This is a page to document some additional methods and techniques implemented in KataGo, such as some things not in (the latest version of) the arXiv paper, or that were invented or implemented or discovered by KataGo later, or that were drawn from other research or literature but not documented elsewhere in KataGo's paper or materials.
(This method has been used in KataGo through all of its runs. It was presented in an early draft of its paper but was cut later for length limitations).
KataGo was possibly the first superhuman selfplay-learning Go bot capable of playing on a wide range of board sizes using the same neural net. It trains the same neural net on all board sizes from 9x9 to 19x19 and reaches superhuman levels on all of them together. Although actual ML applications are often more flexible, in a lot of deep learning literature tutorials and many real ML training pipelines, it's common to require or to preprocess all inputs to be the same size. However, with the right method, it's straightforward to train a neural net that can handle inputs of variable size, even within a single batch.
The method consists of two parts. First, designing the neural net to not intrinsically require a certain size of board. Second, a masking trick that allows mixing multiple board sizes into the same batch during both training and inference, working around the fact that tensors in ML libraries and for GPUs have to be rectangularly sized.
The first part is easier than one might expect. For example, convolution is a local operation that transforms values only based on their neighbors, so a convolutional layer can be applied to any size of input. Many common pooling layers and normalization layers are also size-independent. This means almost all of a standard residual convolutional net can be applied identically regardless of whether the input is 9x9, or 19x19, or 32x32, or 57x193. The only tricky part sometimes is the output head. In a lot of literature, you find that the output head is a set of fully-connected layers mapping C (channels) * H (height) * W (width) values to some final output(s). Such a head has weight dimensions that depend on H and W, so is not size-independent, but it is not hard to construct alternate heads that are. For example, global average pooling the C * H * W channels down to just a fixed C channels before applying a fully-connected head. Or perhaps having a fixed C' different channels that are allowed to attend to spatial subregions of the C * H * W values, where attention weights are computed via convolutions. Or, depending on the application, perhaps the output head can simply be itself convolutional. KataGo uses a mix of these approaches variously for the policy and value heads and auxiliary heads.
With the net non-hardcoded to any size, the second part is how to perform mixed-size batched training so that the learned weights are effective when applied to different sizes. For this, one can mix sizes into the same batch by a masking trick:
- Size the input tensor to the size of the largest input in that batch.
- Zero-pad each entry in the batch independently to fill out the excess space.
- Keep a 0-1 mask of which parts of the tensor are "real" space, rather than excess space, and apply the mask after each operation that would make the excess space nonzero.
- Additionally, if the net contains operations like channelwise average pooling, or other things that depend on the spatial size, use a divisor based on the true spatial size, rather than the tensor size, so that the zeros in the excess space do not dilute the average.
Whenever a convolution "peers over the edge" of its input, it will see only zeros, exactly the same as it would see with a zero-padding convolution if the tensor were properly sized to that entry. After operations like convolution, the padding space may no longer be all zero because the convolution will introduce nonzero values into the excess space. This can be solved simply by masking those entries back to 0, as illustrated below. Most nets add various kinds of scaling or normalization or bias layers between convolutional layers, and the masking can simply be included with that operation (fusing it into the same GPU kernel, if performance is desired) making it very, very cheap.
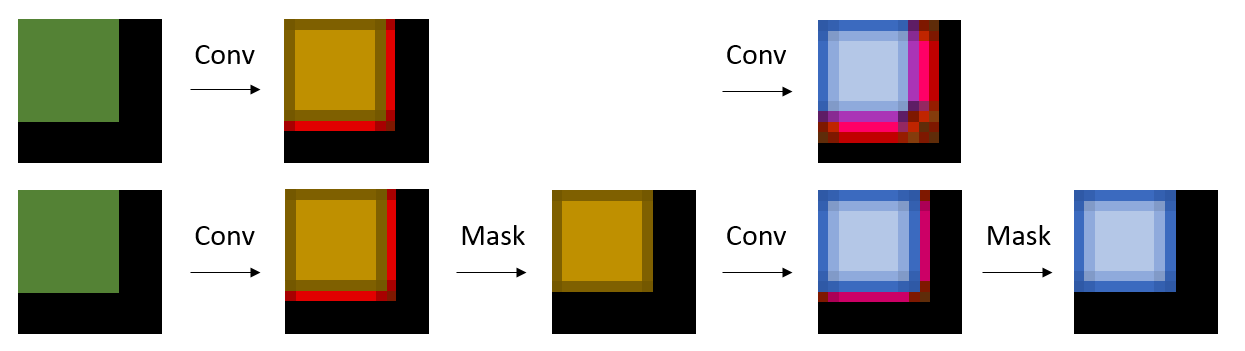 |
| Convolution produces values within oversized tensor area. Top: The next convolution corrupts the final blue square. Bottom: Masking ensures a final result independent of tensor size. |
The result of the above is that that KataGo is able to train a single net on many board sizes at once, generalizing across all of them. Although KataGo's recent 2020 run ("g170") only trained on sizes from 7x7 to 19x19, it appears to extrapolate quite effectively to larger boards, playing at a high level on board sizes in the 20s and 30s with no additional training, demonstrating that the net has learned general rules for how size scaling should affect its predictions. Mixed-size training is also not particularly expensive. At least in early training up to human pro level, KataGo seems to learn at least equally fast and perhaps slightly faster than training on 19x19 alone. This is likely due to massive knowledge transfer between sizes, and because playing smaller boards with lower branching factors and game length might give faster feedback that also speeds up learning on larger boards.
