-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Docker Overview
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping and running applications.
- Standardised Development Environments
- Consistent setup across different machines
- CI/CD of your changes
- Unit Testing
- Deploying to Prod
- Write code locally or using cloud compute using standardised development containers.
- Upon pushing changes, build a docker image and run unit tests
- Push images to prod using a container registry like Docker Hub or Github Container Registry.
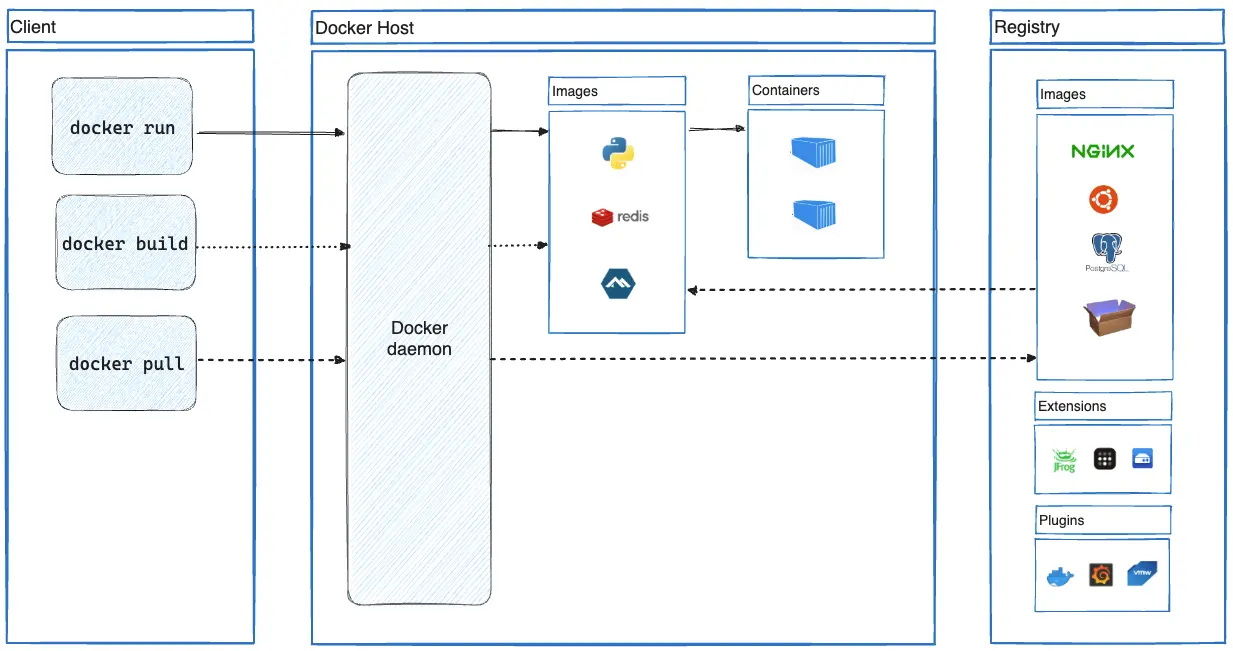
Docker follows a client-server architecture, made up of a client(Docker CLI), a server (Docker Daemon) and a registry.
The Docker client is run through docker or docker compose when orchestrating a set of containers, volumes and networking configurations.
The docker server dockerd manages images, containers, networking and volumes. It communicates with the docker client usually over UNIX sockets.
A Docker registry is a place where docker images are stored.
Examples Include:
- Github Container Registry
- Docker Hub
These are are a read-only template with instructions for creating a docker container. Usually, these are based on another image, but with relevant customisations applied.
Images are built using a Dockerfile to define the steps needed to create an image and run it. Each instruction provided in a dockerfile creates a "layer", particular to that change. This means that when modifying a dockerfile, only the layers changed are rebuilt.
Containers are runnable instances of a specified image, manageable through the docker client. These may be connected to networks, storage and other containers.
When containers are removed, any changes to state that haven't been stored in persistent storage aren't captured.

As Docker containers run using the host's kernel and operating system, they are faster, take up less space and are more efficient compared to a virtual machine.