(how-to-install)=
DeepLabCut can be run on Windows, Linux, or MacOS (see also technical considerations and if you run into issues also check out the Installation Tips page).
-
Everything you need to run DeepLabCut (i.e., our source code and our dependencies) can be installed with
pip install 'deeplabcut[gui,tf]'(for GUI support w/tensorflow) or without the gui:pip install 'deeplabcut[tf]'. -
Please note, there are several modes of installation, and the user should decide to either use a system-wide (see note below), conda environment based installation (recommended), or the supplied Docker container (recommended for Ubuntu advanced users). One can of course also use other Python distributions than Anaconda, but Anaconda is the easiest route.
Install anaconda or use miniconda3 (ideal for MacOS users)!
- Anaconda is an easy way to install Python and additional packages across various operating systems. With Anaconda you create all the dependencies in an environment on your machine.
Download anaconda for your operating system: https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/.
- IF you use a M1 or M2 chip in your MacBook with v12.5+ (typically 2020 or newer machines), you should use miniconda3, which operates with the same principles as anaconda. This is straight forward and explained in detail here: https://docs.conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/install/macos.html. But in short, open the program "terminal" and copy/paste and run:
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-py39_4.12.0-MacOSX-arm64.sh -O ~/miniconda.sh
bash ~/miniconda.sh -b -p $HOME/miniconda
source ~/miniconda/bin/activate
conda init zsh
-
You need to decide if you want to use a CPU or GPU for your models: (Note, you can also use the CPU-only for project management and labeling the data! Then, for example, use Google Colaboratory GPUs for free (read more here and there are a lot of helper videos on our YouTube channel!).
-
CPU? Great, jump to the next section below!
-
NVIDIA GPU? If you want to use your own GPU (i.e., a GPU is in your workstation), then you need to be sure you have a CUDA compatible GPU, CUDA, and cuDNN installed. Please note, which CUDA you install depends on what version of tensorflow you want to use. So, please check "GPU Support" below carefully. Note, DeepLabCut is up to date with the latest CUDA and tensorflow versions!
-
Apple M1/M2 GPU? Be sure to install miniconda3, and your GPU will be used by default.
-
-
Windows/Linux/MacBooks: git clone this repo (in the terminal/cmd program, while in a folder you wish to place DeepLabCut To git clone type:
git clone https://github.com/DeepLabCut/DeepLabCut.git). Note, this can be anywhere, even downloads is fine.) -
Now, in Terminal (or Anaconda Command Prompt for Windows users), go to the DeepLabCut folder. If you cloned the repo onto your Desktop, the command may look like:
cd C:\Users\YourUserName\Desktop\DeepLabCut\conda-environments
To get the location right, a cool trick is to drag the folder and drop it into Terminal. Alternatively, you can (on Windows) hold SHIFT and right-click > Copy as path, or (on Mac) right-click and while in the menu press the OPTION key to reveal Copy as Pathname.
- Now, in the terminal run (Windows/Linux/MacBook Intel chip):
conda env create -f DEEPLABCUT.yaml
- or for Apple M1 / M2 chips:
conda env create -f DEEPLABCUT_M1.yaml
- You can now use this environment from anywhere on your comptuer (i.e., no need to go back into the conda- folder). Just enter your environment by running:
- Ubuntu/MacOS:
source/conda activate nameoftheenv(i.e. on your Mac:conda activate DEEPLABCUTorconda activate DEEPLABCUT_M1) - Windows:
activate nameoftheenv(i.e.activate DEEPLABCUT)
- Ubuntu/MacOS:
Now you should see (nameofenv) on the left of your terminal screen, i.e. (DEEPLABCUT_M1) YourName-MacBook...
NOTE: no need to run pip install deeplabcut, as it is already installed!!! :)
Great, that's it! DeepLabCut is installed!
- We also have docker containers. Docker is the most reproducible way to use and deploy code. Please see our dedicated docker package and page here.
More installation ProTips are also available.
