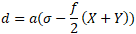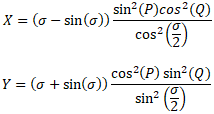A simple Java datatype to store the Latitude and the Longitude. Distance calculations are included.
The formular for the calculation of the distance is from https://www.calculator.net/distance-calculator.html.
Note
For this project I used the Lambert's formula for distance calculations on an earth elipsoid.
double d = a * (o - (f / 2) * (X + Y));
double dis the distance to be calculated, unit: meterais the equatorial radius of the earth, unit: meteromeans σ and stands for the central angle, (we will calculate it later) unit: radiandfis the flattening of the earth, (we will calculate it later)XandYis calculated later.
So to calculate the distance we have to get a, o, f, X and Y.
First we have to get a, the equatorial radius. You can get it by calling my class:
double a = LatLong.radiusEquatorial;
Tip
Alternatively you can go to https://www.heret.de/mathe/erde.shtml and copy the "Äquatorradius", which is 6378137m.
Next we have to calculate o. There is a formula for this on wikipedia:
is our
o. unit: radiandis the latitude of a given point. In our case is
1 the latitude of Point A and
2 the latitude of Point B. unit: radiand
are the differences of the latitudes and longitudes of the two points. unit: radiand
In code it looks like that:
double deltaLongitude = Math.abs(longitudeA - longitudeB);
double o = Math.acos(Math.sin(latitudeA) * Math.sin(latitudeB) + Math.cos(latitudeA) * Math.cos(latitudeB) * Math.cos(deltaLongitude));
Caution
Don't forget to convert the latitude and longitude values from degree to radiand, because the Math.acos(), Math.sin()and Math.cos() need or return angles in radiands.
latitudeA = Math.toRadians(latitudeA);
latitudeB = Math.toRadians(latitudeB);
longitudeA = Math.toRadians(longitudeA);
longitudeB = Math.toRadians(longitudeB);
Now we calculate f. fis the flattening of the earth and is calculated like that:
In code:
f = (a - b) / a;
ais still the equatorial radius of the earth unit: meterbis the polar radius of the earth unit: meter
After that we can calculate X and Y. The calculation of that is a little bit complex and we need some other values.
The formulas are:
Note
For those who don't know, sin²() and cos²() is a short writing for (sin())² and (cos())².
In Code it looks like that:
double X = (o - Math.sin(o)) * ((Math.pow(Math.sin(P), 2) * Math.pow(Math.cos(Q), 2)) / (Math.pow(Math.cos(o / 2), 2)));
double Y = (o + Math.sin(o)) * ((Math.pow(Math.cos(P), 2) * Math.pow(Math.sin(Q), 2)) / (Math.pow(Math.sin(o / 2), 2)));
ois the variable we calculated earlier unit: radiandPandQare Variables which have to be calculated.
So for using the formula we have to calculate P and Q. Here is the formula for that:
P = (β1 + β2)/2
and
Q = (β2 - β1)/2
Now we have to calculate β1 and β2. And as you may already know, there is a formular for this:
tan(β) = (1 - f)tan(ϕ)
That means that you have to calculate one β for each of the two points.
fis the value which we calculated earlier,ϕis the latitude of the given point,
When we have all values, we can calculate X and Y. Here is the Code for that:
betaA = Math.atan((1 - f) * Math.tan(latitudeA));
betaB = Math.atan((1 - f) * Math.tan(latitudeB));
P = (betaA + betaB) / 2;
Q = (betaB - betaA) / 2;
double X = (o - Math.sin(o)) * ((Math.pow(Math.sin(P), 2) * Math.pow(Math.cos(Q), 2)) / (Math.pow(Math.cos(o / 2), 2)));
double Y = (o + Math.sin(o)) * ((Math.pow(Math.cos(P), 2) * Math.pow(Math.sin(Q), 2)) / (Math.pow(Math.sin(o / 2), 2)));
Tip
You can test the code with the Distance Calculator (It uses the same Code).
There are different ways to use the distance calculation with the LatLong class integrated in your project:
-
Use the static distance function of the class:
LatLong.distance(latitudeFromPointA, longitudeFromPointA, latitudeFromPointB, longitudeFromPointB);LatLong PointA = new LatLong(latitudeFromPointA, longitudeFromPointA); LatLong PointB = new LatLong(latitudeFromPointB, longitudeFromPointB); LatLong.distance(PointA, PointB); -
Use the distance function from an LatLong object:
LatLong PointA = new LatLong(latitudeFromPointA, longitudeFromPointA); LatLong PointB = new LatLong(latitudeFromPointB, longitudeFromPointB); PointA.distanceTo(PointB);
There are three different ways to make an object of the LatLong class in your project:
-
LatLong location = new LatLong();Creates an LatLong object with the cooridinates
0, 0. -
LatLong location = new LatLong(latitude, longitude);Creates an LatLong object with the given cooridinates.
-
Location mylocation = getmylocation(); LatLong location = new LatLong(mylocation);In this example we have an (imaginary) function which returns an value of type Location. The constructor converts the Location into an LatLong datatype.
You can set the latitude and longitude values by calling the setLatitude() or the setLongitude() functions:
LatLong location = new LatLong();
location.setLatitude(latitude);
location.setLongitude(longitude);
You can get the latitude and longitude values by calling the getLatitude() or the getLongitude() functions:
LatLong location = new LatLong();
double latitude = location.getLatitude();
double longitude = location.getLongitude();
Returns the euatorial radius in meter:
double eqatorialRadius = LatLong.radiusEquatorial;
Returns the polar radius in meter:
double polarRadius = LatLong.radiusPolar;
The other Constants only return Locations in LatLong Datatype. They are not very useful and you can delete them if you want. They are not used in the program.