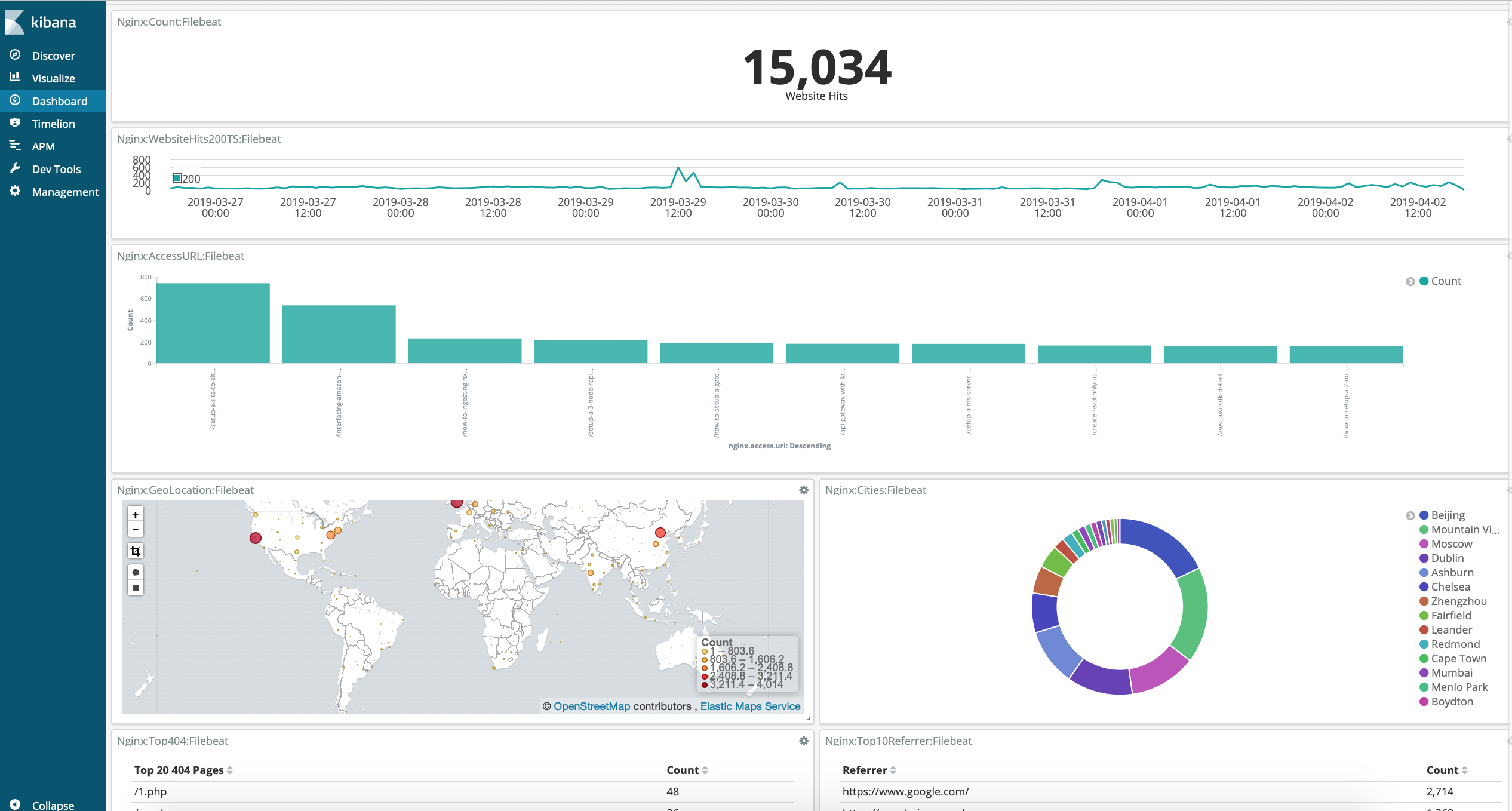
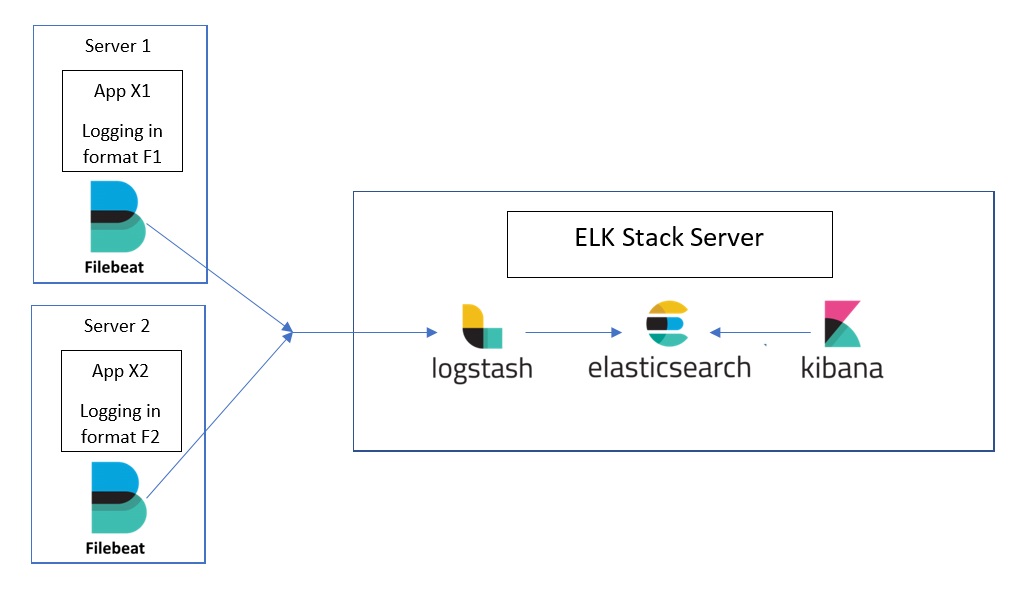
The Elastic Stack is a collection of open-source software produced by Elastic which allows you to search, analyze, and visualize logs generated from any source in any format, a practice known as centralized logging.