If you ever want to update your DLC, just run pip install --upgrade deeplabcut once you are inside your env. If you want to use a specific release, then you need to specify the version you want, such as pip install deeplabcut==2.2. Once installed, you can check the version by running import deeplabcut deeplabcut.__version__. Don't be afraid to update, DLC is backwards compatible with your 2.0+ projects and performance continues to get better and new features are added nearly monthly.
Here are some conda environment management tips: https://kapeli.com/cheat_sheets/Conda.docset/Contents/Resources/Documents/index
Pro Tip: If you want to modify code and then test it, you can use our provided testscripts. This would mean you need to be up-to-date with the latest GitHub-based code though! Please see here on how to get the latest GitHub code, and how to test your installation by following this video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IOWtKn3l33s.
*Note in a fresh ubuntu install, you will often have to run: sudo apt-get install gcc python3-dev to install the GNU Compiler Collection and the python developing environment.
Some users might want to create their own customize env. - Here is an example.
In the terminal type:
conda create -n DLC python=3.8
The only thing you then need to add to the env is deeplabcut (pip install deeplabcut) or pip install 'deeplabcut[gui]' which has wxPython for GUI support. For Windows and MacOS, you just run pip install -U wxPython<4.1.0 but for linux you might need the specific wheel (https://wxpython.org/pages/downloads/index.html).
We have some tips for linux users here, as the latest Ubuntu doesn't easily support a 1-click install: https://deeplabcut.github.io/DeepLabCut/docs/recipes/installTips.html
The ONLY thing you need to do first if you have an NVIDIA GPU and the matching NVIDIA CUDA+driver installed.
- CUDA: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads (just follow the prompts here!)
- DRIVERS: https://www.nvidia.com/Download/index.aspx
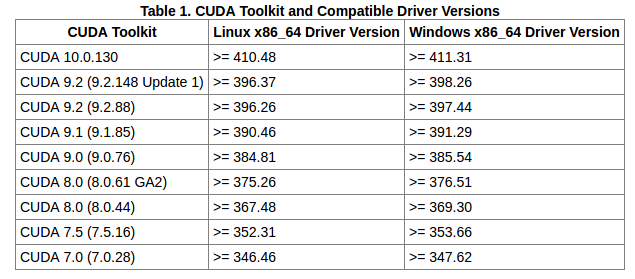
CRITICAL: If you have a GPU, you should FIRST install the NVIDIA CUDA package and an appropriate driver for your specific GPU, then you can use the supplied conda file. Please follow the instructions found here https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu, and more tips below, to install the correct version of CUDA and your graphic card driver. The order of operations matters.
- Here we provide notes on how to install and check your GPU use with TensorFlow (which is used by DeepLabCut and already installed with the Anaconda files above). Thus, you do not need to independently install tensorflow.
FIRST, install a driver for your GPU. Find DRIVER HERE: https://www.nvidia.com/download/index.aspx
- check which driver is installed by typing this into the terminal:
nvidia-smi.
SECOND, install CUDA (versions up to CUDA11 are supported, together with TF2.5): https://developer.nvidia.com/ (Note that cuDNN, https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn, is supplied inside the anaconda environment files, so you don't need to install it again).
THIRD: Follow the steps above to get the DEEPLABCUT conda file and install it!
- All of the TensorFlow versions work with DeepLabCut. But, please be mindful different versions of TensorFlow require different CUDA versions.
- As the combination of TensorFlow and CUDA matters, we strongly encourage you to check your driver/cuDNN/CUDA/TensorFlow versions on this StackOverflow post.
- To check your GPU is working, in the terminal, run:
nvcc -V to check your installed version(s).
-
The best practice is to then run the supplied
testscript.py(this is inside the examples folder you acquired when you git cloned the repo). Here is more information/a short video on running the testscript. -
Additionally, if you want to use the bleeding edge, with yout git clone you also get the latest code. While inside the main DeepLabCut folder, you can run
./reinstall.shto be sure it's installed (more here: https://github.com/DeepLabCut/DeepLabCut/wiki/How-to-use-the-latest-GitHub-code) -
You can test that your GPU is being properly engaged with these additional tips.
