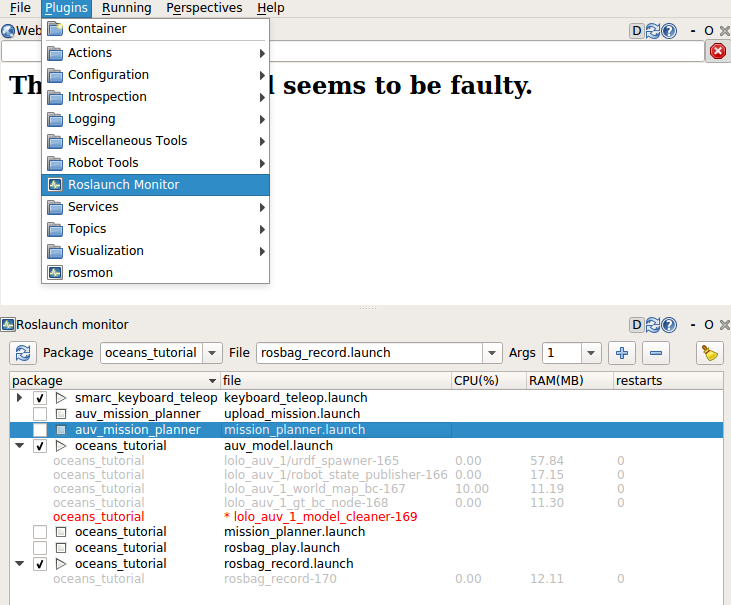
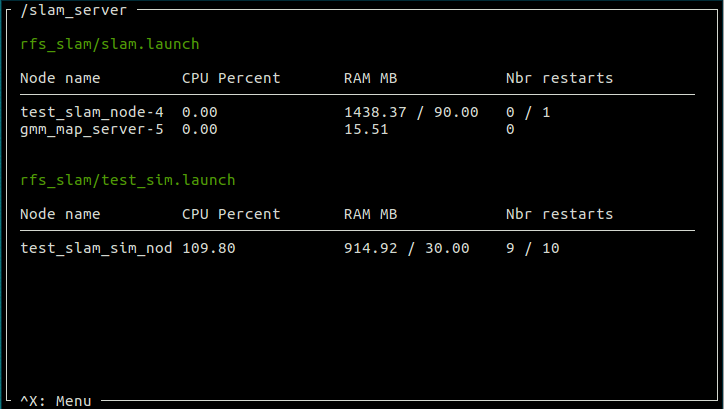
Provides a roslaunch server that can be invoked by actionlib, and that monitors CPU and RAM usage
The interface requires npyscreen: sudo pip install npyscreen
There are four ways of using the monitor server.
All of the them requires first having the launch_server running:
rosrun roslaunch_monitor launch_server.py
rosrun roslaunch_monitor monitor_server.py my_pkg my_file.launch my_parameter:=42
This way requires already having a monitor_server instance running,
same as above. The monitor server may also be invoked without any
arguments. After we have the launch_server and monitor_server
running, we can call the service:
rosservice call /monitor_server/monitor_launch "pkg: 'my_pkg'
launch_file: 'my_file.launch'
parameters: ['my_parameter']
values: ['42']
monitor_cfg: ''"
The service will return the launch_id value, which we may keep
track of if we want to shut down the launch file again,
using the following call:
rosservice call /monitor_server/cancel_launch "launch_id: 2"
We may also configure our launch files programatically, in Python.
This gives us a UI, same as the monitor_server above.
import rospy
from roslaunch_monitor.monitor_app import MonitorApp
rospy.init_node('my_monitor_server')
App = MonitorApp()
slam_monitor_cfg = {'test_slam_node': [{'condition': 'cpu_percent', 'action': 'RESTART', 'limit': 90, 'window': 100},
{'condition': 'nbr_restarts', 'action': 'KILL', 'limit': 1}]}
sim_monitor_cfg = {'test_slam_sim_node': [{'condition': 'ram_mb', 'action': 'RESTART', 'limit': 30, 'window': 10},
{'condition': 'nbr_restarts', 'action': 'KILL', 'limit': 10}]}
App.queue_launch("rfs_slam", "test_sim.launch", sim_monitor_cfg)
App.queue_launch("rfs_slam", "slam.launch", slam_monitor_cfg)
App.run()
You can also launch nodes using the RQT plugin interface as shown below.
Note that you can not use this interface for monitoring, or for killing/restarting
individual nodes.