Outside of Go and board games, the suitability of this method may of course greatly depend on the application. For example, downsampling to make input sizes match might be more suitable than directly mixing sizes via the above method for an image processing application where different-sized images have intrinsic different levels of detail resolution, since variable resolution means the low-level task differs. Whereas in Go, the local tactics always behave the same way per "pixel" of the board. Using the above method might also require some care in the construction of the final output head(s) depending on the task. But regardless, size-independent net architectures and mixing sizes via masking seem like useful tricks to have in one's toolbox.
(This method was used starting in "g170", KataGo's January 2020 to June 2020 run).
KataGo has been successfully training without batch normalization or any other normalization layers by using Fixup Initialization, a simple new technique published in ICLR 2019: https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.09321 (Zhang, Dauphin, and Ma, ICLR 2019).
KataGo's implementation of Fixup was fairly straightforward, with a minor adjustment due to using preactivation residual blocks. Within each residual block we:
-
Replace both of the batch-norm layers with just plain channelwise additive bias layers, initialized to 0.
-
Insert one channelwise multiplicative scaling layer, just before the final convolution, initialized to 1.
-
Initialize the first convolution weights of the block using the normal "He" initialization, except multiplied by
1/sqrt(total number of residual blocks). -
Initialize the second convolution weights of the block to 0.
And lastly, KataGo added a gradient clip. It appears that early in training when the net is still mostly random, rarely KataGo's training will experience batches causing very large gradient steps just due to the nature of the training data and high early learning rate. By forcibly scaling down scaling large activations, batch norm was preventing blowup. However, a gradient clip set at roughly a small constant factor larger than normal early-training gradients appeared to be just as effective. This only affected early training - past that, the gradient is almost never large enough to even come close to the clip limit.
Unlike what the authors of Fixup needed for their experiments, KataGo needed no additional regularization to reproduce and even surpass the quality of the original training.
Dropping batch normalization has resulted in some very nice advantages:
-
Much better performance on the training GPU. Batch norm is surprisingly expensive during gradient updates, removing it sped up training by something like 1.6x or 1.8x. This is not that important overall given that selfplay is most of the cost, but is still nice.
-
Simple logic for the neural net in different contexts. There is no longer a need to behave differently in training versus inference.
-
Because there is no longer cross-sample dependence in a batch or overt batch-size-dependence, easy to write things like multi-GPU training that splits apart batches while achieving mathematically identical results, or to vary the batch size without as much tricky hyperparameter tuning.
-
Avoidance of a few suspected problems caused by batch norm itself. Leela Chess Zero in an older run found an explicit problem caused by batch normalization where due to the rarity of activation of certain channels (but nonetheless highly-important rare activations, apparently used in situations where a pawn is about to promote), batch norm's per-batch normalization was not represented well by the inference-time scaling. Although KataGo did not test in enough detail to be sure, anecdotally KataGo experienced a few similar problems regarding Japanese vs Chinese rules when evaluating rare "seki" positions, which improved in runs without batch norm.
(This method was used starting in "g170", KataGo's January 2020 to June 2020 run).
Although this method is used in KataGo, due to heavy limits on testing resources, it has not been validated as a measurable improvement with controlled runs. The evidence for it should be considered merely suggestive, so this section is just here to describe the idea and intuition. However, to the extent that Dirichlet noise is useful, this method seems to have a much greater-than-baseline chance of noising true blind-spot moves the vast majority of the time, and therefore is included in KataGo's recent runs anyways.
