This is a practice program that takes an input text file of mock computer orders data. The program parses the data and schedules the order based on mock operational restrictions. (e.g profit per order, manufacturing limits, and penalties for cancelled orders)
The txt file is read in as a list of 120 to 200 order in an array like format:
[100,9,8,30]
[101,3,5,47]
[102,5,27,33]
...Each number represents a retail order:
| Order Number | PC Product Number | PC Order Quantity | Profit Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 9 | 8 | 30 |
| 101 | 3 | 5 | 47 |
Each of the PCs require a set of components, and lead time (cycles) to build each PC can vary based on the components being used. For example:
| PC Product Num | Required Components | Required Cycles |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Intel CPU 3GHz, Intel Motherboard, 16GB Ram, 1TB HDD | 4 |
| 1 | Intel CPU 3GHz, Intel Motherboard, 16GB Ram, 2TB HDD | 4 |
Building the PCs took in the following considerations
- Each component also had an associated cost
- There was a limited number of available build cycles. (10,000)
- 18% Discount on any CPU, if the total operational cycle used more than 500 units
- 3% cancellation fee for unfulfilled orders
Given these circumstances the program had to schedule the most profitable orders to produce.
The program takes in the txt file and accounts for the operation limitations and works out the most efficient schedule of orders. Once the program has scheduled the orders, it outputs the print out to a txt file, in the report directory.
TOP LEVEL METRICS
Total orders: 181
Orders Satisfied: 112
Orders Cancelled: 69
Total Cycles Used: 9999
===========================================================
PROFIT AND REVENUE
Total Revenue: $ 4,603,850
Operational / Selling Expenses: $ -1,423,417
Total Cycle Cost: $ -999,900
Total Cancellation Cost: $ -57,084
Gross Profit (after cancellations): $ 2,480,401
Net Profit (including discounts): $ 2,788,021
===========================================================
NO. PC PRODUCED
PC0___________________________27
PC1___________________________28
PC2___________________________0
PC3___________________________28
PC4___________________________81
PC5___________________________53
PC6___________________________65
PC7___________________________115
PC8___________________________186
PC9___________________________161
PC10__________________________153
PC11__________________________240
PC12__________________________90
PC13__________________________184
PC14__________________________247
PC15__________________________125
===========================================================
NO. COMPONENTS USED
Pintel motherboard____________397
Memory 8 GB___________________810
Pintel CPU 5 GHz______________314
IMD CPU 3GHz__________________740
Pintel CPU 3 GHz______________83
Hard disk 1TB_________________936
IMD motherboard_______________1386
Hard disk 2TB_________________847
Memory 16 GB__________________973
IMD CPU 5GHz__________________646
The program is built with and OOP design. Which allowed me to overload numerical operators (>, >= , <, <=, +=).
Order &Order::operator+=(int x) {
this->profit_ += x;
return *this;
}
bool operator>=(const Order &order1, const Order &order2) {
return order1.profit_ >= order2.profit_;
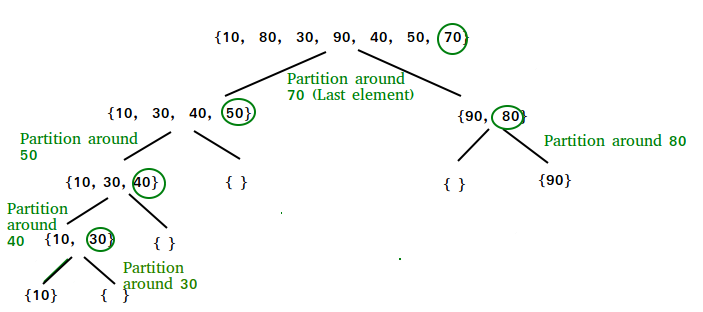
}I then implemented a class with the Quick Sort algorithm, which is a recursive divide and conquer algorithm
To factor in for discounts on CPU purchases, I added an extra weight to each order.
- Read in all orders and calculate the total number of CPUs used.
- For each CPU if there can be over 500 used (minimum for discount), then calculate the difference and multiply by the unit price.
- When using the quick sort, add the extra value calculated in previous step.
The program can simply compiled and run, and it will check the orders directory for any new order bundles.
Options:
- Generate a new bundle of orders and save them to the orders directory
- Explicitly specify path to an order bundle, and will output to console
You can also use the -h flag for more info:
% ./productionScheduling -h
Usage: ./productionScheduling <option(s)> SOURCES
Options:
No arguments results in program scheduling new bundles in the bundle directory
-h,--help Show this help message
-b,--bundle Create new bundle and save to orders path
-r,--report BUNDLE NAME Specify the order bundle path
-rs,--re-schedule Re-schedules all orders in order directory