure Brightness: 2022-04-04 19:20
# Grain Rain: 2022-04-20 02:24
# Start Of Summer: 2022-05-05 12:25
# Grain Buds: 2022-05-21 01:22
# Grain In Ear: 2022-06-05 16:25
# Summer Solstice: 2022-06-21 09:13
# Minor Heat: 2022-07-07 02:38
# Major Heat: 2022-07-22 20:07
# Start Of Autumn: 2022-08-07 12:29
# End Of Heat: 2022-08-23 03:16
# White Dew: 2022-09-07 15:32
# Autumn Equinox: 2022-09-23 01:03
# Cold Dew: 2022-10-08 07:22
# Frost: 2022-10-23 10:35
# Start Of Winter: 2022-11-07 10:45
# Minor Snow: 2022-11-22 08:20
# Major Snow: 2022-12-07 03:46
# Winter Solstice: 2022-12-21 21:48The default timezone is UTC and the language is en so it may be more useful if you specify them:
$ solar_terms_24 list 2022 --timezone=Asia/Taipei --lang=zh-TW
# 小寒: 2022-01-05 17:14
# 大寒: 2022-01-20 10:39
# 立春: 2022-02-04 04:50
# 雨水: 2022-02-19 00:43
# 驚蟄: 2022-03-05 22:43
# 春分: 2022-03-20 23:33
# 清明: 2022-04-05 03:20
# 穀雨: 2022-04-20 10:24
# 立夏: 2022-05-05 20:25
# 小滿: 2022-05-21 09:22
# 芒種: 2022-06-06 00:25
# 夏至: 2022-06-21 17:13
# 小暑: 2022-07-07 10:38
# 大暑: 2022-07-23 04:07
# 立秋: 2022-08-07 20:29
# 處暑: 2022-08-23 11:16
# 白露: 2022-09-07 23:32
# 秋分: 2022-09-23 09:03
# 寒露: 2022-10-08 15:22
# 霜降: 2022-10-23 18:35
# 立冬: 2022-11-07 18:45
# 小雪: 2022-11-22 16:20
# 大雪: 2022-12-07 11:46
# 冬至: 2022-12-22 05:48You can use SolarTerms24::SolarTerms to grab solar terms information of a year, then access one solar term by solar_terms.solar_terms[:winter_solstice] or solar_terms.winter_solstice.
year = 2022
solar_terms = SolarTerms24::SolarTerms.new(year)
solar_term = solar_terms.winter_solstice
solar_term.name
# => "Winter Solstice"
solar_term.date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# => 2022-12-21
# => solar_term.date is a Date object
solar_term.datetime.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# => 2022-12-21 21:48:14
# => solar_term.datetime is a DateTime objectTo specify different timezones and languages, for example, Asia/Taipei and zh-TW
solar_terms = SolarTerms24::SolarTerms.new(year, timezone: 'Asia/Taipei', lang: 'zh-TW')
solar_term = solar_terms.winter_solstice
solar_term.name
# => "冬至"
solar_term.date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# => 2022-12-22
solar_term.datetime.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# => "2022-12-22 05:48:14"24 solar terms methods are:
solar_terms = SolarTerms24::SolarTerms.new(year)
solar_terms.minor_cold
solar_terms.major_cold
solar_terms.start_of_spring
solar_terms.spring_showers
solar_terms.awakening_of_insects
solar_terms.spring_equinox
solar_terms.pure_brightness
solar_terms.grain_rain
solar_terms.start_of_summer
solar_terms.grain_buds
solar_terms.grain_in_ear
solar_terms.summer_solstice
solar_terms.minor_heat
solar_terms.major_heat
solar_terms.start_of_autumn
solar_terms.end_of_heat
solar_terms.white_dew
solar_terms.autumn_equinox
solar_terms.cold_dew
solar_terms.frost
solar_terms.start_of_winter
solar_terms.minor_snow
solar_terms.major_snow
solar_terms.winter_solsticeThese are the supported languages:
- en (English, default)
- ja (Japanese)
- ko (Korean)
- vi (Vietnamese)
- zh-CN (Simpified Chinese)
- zh-TW (Tranditional Chinese)
It uses the gem tzinfo, so all timezones in IANA Time Zone Database are supported. For example,
- UTC (default)
- Asia/Ho_Chi_Minh
- Asia/Seoul
- Asia/Taipei
- Asia/Tokyo
Full list is here
After checking out the repo, run bin/setup to install dependencies. Then, run rake spec to run the tests. You can also run bin/console for an interactive prompt that will allow you to experiment.
To install this gem onto your local machine, run bundle exec rake install. To release a new version, update the version number in version.rb, and then run bundle exec rake release, which will create a git tag for the version, push git commits and the created tag, and push the .gem file to rubygems.org.
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/kevinluo201/solar_terms_24.
The gem is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.