-
Ubuntu users might find this installation guide for a fresh ubuntu install useful as well.
TensorFlow: Here are some additional resources users have found helpful (posted without endorsement):
FFMPEG:
- A few Windows users report needing to install re-install ffmpeg (after windows updates) as described here: https://video.stackexchange.com/questions/20495/how-do-i-set-up-and-use-ffmpeg-in-windows (A potential error could occur when making new videos). On Ubuntu, the command is:
sudo apt install ffmpeg
DEEPLABCUT:
- if you git clone or download this folder, and are inside of it then
import deeplabcutwill import the package from there rather than from the latest on PyPi!
(system-wide-considerations-during-install)=
If you perform the system-wide installation, and the computer has other Python packages or TensorFlow versions installed that conflict, this will overwrite them. If you have a dedicated machine for DeepLabCut, this is fine. If there are other applications that require different versions of libraries, then one would potentially break those applications. The solution to this problem is to create a virtual environment, a self-contained directory that contains a Python installation for a particular version of Python, plus additional packages. One way to manage virtual environments is to use conda environments (for which you need Anaconda installed).
(tech-considerations-during-install)=
-
Computer:
- For reference, we use e.g. Dell workstations (79xx series) with Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, 18.04 LTS, or 20.04 LTS and for versions prior to 2.2, we run a Docker container that has TensorFlow, etc. installed (https://github.com/DeepLabCut/Docker4DeepLabCut2.0). Now we use the new Docker containers supplied on this repo, also available through DockerHub or the
deeplabcut-dockerhelper script.
- For reference, we use e.g. Dell workstations (79xx series) with Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, 18.04 LTS, or 20.04 LTS and for versions prior to 2.2, we run a Docker container that has TensorFlow, etc. installed (https://github.com/DeepLabCut/Docker4DeepLabCut2.0). Now we use the new Docker containers supplied on this repo, also available through DockerHub or the
-
Computer Hardware:
- Ideally, you will use a strong GPU with at least 8GB memory such as the NVIDIA GeForce 1080 Ti or 2080 Ti. A GPU is not necessary, but on a CPU the (training and evaluation) code is considerably slower (10x) for ResNets, but MobileNets are faster (see WIKI). You might also consider using cloud computing services like Google cloud/amazon web services or Google Colaboratory.
-
Camera Hardware:
- The software is very robust to track data from any camera (cell phone cameras, grayscale, color; captured under infrared light, different manufacturers, etc.). See demos on our website.
-
Software:
- Operating System: Linux (Ubuntu), MacOS* (Mojave), or Windows 10. However, the authors strongly recommend Ubuntu! *MacOS does not support NVIDIA GPUs (easily), so we only suggest this option for CPU use or a case where the user wants to label data, refine data, etc and then push the project to a cloud resource for GPU computing steps, or use MobileNets.
- Anaconda/Python3: Anaconda: a free and open source distribution of the Python programming language (download from https://www.anaconda.com/). DeepLabCut is written in Python 3 (https://www.python.org/) and not compatible with Python 2.
pip install deeplabcut- TensorFlow
- You will need TensorFlow (we used version 1.0 in the paper, later versions also work with the provided code (we tested TensorFlow versions 1.0 to 1.15, and 2.0 to 2.5; we recommend TF2.5 now) for Python 3.7, 3.8, or 3.9 with GPU support.
- To note, is it possible to run DeepLabCut on your CPU, but it will be VERY slow (see: Mathis & Warren). However, this is the preferred path if you want to test DeepLabCut on your own computer/data before purchasing a GPU, with the added benefit of a straightforward installation! Otherwise, use our COLAB notebooks for GPU access for testing.
- Docker: We highly recommend advanced users use the supplied Docker container
Return to readme.