| cherry | Windson |
|---|---|
| Download | https://pypi.python.org/pypi/cherry |
| Source | https://github.com/Windsooon/cherry |
| Keywords | text classification |
-
No machine learning knowledge needed, easy to customize
cherry comes with two built-in Chinese models. We only need one line of code to classify text using pre-trained models. No more than 10 lines of code to train your dataset. Moreover, cherry supports custom tokenizer methods, classify methods and stop words.
-
High accuracy, recall rate
On average, the small data set (1000 data contains 4 categories) achieved an accuracy of 96% and a recall rate. In large data sets (50,000 data contains 7 categories, data from here) averaged 97% accuracy and recall rate.
-
Support multiple methods
Support all feature extraction method and classify method in sklearn. you can use
search()to find the optimal algorithm and parameters of a specific data set. -
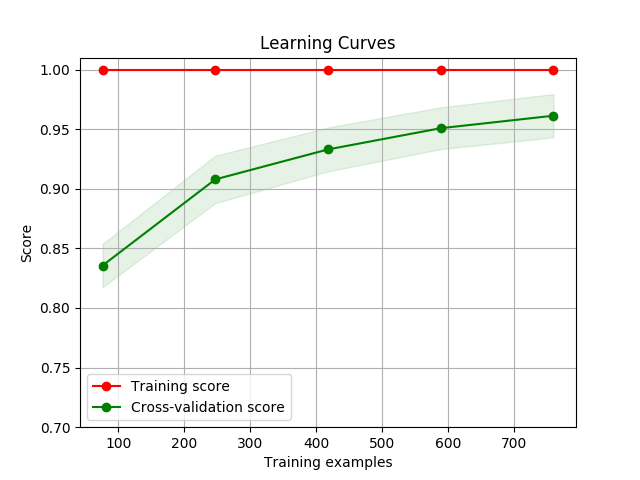
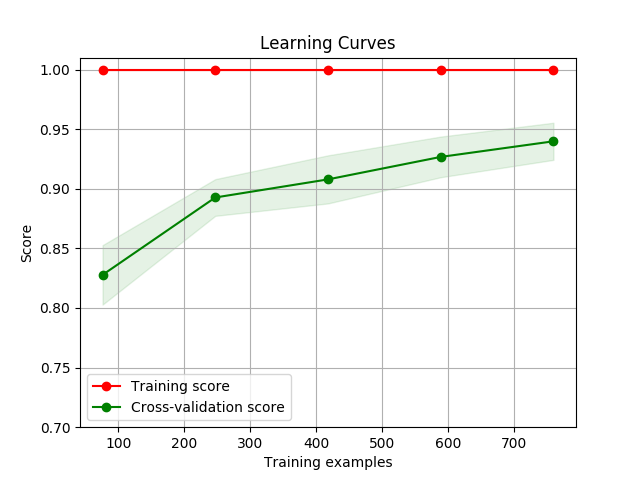
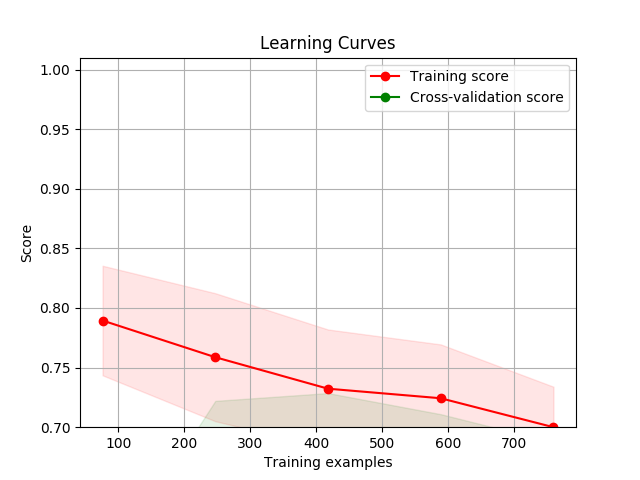
Visualization
Draw a learning curve image to determine if the model is over-fitting or under-fitting with
display()
pip install -U cherry
Because the training data is too large, cherry library does not contain any training data, so the pre-trained models only support the classify() method. The pre-trained models contain two datasets, respectively
- Gamble / Normal / Political / Porn (1000 chinese text data contains 4 categories which model name is 'harmful'.)
