In many graphical applications there is the need to check whether one object is overlapping with some other object. A web browser might check to see if the (x, y) coordinates of a mouse-click overlaps with a button on the screen so that it can submit the form. A game will check to see if two objects are overlapping to determine if there was a collision. A CAD program might check for overlapping objects to determine if a given layout is feasible.
One basic scenario would be to check whether a given (x, y) coordinate is overlapping with some object. A simple technique is to wrap the entire object in a rectangle called a bounding box and then check whether the point is located within that box. A point is overlapping as long as it meets the following conditions:
- The
xcoordinate is greater than or equal to the left edge of the box. - The
xcoordinate is less than or equal to the right edge of the box. - The
ycoordinate is greater than or equal to the bottom edge of the box. - The
ycoordinate is less than or equal to the top edge of the box.
y ↑
|
|
|
| width
| +----------+
| | |
| | | height
| | |
| +----------+
| (x,y)
|
|
|
------+----------------------------→
(0,0)| x
|
|
Create a BoundingBox class to represent the rectangle. The initialize method should take these arguments in the following order:
xcoordinateycoordinatewidthheight
The BoundingBox class should have the following instance methods:
widthreturns the width of the box.heightreturns the height of the box.leftreturns the left edge of the box.rightreturns the right edge of the box.topreturns the top edge of the box.bottomreturns the bottom edge of the box.contains_point?(x, y)returns true if the given (x, y) coordinate is within the box.
Use a Cartesian coordinate system where values along the x axis increase moving to the right and values along the y axis increase moving up.
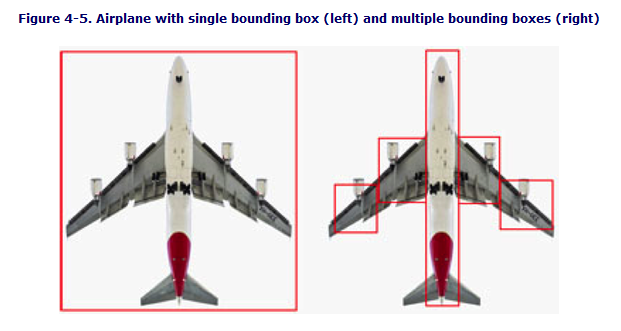
For some objects a single rectangle does not match the shape of the object and covers too much area. One solution is to use multiple, smaller bounding boxes to get more fine-grained control over the bounding area as shown in the following image:
Create a BoundingArea class that represents a collection of individual bounding boxes. It should implement the following method:
boxes_contain_point?(x, y)returns true if the given (x, y) coordinate is contained within any of the bounding boxes for this area.
Placeholders for both classes can be found in lib/bounding_box.rb and lib/bounding_area.rb. A test suite for the two classes has been supplied and can be run with the following command:
$ rspec spec
You should receive the following errors:
FFFFFFFFFFFF
Failures:
1) BoundingArea#boxes_contain_point? is always false for an empty bounding area
Failure/Error: empty_area = BoundingArea.new([])
ArgumentError:
wrong number of arguments (1 for 0)
# ./spec/bounding_area_spec.rb:7:in `initialize'
# ./spec/bounding_area_spec.rb:7:in `new'
# ./spec/bounding_area_spec.rb:7:in `block (3 levels) in <top (required)>'
<more failures here>
Finished in 0.00778 seconds
12 examples, 12 failures
Failed examples:
<more failures here>
Review the files in the spec directory to determine how the BoundingBox and BoundingArea classes are used. By doing so, you will determine the appropriate method names, the arguments for these methods, and the appropriate return values for these methods in each class. Start by implementing the BoundingBox class. If you would like to run only the BoundingBox tests, use this command: rspec ./spec/bounding_box_spec.rb. Once all of the tests for BoundingBox are passing, implement the BoundingArea class.