| layout | title |
|---|---|
rmilter |
Rspamd milter |
Rmilter is used to integrate rspamd and milter compatible MTA, for example postfix or sendmail.
Rmilter can also do other useful stuff:
- Clamav scanning (via unix or tcp socket).
- Rspamd scanning
- Greylisting with redis upstream
- Ratelimit with redis upstream
- Auto-whitelisting (internal and via redis upstream)
- Replies check (whitelisting replies to sent messages)
- Passing messages and/or their headers to beanstalk servers
All rmilter configuration is placed in rmilter.conf file.
The configuration file has format:
name = value ;
Value may be:
- String (may not contain spaces)
- Quoted string (if string may contain spaces)
- Numeric value
- Flag (
yes/noortrue/false) - IP or network (eg.
127.0.0.1,192.168.1.0/24,[::1]/128) - Socket argument (eg.
host:portor/path/to/socketorfd:3for systemd socket) - Regexp (eg.
/Match\*/) - List (eg.
value1, value2, value3) - Recipients list (
user, user@domain, @domain) - Time argument (eg.
10s,5d)
Some directives MUST be specified only in specified sections. Section definition looks like:
section_name {
section_directive;
...
}
- clamav - clamav definitions
- spamd - rspamd definitions
- limits - limits definitions
- greylisting - greylisting definitions
- rule - regexp rule definition (a section per rule)
Directives that can be defined in config file:
Defines global options.
pidfile: specify path to pidfile- Default:
/var/run/rmilter.pid
- Default:
tempdir: specify path to temporary directory. For maximum performance it is recommended to put it on memory file system.- Default:
$TMPDIR
- Default:
bind_socket: socket credits for local bind:- Default:
bind_socket = unix:/var/tmp/rmilter.sock
unix:/path/to/file- bind to local socketinet:[port@host]- bind to inet socket
- Default:
max_size: maximum size of scanned message for clamav, spamd and dcc.- Default:
0 (no limit)
- Default:
strict_auth: strict checks for mails from authenticated senders- Default:
no
- Default:
spf_domains: list of domains that would be checked with spf- Default:
empty (spf disabled)
- Default:
use_dcc: flag that specify whether we should use dcc checks for mail- Default:
no
- Default:
whitelist: global recipients whitelist- Default:
no
- Default:
our_networks: treat mail from these networks as mail from authenticated users (see alsostrict_auth)- Default:
empty
- Default:
Back to top.
Specifies clamav antivirus scanners.
servers: clamav socket definitions in format:/path/to/filehost[:port]Sockets are separated by,
- Default:
empty
connect_timeout: timeout in miliseconds for connecting to clamav- Default:
1s
- Default:
port_timeout: timeout in miliseconds for waiting for clamav port response- Default:
4s
- Default:
results_timeout: timeout in miliseconds for waiting for clamav response- Default:
20s
- Default:
error_time: time in seconds during which we are counting errors- Default:
10
- Default:
dead_time: time in seconds during which we are thinking that server is down- Default:
300
- Default:
maxerrors: maximum number of errors that can occur during error_time to make rmilter thinking that this upstream is dead- Default:
10
- Default:
whitelist: list of ips or nets that should be not checked with spamd- Default:
empty
- Default:
Back to top.
Specifies rspamd or spamassassin spam scanners.
servers: spamd (or rspamd) socket definitions in format:/path/to/filehost[:port]r:/path/to/file- for rspamd protocolr:host[:port]- for rspamd protocol
connect_timeout: timeout in miliseconds for connecting to spamd- Default:
1s
- Default:
results_timeout: timeout in miliseconds for waiting for spamd response- Default:
20s
- Default:
error_time: time in seconds during which we are counting errors- Default:
10
- Default:
dead_time: time in seconds during which we are thinking that server is down- Default:
300
- Default:
maxerrors: maximum number of errors that can occur during error_time to make rmilter thinking that this upstream is dead- Default:
10
- Default:
reject_message: reject message for spam (quoted string)- Default:
Spam message rejected; If this is not spam contact abuse team
- Default:
spamd_soft_fail: if action is not reject use it for other actions (flag)- Default:
true
- Default:
spamd_greylist: greylist message only if action is greylist (flag)- Default:
true
- Default:
spam_header: add specified header if action is add_header and spamd_soft_fail os turned on- Default:
X-Spam
- Default:
rspamd_metric: rspamd metric that would define whether we reject message as spam or not (quoted string)- Default:
default
- Default:
whitelist: list of ips or nets that should be not checked with spamd- Default:
empty
- Default:
extended_spam_headers: add extended spamd headers to messages, is useful for debugging or private mail servers (flag)- Default:
false
- Default:
spamd_never_reject: never reject a message even if spamd action isreject, add header instead (flag)- Default:
false
- Default:
spamd_temp_fail: return temporary failure if spam servers could not be reached (ignore otherwise) (flag)- Default:
false
- Default:
spamd_spam_add_header: additionaly add header (from combination of spam_header and spam_header_value) on rewrite (flag)- Default:
yes
- Default:
Back to top.