The Elastic Stack has four main components:
1 . Elasticsearch - Elasticsearch is a search and analytics engine. The open source, distributed,RESTful, JSON-based search engine. Easy to use, scalable and flexible, it earned hyper-popularity among users and a company formed around it, you
know, for search.
2 . Logstash - Logstash is a light-weight, open-source, server-side data processing pipeline that allows you to collect data from a variety of sources, transform it on the fly, and send it to your desired destination.sh it is more flexible to do it.
3 . Kibana - Kibana lets you visualize your Elasticsearch data and navigate the Elastic Stack so you can do anything from tracking query load to understanding the way requests flow through your apps.
4 . Beat - Beats are open source data shippers that you install as agents on your servers to send operational data to Elasticsearch.
This tutorial provides you how to install the Elastic Stack on a CentOS 7 server. At the end of this tutorial, you will have all of these components installed on a single server, referred to as the Elastic Stack server.
-
Versions
-
Prerequisites
-
Installation instructions
-
Resources
-
Contributors
Versions :
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| Elasticksearch | 6.8.8 |
| Kibana | 6.8.8 |
| Logshtash | 6.8.8 |
| Filebeat | 6.8.8 |
-
- Note: When installing the Elastic Stack, you should use the same version across the entire stack. In this project we used Versions are listed above.
For this project , we created image in South America (São Paulo) region and lunched our instance in US East (N. Virginia)us-east-1 since we had to use VPC prepared by Team 1. We lunched the instance with the following specifications for our Elastic Stack server:
OS: CentOS 7
RAM: 4GB
CPU: 2
Before you start with this tutorial, make sure you are logged into your server with a user with sudo privileges or with the root user.
-
Nginx installed on your server, which you will configure later in this guide as a reverse proxy for Kibana.
- Follow our guide on How To Install Nginx ( Nginx version: nginx/1.17.10 ) on CentOS 7 to set this up. Click here
-
Java 8 — which is required by Elasticsearch and Logstash installed on your server.
- Follow our guide on How To Install Java 8 ( Open JDK 8 version “1.8.0_242” ) on CentOS 7 to set this up. Click Here
-
Both of the following DNS records set up for your server.
-
An A record with team3acirrustech.com pointing to your server’s public IP address.
-
An A record with www.team3acirrustech.com pointing to your server’s public IP address.
-
We used team3acirrustech.com domain name for our project but you can use your own domain name.
Step 1 . Elasticsearch
Follow our guide on How To Install Elasticsearch on CentOS 7. Click Here
Follow our guide on How To Install Kibana on CentOS 7. Click Here
Follow our guide on How To Install Logstash on CentOS 7. Click Here
Follow our guide on How To Install Filebeat on CentOS 7. Click Here
Sources:
https://guides.github.com/features/wikis/
This tutorial created by Evolve Cyber February batch 2020 Team-3 members listed below with hours contributed:
-
Meryem Elibal - [email protected] - Team hours -15 hours total - 20 hours
-
Rasheed Balogun - [email protected] - Team hour-18 hours Total -30 hours
-
Davronbek Normuradov - [email protected] - Team hour-18 Total - 25 hours
-
Azymberdi Gutdanov - [email protected] -Team hours 18 Total - 30 hours
-
Solongo Ganbold [email protected] - Team hours -18 hours Total - 27 hours
-
Sophie Kamil - [email protected] -Team hours -18 hours Total - 26 hours
-
AdnanK - [email protected] - Team hours 9hours joined to group late