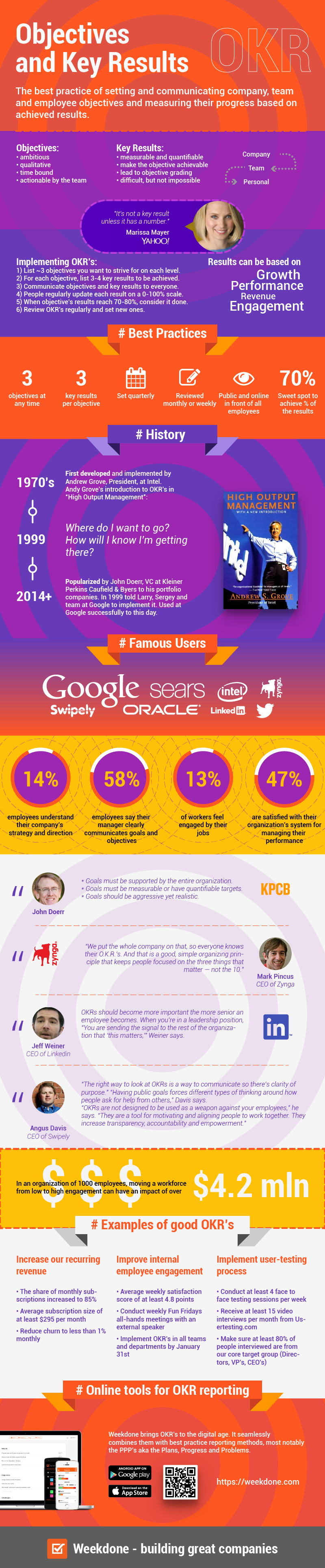
Objective - Key Results (OKR) are used to tell the direction of a business and how to get there. OKRs are made up of a high level objective, a more detailed description of why that objective is important, a summary of how the objective aligns with the broader goals of both the person’s team and the company, and the three to five key results that will help them achieve that goal.
From the mission & vision, you can derive your Objectives and the Todos are the things you do to achieve your Key Results.
They should be public.
- Ambitious
- Uncomfortable
- Qualitative
- Measurable: They should be easy to grade
- Quantitative
- They can be based on:
- Growth
- Engagement
- Revenue
- Performance
- Quality
- Set them annually and quartely
- A quarter and a year are timeframes in which you really can achieve something. The same timeframes are also used to evaluate companies
- Don't have too many
- 5 Objectives with 4 Key Results each is your maximum per quarter
- Having more will only distract you from what really needs to be done.
- Make them challenging.
- Research demonstrates that people who set challenging targets achieve more.
- Expect to get to 70-80% of your challenging target.
- A KR must have a number.
- Number enable objective evaluation and create a learning process
- Only Key Results get graded. An Objective's grade is the average of its Key Results.
- A good Key Result always enables objetive grading.
- Objetive grading is necessary for learning
- Grading shall never be used for employee evaluation
- Use a scale from 0 to 1.
- Getting to 70-80% of your target will result in a .7 or .8 grade
- Grade your OKRs at the beginning of the next quarter
- If you constantly score a 1, your OKRs were not challenging enough.
- You should score a .7 or .8
- Lower grades should not be punished.
- You set too many OKRs per quarter
- You set OKRs for a week or a month
- You set a metric-driven Objective: The Objective needs to be inspirational, a call-to-action for all the people in the company
- Your Key Results are tasks, not results
- You don’t set confidence levels
- You use the four-square as a status, not as a conversation
- You Make OKRs part of the performance review
- There is the risk for sandbagging
- Why would you gamble your livelihood on bold goals when you can set goals you can actually meet.
- There is the risk for sandbagging
- You sell barbeques online.
- You want to grow revenue to 1 million this quarter (objective)
- Rank Top 3 in Google's Search Results for 'buy barbeque'
- Run a 20%- discount-campaign in 2 national newspaper
- You want to grow revenue to 1 million this quarter (objective)
- Objective: Tell you where to go
- Key Results: Tell you how to get there