Back | Next | Contents
Transfer Learning
Transfer learning is a technique for re-training a DNN model on a new dataset, which takes less time than training a network from scratch. With transfer learning, the weights of a pre-trained model are fine-tuned to classify a customized dataset. In these examples, we'll be using the ResNet-18 network, although you can experiment with other networks too.
Although training is typically performed on a PC, server, or cloud instance with discrete GPU(s) due to the often large datasets used and the associated computational demands, by using transfer learning we're able to re-train various networks onboard Jetson to get started with training and deploying our own DNN models.
PyTorch is the machine learning framework that we'll be using, and example datasets along with training scripts are provided to use below, in addition to a camera-based tool for collecting and labelling your own training datasets.
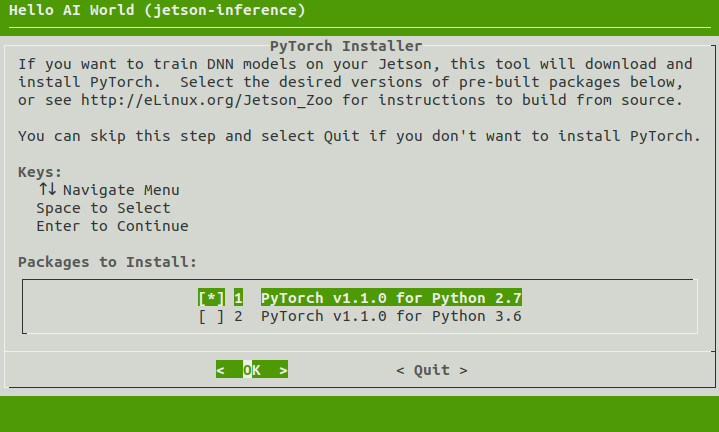
If you optionally chose to install PyTorch back when you built the repo, it should already be installed on your Jetson to use. Otherwise, if you want to proceed with transfer learning, you can install it now:
$ cd jetson-inference/build
$ ./install-pytorch.shnote: the automated PyTorch installation tool requires JetPack 4.2 or newer.
for other versions, seehttp://eLinux.org/Jetson_Zooto build from source.
You can test that PyTorch was installed correctly and detects your GPU by executing these commands from an interactive Python shell - run python or python3 from a terminal:
>>> import torch
>>> print(torch.__version__)
>>> print('CUDA available: ' + str(torch.cuda.is_available()))
>>> a = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(2).zero_()
>>> print('Tensor a = ' + str(a))
>>> b = torch.randn(2).cuda()
>>> print('Tensor b = ' + str(b))
>>> c = a + b
>>> print('Tensor c = ' + str(c))>>> import torchvision
>>> print(torchvision.__version__)Note that the torch version should be reported as 1.1.0 and the torchvision version should be 0.3.0.
If you're using Jetson Nano, you should mount 4GB of swap space, as training uses up a lot of extra memory.
Run these commands on Nano to create a swap file:
sudo fallocate -l 4G /mnt/4GB.swap
sudo mkswap /mnt/4GB.swap
sudo swapon /mnt/4GB.swapThen add the following line to the end of /etc/fstab to make the change persistent:
/mnt/4GB.swap none swap sw 0 0Now your swap file will automatically be mounted after reboots. To check the usage, run swapon -s or tegrastats.
Below are step-by-step instructions to re-training models on some example datasets with transfer learning, in addition to collecting your own data to create your own customized models:
- Re-training on the Cat/Dog Dataset
- Re-training on the PlantCLEF Dataset
- Collecting your own Datasets
This table contains a summary of the datasets and their associated training times:
| Dataset | Size | Classes | Training Images | Time per Epoch* | Training Time** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cat/Dog |
800MB | 2 | 5,000 | ~7-8 minutes | ~4 hours |
PlantCLEF |
1.5GB | 20 | 10,475 | ~15 minutes | ~8 hours |
* Approximate time for one complete training pass over the dataset with Jetson Nano
** Approximate time for training the model for 35 epochs with Jetson Nano
Next | Re-training on the Cat/Dog Dataset
Back | Running the Live Camera Segmentation Demo
© 2016-2019 NVIDIA | Table of Contents