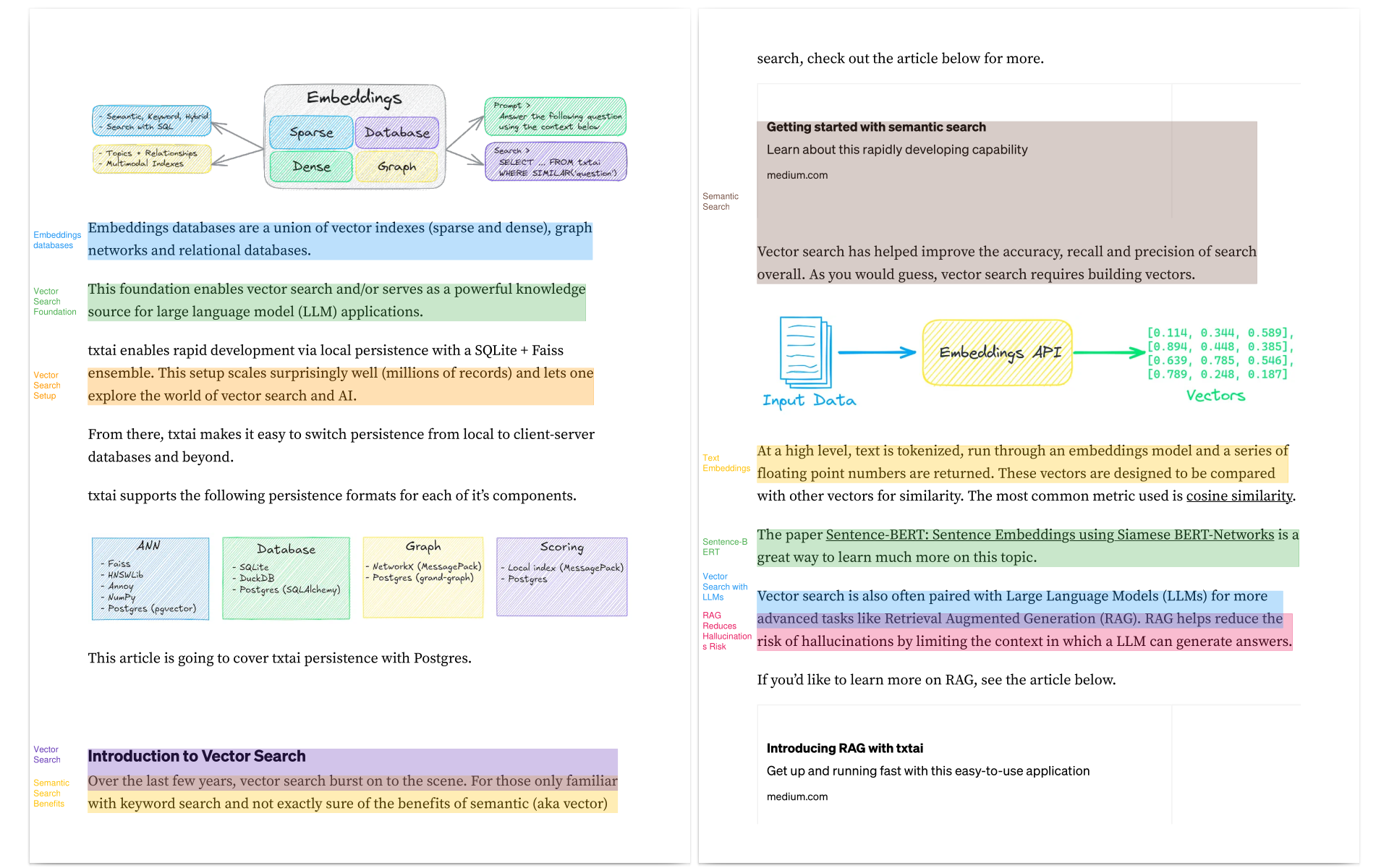
Automatically annotate papers using LLMs
annotateai automatically annotates papers using Large Language Models (LLMs). While LLMs can summarize papers, search papers and build generative text about papers, this project focuses on providing human readers with context as they read.
A one-line call does the following:
- Reads the paper
- Finds the title and important key concepts
- Goes through each page and finds sections that best emphasis the key concepts
- Reads the section and builds a concise short topic
- Annotates the paper and highlights those sections
The easiest way to install is via pip and PyPI
pip install annotateai
Python 3.9+ is supported. Using a Python virtual environment is recommended.
annotateai can also be installed directly from GitHub to access the latest, unreleased features.
pip install git+https://github.com/neuml/annotateai
Python 3.9+ is supported
annotateai can annotate any PDF but it works especially well for medical and scientific papers. The following shows a series of examples using papers from arXiv.
This project also works well with papers from PubMed, bioRxiv and medRxiv!
The examples below use an AutoAWQ model, make sure to install that dependency first.
pip install annotateai autoawq[kernels]
The primary input parameter is the path to the LLM. This project is backed by txtai and it supports any txtai-supported LLM.
from annotateai import Annotate
# This model works well with medical and scientific literature
annotate = Annotate("NeuML/Llama-3.1_OpenScholar-8B-AWQ")This paper proposed RAG before most of us knew we needed it.
annotate("https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.11401")Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.11401
This paper builds the largest open-source video generation model. It's trending on Papers With Code as of Dec 2024.
annotate("https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.03603v2")Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.03603v2
This paper was presented at the 38th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024) Track on Datasets and Benchmarks.
annotate("https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.14657")Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.14657
The default mode for an annotate instance is to automatically generate the key concepts to search for. But these concepts can be provided via the keywords parameter.
annotate("https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.11401", keywords=["hallucinations", "llm"])This is useful for situations where we have a large batch of papers and we want it to identify a specific set of concepts to help with a review.
The progress bar can be disabled as follows:
annotate("https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.11401", progress=False)