This series will involve exercises to practice and learn docker.But, before that let's dive-in a litle and understand Docker by answering a few Wh-questions realted to it.
Docker is a tool designed to make it easier to create, deploy, and run applications by using containers. Docker combines all the dependencies into a container allowing it to run independent of environment.
To understand how docker works, let us take an example of frozen food. You went to market and brought one of the packets and then cooked it directly using oil or water, whatever is required. It does not matter if the raw material required to make the dish is available around you or you know how to cook it. All you need is the packet and some oil.And now you cooked it perfectly.
Similarly,The Docker works. The Packet here is the Image of the application, the oil- Docker CLI.
The user need not to worry about the dependencies like the condition or the recipe in the former case, all that is handled by Docker.
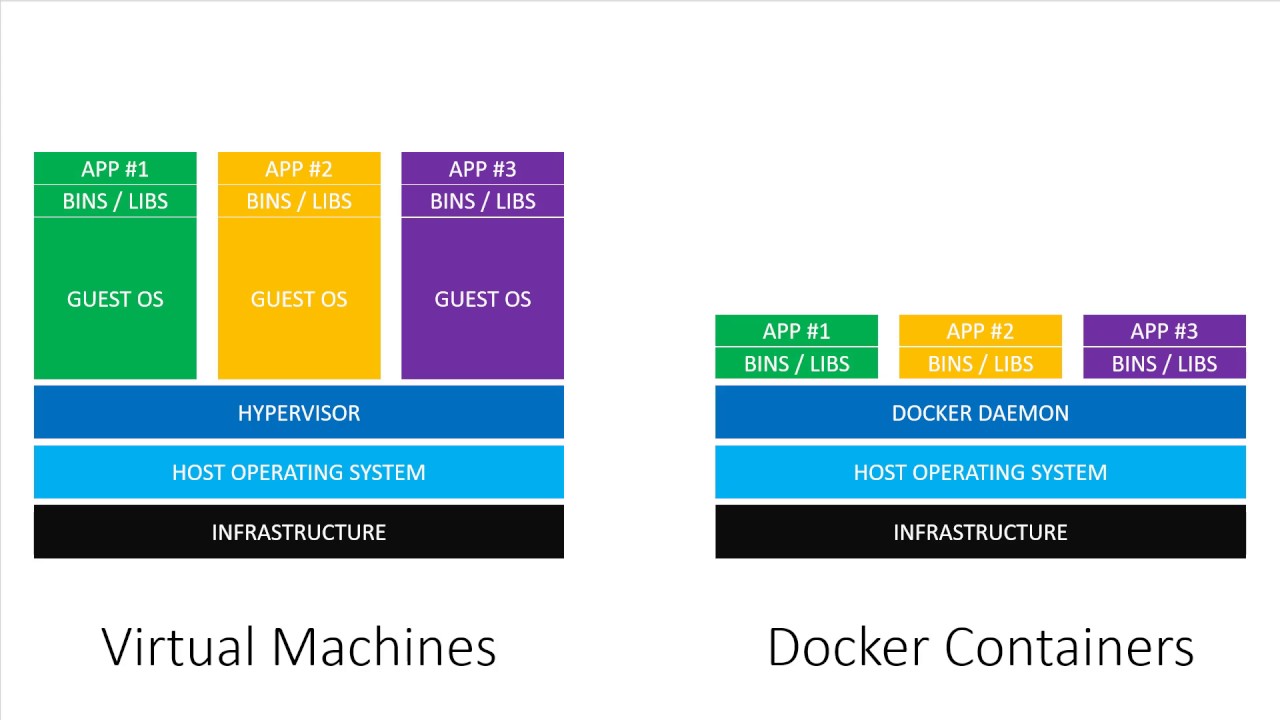
Containers are analogous to VM, but the main difference is the shared Kernel in Containers. For every replica of an application a new Guest OS is used in VM which consumes the majority of resources available for the container. While in Containers the host is shared thus saving the resources for the processes running.
Another difference between is the space consumed by an application. Size of ubuntu on a VM is approx 2 GB, While the size of ubuntu image is just 188 MB. The storage makes is more convenient to use Docker.
For better understanding check out this video or this article.
To create a Docker Image, a set of instrctuions are written in a Dockerfile. Which compiles to form a Docker Image containing all the dependencies and processes in the form of layers for the application.
The working state of an Image is called a Container.
Docker images are stored in Docker Registry . User can interact his/her image of an application using simple Docker commands push and pull.
All the images are stored on Docker Registery with tags for multiple versions, thus a user can deal with multiple versions of same applications using the tags.
The Images on Registry can either be private or public depending on users need.
The fundamentals about Docker has been covered up with these Wh-Questions.
We will go through a Practical approach with next article for better understnding of using Docker.
Thankyou❤