To give some background: to help unexpected new good moves to have a chance of being explored, AlphaZero-style self-play training replaces 25% of the root policy prior mass with Dirichlet-distributed noise, with Dirichlet alpha parameter of 0.03 per move. KataGo uses a "total alpha" of 10.83 = 361 * 0.03 divided across legal moves, such that the Dirichlet alpha parameter for each legal move on the empty 19x19 board matches that of AlphaZero's. Since the sum of the alphas is 10.83, interpretively this can be loosely thought of as selecting "about 10.83" legal moves at random with replacement and putting about 25% / 10 = 2.5% policy prior on each one (specifically, via a Polya's urn process). The Dirichlet alpha scales the likelihood of selection, so when alpha is spread uniformly, each legal move is equally likely to be selected.
When examining positions by hand, one finds that the vast majority of the time, even "blind spot" moves with very low policy priors have higher policy prior than most legal moves on the board. Even if the absolute prior is low, like only 0.05%, this is often still much higher than most obviously bad moves (moves on the first line, moves that add stones within one's own completely alive territory, moves that threaten absolutely nothing, etc.).
Therefore, KataGo tries to shape the Dirichlet noise to increase the likelihood that such moves are noised and explored. Using an arbitrary formula based on the log of the policy prior (see the code for details), KataGo distributes only half of the total alpha uniformly, and concentrates the other half of the alpha on the smaller subset of moves that still have a policy much higher in logits than most other legal moves.
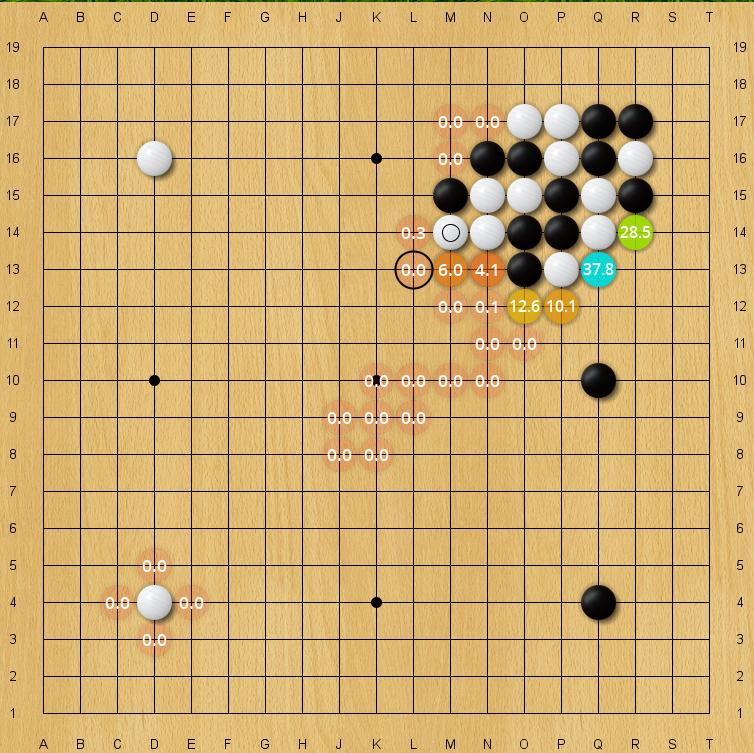 |
| Blind spot for an older 40-block KataGo net, policy prior. The correct move L13 has only an 0.008% policy prior on this evaluation, but is still higher than almost all arbitrary moves on the board. (Every unlabeled move is lower in policy prior than it). |
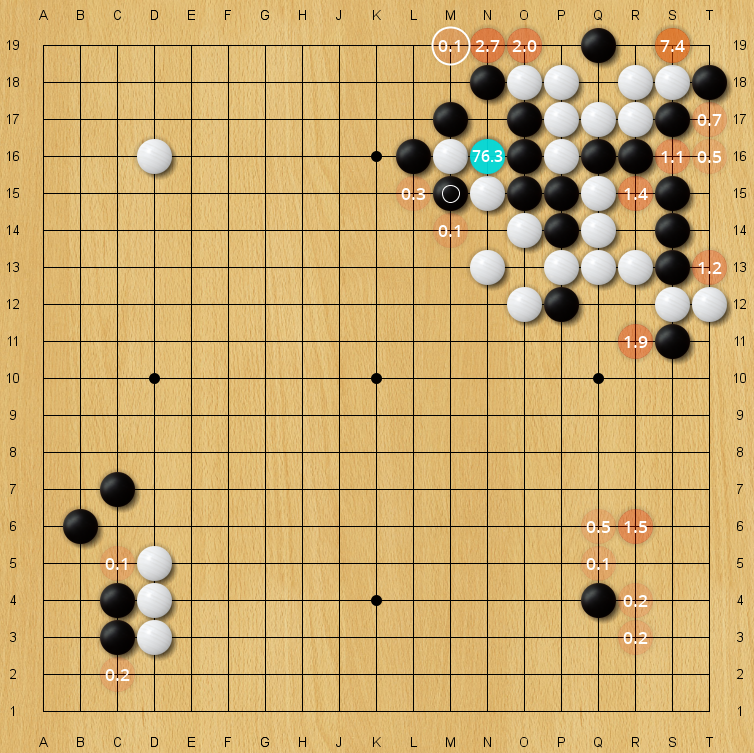 |