- Lottery ticket / Finance / Estate / Home / Tech / Society / Sport / Game / Entertainment (50000 chinese news contains 7 categories which model name is 'news',)
Using the pre-trained model for text classification is simple. You can specify two parameters in classify(). text is a list of text to be classified. The models is the model name (Like harmful, news).
>>> res = cherry.classify(model='harmful', text=['她们对计算机很有热情,也希望学习到数据分析,网络爬虫,人工智能等方面的知识,从而运用在她们工作上'])
>>> res.word_list
[(2, '她们'), (1, '网络'), (1, '热情'), (1, '方面'), (1, '数据分析'), (1, '希望'), (1, '工作'), (1, '学习'), (1, '从而')]
>>> res.probability
# The probabilities of the text from different categories
array([[4.43336608e-03, 9.95215198e-01, 3.51419231e-04, 1.68657851e-08]])
res object contains word_list and probability. word_list contains the first 20 words in the text to be classified (in descending order of appearance frequency), and probability contains the probability under the corresponding category index (the index is consistent with the last category of each training data).
There are two ways to use a custom dataset. First, you can pass the training data and its label to the train() API. For more details, checkout out Training. Second, you can use your own dataset for training as shown below.
The dataset should include two files (just like the example in example/data_example)
- training data
data.xxx(file name begins withdata) - stop words
stop_words.xxx(file name begin withstop_words)
Each row in the data.xxx represents a training data, it should end with ',' + 'category index':
This is a training data,0
This is another training data,1
...
cherry will extract the last index (0, 1, etc.) of each row as an index for the output of res.probability
Each row in the stop_words.xxx should include a stop word like this:
because
before
both
...
- Create a new folder
your_folderinside thedatafolder, your data, stop words file and cache will be stored in this folder. - Put
data.xxxandstop_words.xxxintoyour_folder,your_folderis the model name you will use later in all of the APIs.
Before training, you can use a custom tokenizer function. cherry uses jieba to support Chinese tokenizer by default (under base.py/tokenizer()). The tokenizer function should accept the text as input and return a list that includes all the tokens. For English, you can use nltk by uncommenting the code inside base.py:
# base.py
def tokenizer(text):
'''
You can use your tokenizer function here, by default,
this function only works for Chinese
'''
# For English:
# from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
# return [t.lower() for t in word_tokenize(text) if len(t) > 1]
return [t for t in jieba.cut(text) if len(t) > 1]
>>> cherry.train(model='your_folder_name')
That is it,You can also pass the data to the train() function. For instance,
>>> from sklearn import datasets
>>> iris = datasets.load_iris()
>>> x_data, y_data = iris.data, iris.target
>>> cherry.train(model='your_folder_name', x_data=x_data, y_data=y_data)
You still have to create your_folder to store the cache files. By default, cherry will use CountVectorizer for feature extraction and MultinomialNB for text classification. You can also pass the feature extraction function and classify function to the train() API if you are familiar with sklearn.
>>> from sklearn import datasets
>>> iris = datasets.load_iris()
>>> x_data, y_data = iris.data, iris.target
>>> cherry.train(model='your_folder_name', clf_method='SGD', vectorizer_method ='Tfidf ', x_data=x_data, y_data=y_data)
For more details, you can have a look at API. For unbalanced dataset you can custome priori probability.
>>> from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
>>> mnb = MultinomialNB(class_prior=[0.4, 0.15, 0.15, 0.15, 0.15, 0.1])
>>> cherry.train(model='your_folder')
>>> res = cherry.classify(model='your_data_name', text=['your text'])
In order to save memory, you can use HashingVectorizer or TfidfVectorizer for feature extraction for big dataset.