Defines redis servers for grey/whitelisting and ratelimits.
servers_grey: redis servers for greylisting in format:host[:port][, host[:port]].- Default:
empty
- Default:
servers_white: redis servers for whitelisting in format similar to that is used in servers_grey- Default:
empty
- Default:
servers_limits: redis servers used for limits storing, can not be mirrored- Default:
empty
- Default:
connect_timeout: timeout in miliseconds for connecting to redis- Default:
1s
- Default:
error_time: time in seconds during which we are counting errors- Default:
10
- Default:
dead_time: time in seconds during which we are thinking that server is down- Default:
300
- Default:
maxerrors: maximum number of errors that can occur during error_time to make rmilter thinking that this upstream is dead- Default:
10
- Default:
Back to top.
Defines beanstalk servers for copying messages with certain properties.
servers: beanstalk servers for pushing headers in format:host[:port][, host:port]- Default:
empty
- Default:
copy_server: address of server to which rmilter should send all messages copies- Default:
empty
- Default:
spam_server: address of server to which rmilter should send spam messages copies- Default:
empty
- Default:
connect_timeout: timeout in miliseconds for connecting to beanstalk- Default:
1s
- Default:
error_time: time in seconds during which we are counting errors- Default:
10
- Default:
dead_time: time in seconds during which we are thinking that server is down- Default:
300
- Default:
maxerrors: maximum number of errors that can occur during error_time to make rmilter thinking that this upstream is dead- Default:
10
- Default:
id_regexp: regexp that defines for which messages we should put the whole message to beanstalk, not only headers, now this regexp checks onlyIn-Reply-Toheaders- Default:
empty
- Default:
send_beanstalk_headers: defines whether we should send headers to beanstalk servers (from servers option)- Default:
no
- Default:
send_beanstalk_copy: defines whether we should send copy of messages to beanstalk server (from copy_server option)- Default:
no
- Default:
send_beanstalk_spam: defines whether we should send copy of spam messages to beanstalk server (from spam_server option)- Default:
no
- Default:
Back to top.
Greylisting related options.
timeout (required): time during which we mark message greylisted- Default:
300s
- Default:
expire (required): time during which we save a greylisting record- Default:
1d
- Default:
whitelist: list of ip addresses or networks that should be whitelisted from greylisting- Default:
empty
- Default:
awl_enable: enable internal auto-whitelist mechanics- Default:
no
- Default:
awl_pool: size for in-memory auto whitelist- Default:
10M
- Default:
awl_hits: number of messages (from this ip) that passes greylisting to put this ip into whitelist- Default:
10
- Default:
awl_ttl: time to live for ip address in auto whitelist- Default:
3600s
- Default:
Back to top.
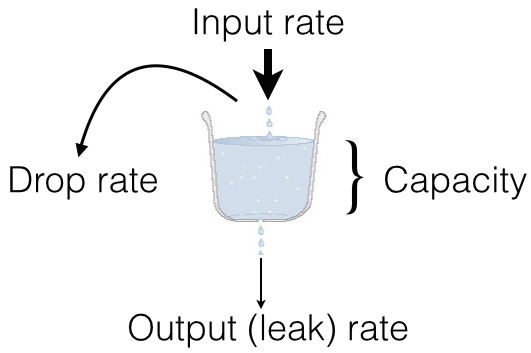
Rate limits are implemented as leaked bucket, so first value is bucket burst - is peak value for messages in bucket (after reaching it bucket is counted as overflowed and new messages are rejected), second value is rate (how much messages can be removed from bucket each second). It can be schematically displayed as following:
limit_whitelist_ip: don't check limits for specified ips- Default:
empty
- Default:
limit_whitelist_rcpt: don't check limits for specified recipients- Default:
no
- Default:
limit_bounce_addrs: list of address that require more strict limits- Default:
postmaster, mailer-daemon, symantec_antivirus_for_smtp_gateways, null, fetchmail-daemon
- Default:
limit_bounce_to: limits bucket for bounce messages (only rcpt to)- Default:
5:0.000277778
- Default:
limit_bounce_to_ip: limits bucket for bounce messages (only rcpt to per one source ip)- Default:
5:0.000277778
- Default:
limit_to: limits bucket for non-bounce messages (only rcpt to)- Default:
20:0.016666667
- Default:
limit_to_ip: limits bucket for non-bounce messages (only rcpt to per one source ip)- Default:
30:0.025
- Default:
limit_to_ip_from: limits bucket for non-bounce messages (msg from, rcpt to per one source ip)- Default:
100:0.033333333
- Default:
Back to top.