| Blind spot for an older 40-block KataGo net, policy prior. The correct move M19 has only an 0.11% policy prior on this evaluation, but is still higher than almost all arbitrary moves on the board. (Every unlabeled move is lower in policy prior than it). |
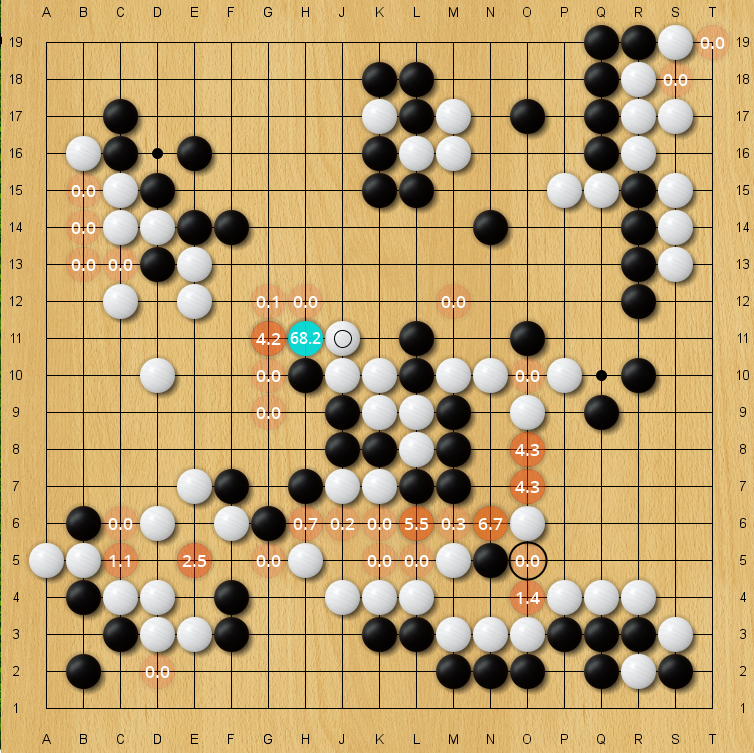 |
| Blind spot for an older 40-block KataGo net, policy prior. The correct move O5 has only an 0.03% policy prior on this evaluation, but is still higher than almost all arbitrary moves on the board. (Every unlabeled move is lower in policy prior than it). |
Note that the ability of KataGo's to discriminate between moves even in such extreme realms of unlikelihood, is improved by policy target pruning as described in KataGo's paper. Without policy target pruning, moves with policy prior like 0.008% might be obscured by the haze of probability mass assigned uniformly to all moves in the neural net's attempt to predict the background of noise playouts, which in turn would probably make this technique of shaped Dirichlet noise less effective.
(This method was used starting in "g170", KataGo's January 2020 to June 2020 run).
KataGo uses the same technique as SAI used to stabilize some of its early runs and improve exploration and counter the above dynamic - which is to use a softmax temperature slightly above 1 applied to the policy prior before adding Dirichlet noise or using the policy prior in the search. In KataGo's g170 run, this temperature was 1.25 for the early game, decaying exponentially to 1.1 for the rest of the game with a halflife in turns of the board dimensions (e.g. 9, or 19). The scaling is applied only at the root node.
Viewed in logit space, this is equivalent to scaling all logits towards 0 by a factor of 1.1, or 1.25, and requires the MCTS search to affirmatively "push back" against this force to maintain policy sharpness. This ensures that moves will not decay in policy prior if the MCTS search finds them to have a utility comparable that of the the best other moves with no evidence that the move is worse.
