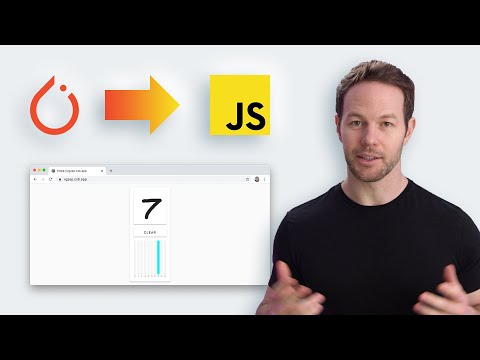
Run PyTorch models in the browser with JavaScript by first converting your PyTorch model into the ONNX format and then loading that ONNX model in your website or app using ONNX.js. In the video tutorial below, I take you through this process using the demo example of a handwritten digit recognition model trained on the MNIST dataset.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vs730jsRgO8
Note: The model used in this demo is not very accurate, it will often misclassify digits. It's only meant to be used as a proof of concept. It's the same model that was used in PyTorch's MNIST example. You can find more accurate image classification models here: Papers With Code - Image Classification
├── degug_demo
│ ├── debug.html (A debug test to make sure the generated ONNX model works.
│ │ Uses ONNX.js to load and run the generated ONNX model.)
│ │
│ └── onnx_model.onnx (A copy of the generated ONNX model that will be loaded
│ for debugging.)
│
├── full_demo
│ ├── index.html (The full demo's HTML code.)
│ │
│ ├── onnx_model.onnx (A copy of the generated ONNX model. Used by script.js.)
│ │
│ ├── script.js (The full demos's JS code. Loads the onnx_model.onnx and
│ │ predicts the drawn numbers.)
│ │
│ └── style.css (The full demo's CSS.)
│
├── convert_to_onnx.py (Converts a trained PyTorch model into an ONNX model.)
│
├── inference_mnist_model.py (The PyTorch model description. Used by
│ convert_to_onnx.py to generate the ONNX model.)
│
├── inputs_batch_preview.png (A preview of a batch of augmented input data.
│ Generated by preview_mnist_dataset.py.)
│
├── onnx_model.py (The ONNX model generated by convert_to_onnx.py.)
│
├── preview_dataset.py (For testing out different types of data augmentation.)
│
├── pytorch_model.pt (The trained PyTorch model parameters. Generated by
│ train_mnist.model.py and used by convert_to_onnx.py to
│ generate the ONNX model.)
│
└── train_mnist_model.pt (Trains the PyTorch model and saves the trained
parameters as pytorch_model.pt.)
- Faster inference times with smaller models.
- Easy to host and scale (only static files).
- Offline support.
- User privacy (can keep the data on the device).
- Faster load times (don't have to download the model).
- Faster and consistent inference times with larger models (can take advantage of GPUs or other accelerators).
- Model privacy (don't have to share your model if you want to keep it private).