After training, cherry will create cache files under your_folder. You can classify your data use classify():
>>> res = cherry.classify(model='harmful', text=['她们对计算机很有热情,也希望学习到数据分析,网络爬虫,人工智能等方面的知识,从而运用在她们工作上'])
>>> res.word_list
[(2, '她们'), (1, '网络'), (1, '热情'), (1, '方面'), (1, '数据分析'), (1, '希望'), (1, '工作'), (1, '学习'), (1, '从而')]
>>> res.probability
# The probabilities
array([[4.43336608e-03, 9.95215198e-01, 3.51419231e-04, 1.68657851e-08]])
performance() calculates the CV score after splitting the training data into n_splits
>>> cherry.performance(model='harmful', n_splits=5)
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.98 1.00 0.99 44
1 0.96 0.88 0.92 52
2 0.90 0.96 0.93 49
3 1.00 1.00 1.00 45
accuracy 0.96 190
macro avg 0.96 0.96 0.96 190
weighted avg 0.96 0.96 0.96 190
You can use thedisplay() API to display the learning curve using different feature extraction functions and classify functions.
>>> cherry.display(model='harmful', clf_method='SGD')
You can pass the parameters you want to search, then calculate its best score
>>> parameters = {
... 'clf__alpha': [0.1, 0.5, 1],
... 'clf__fit_prior': [True, False]
... }
>>> cherry.search(model='harmful', parameters)
score is 0.9199693815090905
clf__alpha: 0.1
clf__fit_prior: True
def train(model, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None)
-
model (string)
training model, default None, include
harmfulandnews -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
feature extraction function,default
CountVectorizer(). You can pass feature extraction function from sklearn.Short text suggests using
CountVectorizer(),long text suggests usingTfidfVectorizer(),big dataset can useHashingVectorizer()to save memory. -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up feature extraction function (only when
vectorizerisNone). ShortcutCountcorrespondCountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizeris the tokenizer function inbase.py.TfidfcorrespondTfidfVectorizerandHashingcorrespondHashingVectorizer. -
clf (sklearn object)
classify function, you can pass classify function from sklearn, by default is
MultinomialNB() -
clf_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up classify function (only when
clfisNone),MNBcorrespondMultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGDcorrespondSGDClassifier,RandomForestcorrespondRandomForestClassifier,AdaBoostcorrespondAdaBoostClassifier. -
x_data (numpy array)
training text data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel -
y_data (numpy array)
correspond labels data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel
-
text (list)
text data to be classified
-
model
modelto be used,pre-trained models includeharmfulandnews. -
N
the token number in the
word_list
Object return from classify
-
word_list
The top N most common tokens in the classified text
-
probability
Correspond probabilities from the classified text
array([[4.43336608e-03, 9.95215198e-01, 3.51419231e-04, 1.68657851e-08]])
def performance(model, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None, n_splits=5, output='Stdout')
-
model (string)
modelto be used,pre-trained model includesharmfulandnews. -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
feature extraction function,default
CountVectorizer(). You can pass feature extraction function from sklearn.Short text suggests using
CountVectorizer(),long text suggests usingTfidfVectorizer(),big dataset can useHashingVectorizer()to save memory. -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up feature extraction function (only when
vectorizerisNone). ShortcutCountcorrespondCountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizeris the tokenizer function inbase.py.TfidfcorrespondTfidfVectorizerandHashingcorrespondHashingVectorizer. -
clf (sklearn object)
classify function, you can pass classify function from sklearn, by default is
MultinomialNB() -
clf_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up classify function (only when
clfisNone),MNBcorrespondMultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGDcorrespondSGDClassifier,RandomForestcorrespondRandomForestClassifier,AdaBoostcorrespondAdaBoostClassifier. -
x_data (numpy array)
training text data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel -
y_data (numpy array)
correspond labels data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel -
n_splits (int)
K to use when using Kfold for cross validation
-
output (file path)
The file path include all the export data, by default is terminal.