The motivation for this is to observe that in the baseline AlphaZero algorithm, due to the dynamics of the PUCT formula, there is a slight tendency for the most-preferred move in a position to become yet more strongly preferred, even when that move is valued only equally to its alternatives. If one runs an MCTS search with a given policy prior but where the utility value of a move is equal and fixed to that of the best other moves, due to the +1 in the denominator of the formula and the discretization of the search, the MCTS visit distribution will generally be sharper than the prior, despite zero evidence having been obtained by the search that the move is better than its alternatives. Additionally, in early opening positions in games like Go, the policy sometimes becomes opinionated a little too quickly between nearly-equal moves to explore well. It may be that the search disfavors a given move due to consistently undervaluing a tactic, so the entire training window fills with data that reinforces that, so the policy for the move converges to nearly zero, preventing exploration of that move and the chance to learn otherwise, even if the difference is slight. (Dirichlet noise helps, but alone doesn't prevent this). Having a restoring force pushing the policy back towards uniform among moves that are extremely similarly-valued improves exploration, so here too policy softmax temperature is helpful.
(This method was used starting in "g170", KataGo's January 2020 to June 2020 run).
KataGo overweights the frequency of training samples where the policy training target was "highly surprising" relative to the policy prior. Conveniently, in the process of generating self-play training data we can know exactly how surprising one of the most recent neural nets would have found that data since we can just look at the policy prior on the root node. This method is one of the larger improvements in KataGo's training between its g170 run and earlier runs.
In detail: normally KataGo would record each position that was given a "full" search instead of a "fast" search (see "Playout Cap Randomization" here KataGo's paper for understanding "full" vs "fast" searches) with a "frequency weight" of 1 in the training data, i.e. writing it into the training data once. With Policy Surprise Weighting, instead, among all full-searched moves in the game, KataGo redistributes their frequency weights so that about half of the total frequency weight is assigned uniformly, giving a baseline frequency weight of 0.5, and the other half of the frequency weight is distributed proportional to the KL-divergence from the policy prior to the policy training target for that move. Then, each position is written down in the training data floor(frequency_weight) many times, as well as an additional time with probability to frequency_weight - floor(frequency_weight). This results in "surprising" positions being written down much more often.
In KataGo the method used is not like importance sampling where the position is seen more often but the gradient of the sample is scaled down proportionally to the increased frequency, to avoid bias. We simply sample the position more frequently, using full weight for the sample. The purpose of the policy is simply to suggest moves for MCTS exploration, and unlike a predictive classifier, or stochastically sampling a distribution, or other similar methods where having an unbiased output is good, biasing rare good moves upward and having them learned a bit more quickly seems fairly innocuous (and in the theoretical limit of optimal play, any policy distribution supported on the set of optimal moves is equally optimal).
Some additional minor notes:
- Due to an arbitrary implementation choice, KataGo uses the noised softmaxed root policy prior, rather than the raw prior. Possibly using the raw prior would be very slightly better, although it might require changing other hyperparameters.
- The frequency weight of a full search is actually not always 1. It might be lower near the end of the game due to KataGo's "soft resignation" scheme where instead of resigning a self-play training game, KataGo simply conducts faster and lower-weighted searches to finish the game past the point where AlphaZero or Leela Zero would have resigned, to avoid introducing pathological biases in the training data.
- KataGo allows "fast" searches to get a nonzero frequency weight if despite the lower number of playouts, the fast search still found a result that was very surprising, using a somewhat arbitrary and not-particularly-carefully-tuned cutoff threshold for the required KL-divergence to be included.
- Additionally, in KataGo we also add a small weight for surprising utility value samples, rather than just surprising policy samples, but this is much more experimental and unproven.
(This method was discovered a few months after the end of KataGo's "g170" run).
As of late 2020, KataGo has tentatively found a heuristic method of improving MCTS search evaluation accuracy in Go. Fascinatingly, it is of the same flavor as older methods like RAVE in classic MCTS bots, or the history heuristic in alpha-beta bots, or pattern-based logic in Go bots between 2010 and 2015. Many of these methods have fallen out of use in post-AlphaZero MCTS due to being no longer helpful and often harmful, intuitively due to the fact that compared to a neural net that actually "understands" the board position, such blind heuristics are vastly inferior. Possibly the reason why this method could still have value is because rather than attempting to provide an absolute estimate of utility value, it instead focuses on online-learning of some correlated errors, or bias in the value from the neural net at nodes relative to values from deeper search in the node's subtree.