Dkim can be used to sign messages by. Dkim support must be provided by opendkim library.
header_canon: canonization of headers (simple or relaxed)- Default:
simple
- Default:
body_canon: canonization of body (simple or relaxed)- Default:
simple
- Default:
sign_alg: signature algorithm (sha1andsha256)- Default:
sha1
- Default:
auth_only: sign mail for authorized users only- Default:
yes
- Default:
domain: domain entry must be enclosed in a separate sectionkey- path to private keydomain- domain to be used for signing (this matches with SMTP FROM data). If domain is*then rmilter tries to search key in thekeypath askeypath/domain.selector.keyfor any domain.selector- dkim DNS selector (e.g. for selector dkim and domain example.com DNS TXT record should be fordkim._domainkey.example.com).
sign_networks- specify internal network to perform signing as well- Default:
empty
- Default:
Back to top.
- DKIM test from and create signing context (MAIL FROM)
- Ratelimit (RCPT TO)
- Greylisting (DATA)
- Ratelimit (EOM, set bucket value)
- Rules (EOM)
- SPF (EOM)
- Message size (EOM) if failed, skip clamav, dcc and spamd checks
- DCC (EOM)
- Spamassassin (EOM)
- Clamav (EOM)
- Beanstalk (EOM)
- DKIM add signature (EOM)
Back to top.
- rcpt - bucket for rcpt filter
- rcpt:ip - bucket for rcpt_ip filter
- rcpt:ip:from - bucket for rcpt_ip_from filter
- rcpt: - bucket for bounce_rcpt filter
- rcpt:ip: - bucket for bounce_rcpt_ip filter
- md5(from . ip . to) - key for greylisting triplet (hexed string of md5 value)
Back to top.
There are several useful settings for postfix to work with this milter:
smtpd_milters = unix:/var/run/rmilter/rmilter.sock
milter_mail_macros = i {mail_addr} {client_addr} {client_name} {auth_authen}
milter_protocol = 6
Back to top.
This section contains a number of useful configuration recipies and best practices for rmilter.
With this setup you should generate keys and store them in /etc/dkim/<domain>.<selector>.key
This could be done, for example by using opendkim-genkey:
opendkim-genkey --domain=example.com --selector=dkim
That will generate dkim.private file with private key and dkim.txt with the suggested TXT record for your domain.
dkim {
domain {
key = /etc/dkim;
domain = "*";
selector = "dkim";
};
header_canon = relaxed;
body_canon = relaxed;
sign_alg = sha256;
};
Please note, that rmilter will sign merely mail for the authenticated users, hence you should also ensure that {auth_authen} macro
is passed to milter on MAIL FROM stage:
milter_mail_macros = i {mail_addr} {client_addr} {client_name} {auth_authen}
Back to top.
It is possible to store Message-ID headers for authenticated users and whitelist replies to that messages by using of rmilter. To enable this
feature, please ensure that you have redis server running and add the following lines to redis section:
redis {
...
# servers_id - redis servers used for message id storing, can not be mirrored
servers_id = localhost;
# id_prefix - prefix for extracting message ids from redis
# Default: empty (no prefix is prepended to key)
id_prefix = "message_id.";
}
Back to top.
Sometimes it might be useful to watch how messages are processed by rspamd. For this purposes, rmilter
can mirror some percentage of messages to beanstalk service and check them using rspamc.
First of all, install beanstalk in your system (in this example I assume that beanstalk is running on port 11300). Then grab
a small routine bean-fetcher. This routine would get messages from beanstalk and feed them to
rspamc. Here is an example configuration file:
[instance1]
host = 127.0.0.1
port = 11300
command = /usr/bin/rspamc --mime --ucl --exec '/usr/lib/dovecot/dovecot-lda -d user'It is also possible, for example, to compare output for different rspamd versions or rules sets:
[instance1]
host = 127.0.0.1
port = 11300
command = [ "/usr/bin/rspamc --mime --ucl --exec '/usr/lib/dovecot/dovecot-lda -d user1'", "/usr/bin/rspamc -h other_host:11333 --mime --ucl --exec '/usr/lib/dovecot/dovecot-lda -d user2'" ]Then setup rmilter to mirror some traffic:
beanstalk {
copy_server = localhost:11300;
send_beanstalk_copy = yes;
# Please note that copy probability is floating point number from 0.0 to 1.0
copy_probability = 0.1;
}
Afterwards, it might be useful also to setup dovecot-sieve for sorting messages between folders by their spam scores:
require ["copy", "fileinto"];
if header :contains "X-Spam-Symbols" "BAYES_SPAM" {
fileinto :copy "bayes_spam";
}
if header :contains "X-Spam-Symbols" "BAYES_HAM" {
fileinto :copy "bayes_ham";
}
if header :is "X-Spam-Action" "reject" {
fileinto "Spam";
}
if header :is "X-Spam-Action" "add header" {
fileinto "Probable";
}
if header :is "X-Spam-Action" "no action" {
fileinto "Ham";
}
if header :is "X-Spam-Action" "greylist" {
fileinto "Greylist";
}
This script sort messages according their spam action and also copies messages with statistics symbols BAYES_HAM and BAYES_SPAM to the appropriate folders for further analysis.
Back to top.