[Update] The paper is accepted by NeurIPS 2024!
This repository contains the code for the paper Invisible Image Watermarks Are Provably Removable Using Generative AI.
If you find this repository useful, please cite our paper:
@article{zhao2023invisible,
title={Invisible Image Watermarks Are Provably Removable Using Generative AI},
author={Zhao, Xuandong and Zhang, Kexun and Su, Zihao and Vasan, Saastha and Grishchenko, Ilya and Kruegel, Christopher and Vigna, Giovanni and Wang, Yu-Xiang and Li, Lei},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01953},
year={2023}
}
We propose a family of regeneration attacks to remove invisible image watermarks. The attack method effectively removes invisible watermarks.
Our attack first maps the watermarked image to its embedding, which is another representation of the image. Then the embedding is noised to destruct the watermark. After that, a regeneration algorithm reconstructs the image from the noisy embedding. As shown in the figure below:
First, install the dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txtThen you can try the demo in demo.ipynb.
For Regen-Diffusion, you can set the DiffWMAttacker noise_step=30/60/100... to control the noise level. The larger the noise_step, the more noise is added to the image, and the watermark is more likely to be removed.
For Regen-VAE, you can set the VAEWMAttacker quality=6/5/4/3/2/1 to control the noise level. The smaller the quality, the more noise is added to the image, and the watermark is more likely to be removed.
This demo attacks invisible-watermark which is used in stable diffusion.
In short, our method can be described using the following equation (1)
where
The embedding function
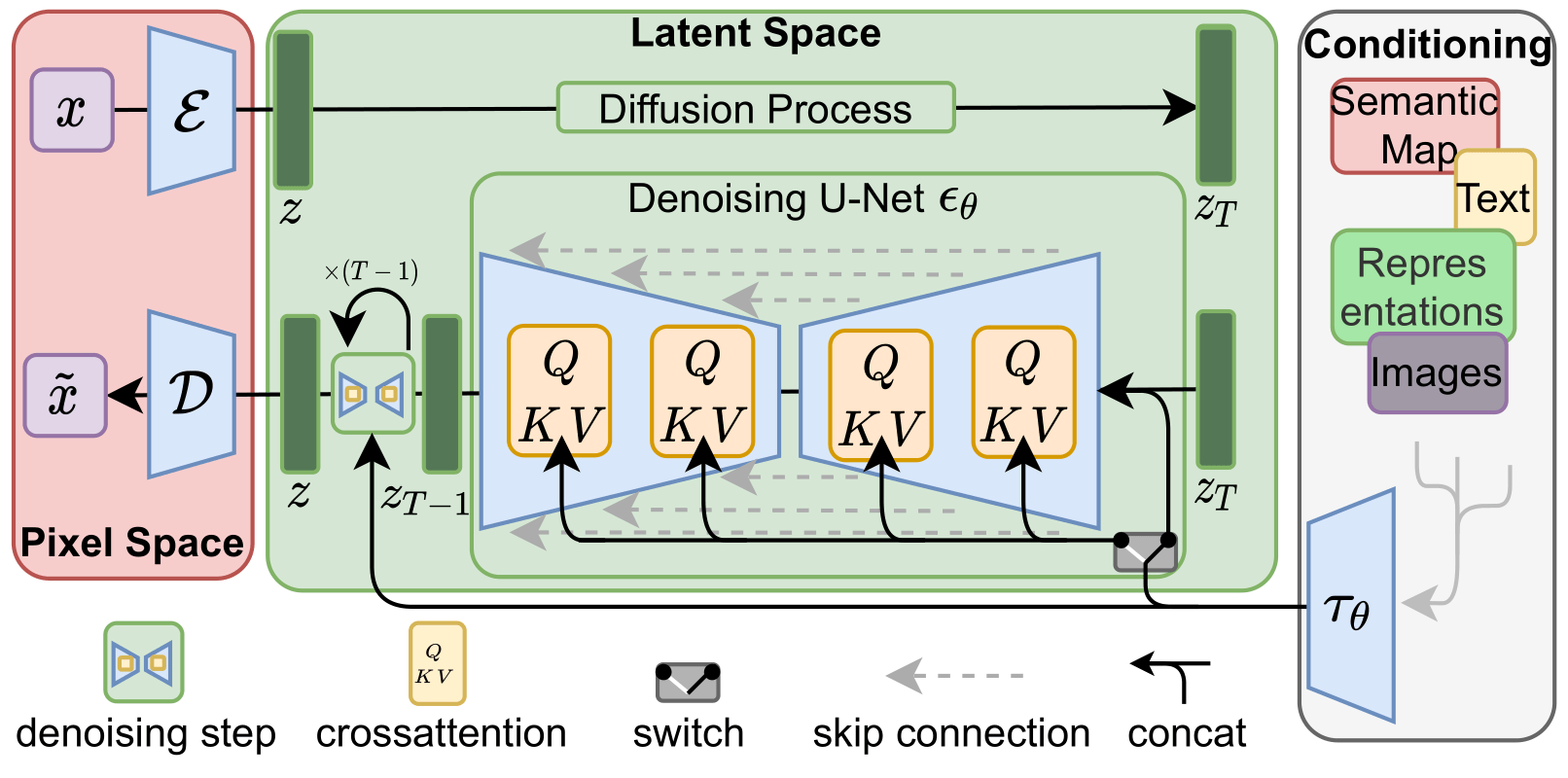
Here let's look at how Stable Diffusion can instantiate our algorithm (see this blog for more information on Stable Diffusion).
The above figure shows the architecture of Stable Diffusion.
The destructive process in our algorithm corresponds to adding noise to the image until a certain time step
where
After obtaining the noised representation