An education company named X Education sells online courses to industry professionals. On any given day, many professionals who are interested in the courses land on their website and browse for courses.
The company markets its courses on several websites and search engines like Google. Once these people land on the website, they might browse the courses or fill up a form for the course or watch some videos. When these people fill up a form providing their email address or phone number, they are classified to be a lead. Moreover, the company also gets leads through past referrals. Once these leads are acquired, employees from the sales team start making calls, writing emails, etc. Through this process, some of the leads get converted while most do not. The typical lead conversion rate at X education is around 30%.
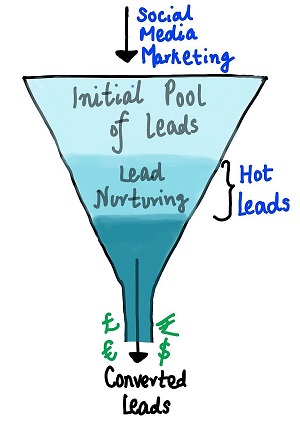
Now, although X Education gets a lot of leads, its lead conversion rate is very poor. For example, if, say, they acquire 100 leads in a day, only about 30 of them are converted. To make this process more efficient, the company wishes to identify the most potential leads, also known as ‘Hot Leads’. If they successfully identify this set of leads, the lead conversion rate should go up as the sales team will now be focusing more on communicating with the potential leads rather than making calls to everyone. A typical lead conversion process can be represented using the following funnel:
Lead Conversion Process - Demonstrated as a funnel
As you can see, there are a lot of leads generated in the initial stage (top) but only a few of them come out as paying customers from the bottom. In the middle stage, you need to nurture the potential leads well (i.e. educating the leads about the product, constantly communicating etc. ) in order to get a higher lead conversion.
X Education has appointed you to help them select the most promising leads, i.e. the leads that are most likely to convert into paying customers.The company requires you to build a model wherein you need to assign a lead score to each of the leads such that the customers with higher lead score have a higher conversion chance and the customers with lower lead score have a lower conversion chance.The CEO, in particular, has given a ballpark of the target lead conversion rate to be around 80%.
We have been provided with a leads dataset from the past with around 9000 data points. This dataset consists of various attributes such as Lead Source, Total Time Spent on Website, Total Visits, Last Activity, etc. which may or may not be useful in ultimately deciding whether a lead will be converted or not. The target variable, in this case, is the column ‘Converted’ which tells whether a past lead was converted or not wherein 1 means it was converted and 0 means it wasn’t converted.
Another thing about the data is that we also need to check out whether there are the levels present in the categorical variables.
Many of the categorical variables have a level called 'Select' which needs to be handled because it is as good as a null value.
There are quite a few goals for this case study.
- Build a logistic regression model to assign a lead score between 0 and 100 to each of the leads which can be used by the company to target potential leads. A higher score would mean that the lead is hot, i.e. is most likely to convert whereas a lower score would mean that the lead is cold and will mostly not get converted.
- Provide recommendations to the company for which leads to contact for better conversion rate.
- Manushree Jain
- Harsha Vardhan Tamma
- Arutla Uma Maheshwar Reddy