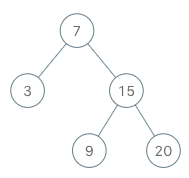
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器。你将使用二叉搜索树的根节点初始化迭代器。
调用 next() 将返回二叉搜索树中的下一个最小的数。
示例:
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root); iterator.next(); // 返回 3 iterator.next(); // 返回 7 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true iterator.next(); // 返回 9 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true iterator.next(); // 返回 15 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true iterator.next(); // 返回 20 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 false
提示:
next()和hasNext()操作的时间复杂度是 O(1),并使用 O(h) 内存,其中 h 是树的高度。- 你可以假设
next()调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用next()时,BST 中至少存在一个下一个最小的数。
题目标签:Stack / Tree / Design
题目链接:LeetCode / LeetCode中国
| Language | Runtime | Memory |
|---|---|---|
| java | 60 ms | 52.6 MB |
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class BSTIterator {
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<>();
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
public int next() {
TreeNode t = stk.pop();
int val = t.val;
t = t.right;
while (t != null) {
stk.push(t);
t = t.left;
}
return val;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
public boolean hasNext() {
return !stk.empty();
}
}
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj.next();
* boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext();
*/