While possibly similar things have been invented and published elsewhere, as of late 2020 I am personally unaware of anything quite like this that has been successful in post-AlphaZero MCTS bots. This method adjusts only the utility estimates of MCTS search tree nodes. Exploration and the PUCT formula remain unchanged except for taking the new utility values as input. The method is as follows:
Firstly, we write the relationship that defines MCTS utility of a search tree node in a mathematically equivalent but slightly different form than usually presented. Normally in AlphaZero-style MCTS, the MCTS utility estimate for a node at during the search is the running average of the raw heuristic utility estimates from the neural net or other evaluation function - which here we call "NodeUtility" - averaged over all playouts that passed through that node. Here, rather than expressing it as a running statistical average of the playouts that have been sent through that node, we define it as a recurrence based on its children. Define the MCTS utility of each search node n in terms of the raw heuristic utility estimate of that node and of the utility of its children c by:
For a node that has at least one child, we also track the observed error of the neural net's raw utility prediction relative to its subtree, which we presume is probably a more accurate estimate due to the deeper search:
In normal MCTS search, we would have NNUtility = NodeUtility (i.e. the neural net's raw value estimate of node are what get averaged in the running statistics), but as we will see below, for this method we distinguish the two.
We bucket all nodes in the search tree using the following combination as the key:
- The player who made the last move.
- The location of the last move (treating "pass" as a location).
- The location of the move before last move (treating "pass" as a location).
- If the last move was not a pass, the 5x5 pattern (Black, White, Empty, Off-board) surrounding the last move, as well as which stones in that pattern were in atari.
- If the previous move made a move illegal due to ko ban, the location of that ko ban.
For each bucket B, we define its weighted average observed bias:
where ChildVisits(n) = Visits(n) - 1 is the total number of visits to children of that node.Then, instead of defining NodeUtility to be equal to the neural net's utility prediction on that node (as in normal MCTS), we define NodeUtility to be a "bias-corrected" value that adjusts the raw neural net evaluation:
Every time a playout finishes, while walking back up the tree, in process of recomputing each node's MCTS utility to take into account the result, for that node's bucket we also recompute the bucket's ObsBias based on the updated ObsError for that node. Then, we also immediately retrieve that ObsBias value to update this node's NodeUtility. This also applies to leaf nodes that are not game-terminal positions - when a node is created at the end of a search tree branch, it immediately retrieves the ObsBias for the bucket it belongs to (although, of course, since the node has no children yet with which to compute its own error, it does not affect the bucket's ObsBias yet).
The rest of MCTS proceeds as normal and behaves exactly like it would except using these bias-adjusted NodeUtility values instead of the original NNUtility values (and which, unlike the NNUtility values, can "retroactively" update later as the bucket values change), and the resulting MCTSUtility values that result from averaging them.
In KataGo, currently we only retrieve a new ObsBias value for a node from its bucket as we walk through that node following a playout. Nodes in other parts of the tree may grow slightly stale as the observed bias for their bucket changes, but will update the next time they are visited. KataGo also has a bit of handling that carries over part of the weigh of buckets during search tree reuse between turns when some parts of the tree are lost but others remain. KataGo currently finds lambda = 0.35 and alpha = 0.8 to be a very significant improvement over normal MCTS, ranging from 30 to 60 Elo.
The intuition behind all of this is to correct for persistent biases in the neural net's evaluation regarding certain sequences of play in an online fashion. For example, the neural net might persistently judge a particular sequence of moves as initially promising, but will realize upon deeper search that actually the result is bad. This tactic may be explored in many different branches of the search tree, over and over, each time being judged promising, explored, and giving a bad result. Or, the reverse may happen, with a repeated tactic always coming out better than the net initially predicts. By bucketing nodes by the local pattern, once one of the explorations of a tactic has gone deep enough to realize a more accurate evaluation, subsequent explorations of that tactic elsewhere will use neural net evaluations that are bias-corrected proportional to the weighted average observed error between the neural net at the start of the tactic and the subtrees of the search that explore the tactic.
By only averaging errors in a bucket rather than absolute utilities, we continue to leverage the neural net's overall ability to predict the utility far more accurately than any crude heuristic. Each different place in a search tree that a tactic is visited, changes may have occurred elsewhere on the board that significantly affect the overall expected utility in a way that only a sophisticated net can judge in absolute terms. However, the error in the neural net's evaluation of this local tactic relative to that overall level may still be consistent. This is possibly the reason why at least in early testing, this method seems still beneficial, whereas other methods that deal with absolute utlities, like RAVE, are not so useful in modern bots.