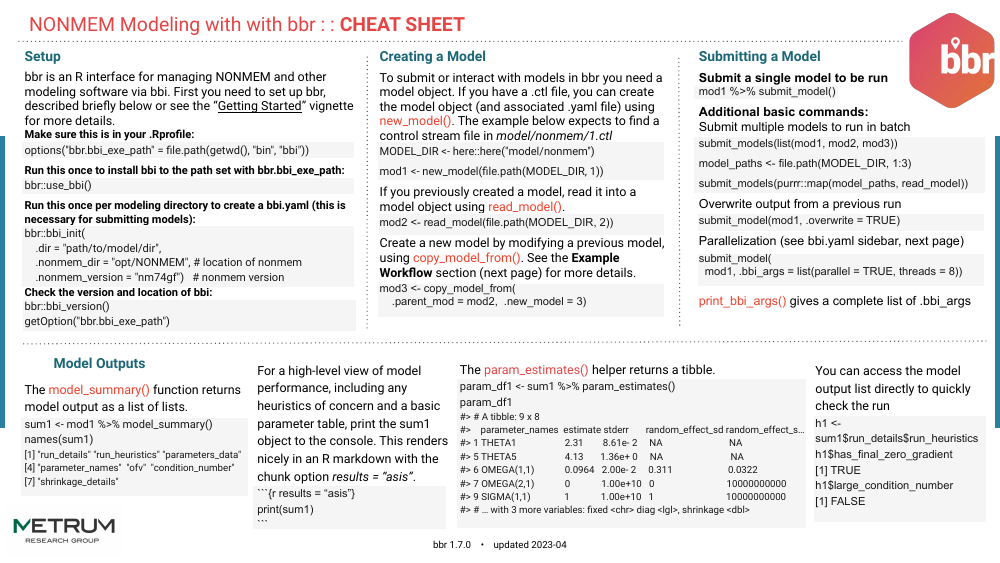
bbr helps manage the entire modeling workflow from within R. Users can
submit models, inspect output and diagnostics, and iterate on models.
Furthermore, workflow tools—such as simple tagging of models and model
inheritance trees—make reproducibility and external review more
streamlined.
bbr supports running NONMEM models via the
bbi command-line tool,
with a focus on non-Bayesian methods. The
bbr.bayes package
extends bbr to enable Bayesian estimation through either NONMEM or
Stan.
You can install the latest released version of bbr via MPN
snapshots from any snapshot
date in 2021 or later. (An earlier version of this package was available
under the name rbabylon in snapshot dates 2020-03-07 through
2020-12-21.)
You can also install development versions of bbr by downloading the
source files for the latest version from
https://s3.amazonaws.com/mpn.metworx.dev/releases/bbr/ or get the
latest development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("metrumresearchgroup/bbr", ref = "main")You can find documentation and a “Getting Started” vignette that shows
users how to set up bbr and demonstrates the basic modeling workflow
here.
There are several other vignettes, and more are being added as new functionality is rolled out. A complete list can be found here.
- Getting Started with
bbr
– Some basic scenarios for modeling with NONMEM using
bbr, introducing you to its standard workflow and functionality. - Using the based_on
field
– How to use the
based_onfield to track a model’s ancestry through the model development process, as well how to leverageconfig_log()to check whether older models are still up-to-date. - Creating a Model Summary
Log
– How to use
summary_log()to extract model diagnostics like the objective function value, condition number, and parameter counts.
bbr uses pkgr to manage
development dependencies and renv to
provide isolation. To replicate this environment,
-
clone the repo
-
install pkgr
-
open package in an R session and run
renv::init(bare = TRUE)- install
renv> 0.8.3-4 into default.libPaths()if not already installed
- install
-
run
pkgr installin terminal within package directory -
restart session
Then, launch R with the repo as the working directory (open the project in RStudio). renv will activate and find the project library.