def search(model, parameters, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None, method='RandomizedSearchCV', cv=3, iid=False, n_jobs=1)
-
model (string)
modelto be used,pre-trained model includesharmfulandnews. -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
feature extraction function,default
CountVectorizer(). You can pass feature extraction function from sklearn.Short text suggests using
CountVectorizer(),long text suggests usingTfidfVectorizer(),big dataset can useHashingVectorizer()to save memory. -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up feature extraction function (only when
vectorizerisNone). ShortcutCountcorrespondCountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizeris the tokenizer function inbase.py.TfidfcorrespondTfidfVectorizerandHashingcorrespondHashingVectorizer. -
clf (sklearn object)
classify function, you can pass classify function from sklearn, by default is
MultinomialNB() -
clf_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up classify function (only when
clfisNone),MNBcorrespondMultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGDcorrespondSGDClassifier,RandomForestcorrespondRandomForestClassifier,AdaBoostcorrespondAdaBoostClassifier. -
x_data (numpy array)
training text data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel -
y_data (numpy array)
correspond labels data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel -
method (string)
'RandomizedSearchCV' or 'GridSearchCV' from sklearn, default it 'RandomizedSearchCV'
-
cv (int)
K to use when using Kfold for cross validation
-
iid (boolean)
checkout out [here](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV.html
-
n_jobs (int)
Number of processors to use
def display(model, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None)
-
model (string)
modelto be used,pre-trained model includesharmfulandnews. -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
feature extraction function,default
CountVectorizer(). You can pass feature extraction function from sklearn.Short text suggests using
CountVectorizer(),long text suggests usingTfidfVectorizer(),big dataset can useHashingVectorizer()to save memory. -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up feature extraction function (only when
vectorizerisNone). ShortcutCountcorrespondCountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizeris the tokenizer function inbase.py.TfidfcorrespondTfidfVectorizerandHashingcorrespondHashingVectorizer. -
clf (sklearn object)
classify function, you can pass classify function from sklearn, by default is
MultinomialNB() -
clf_method (string)
cherry supports use shortcut to set up classify function (only when
clfisNone),MNBcorrespondMultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGDcorrespondSGDClassifier,RandomForestcorrespondRandomForestClassifier,AdaBoostcorrespondAdaBoostClassifier. -
x_data (numpy array)
training text data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel -
y_data (numpy array)
correspond labels data, if
x_dataandy_datais None, cherry will try to find the text files data inmodel
-
无需机器学习知识,开箱即用,定制简单
cherry 自带两个预训练模型,使用预训练模型进行分类只需一行代码。使用自己的数据集进行定制训练也只需要十行代码。同时 cherry 支持自定义分词算法,分类算法以及 stop words 词库。
-
高精确率,召回率
在小型数据集(4个类别 共 1000条 数据)平均达到 96% 精确率以及召回率。在大型数据集(7个类别 共 5万条 数据,数据来自这里)平均达到 97% 精确率以及召回率。
-
支持多种自定义算法
定制模式下,支持 sklearn 中所有特征工程函数以及分类器。并可以通过
search()找出特定数据集的最优算法以及参数。 -
可视化
轻松绘制学习曲线图像,判断模型是否过拟合或者欠拟合。
pip install -U cherry
由于数据量过大,cherry 库并没有包含训练数据,所以预训练模型只支持 classify() 方法,使用其他方法需使用自定义数据集。 预训练模型包含 2个 数据集,分别是:
- 赌博 / 正常 / 政治 / 色情 (
model='harmful',4个 类别包含约 1000条 中文句子) - 彩票 / 科技 / 财经 / 房产 / 社会 / 体育 / 娱乐 (
model=news,7个 类别包含约 45000条 中文新闻)
使用预训练模型进行文本分类非常简单,只需要直接调用 classify() 方法,可以指定两个参数,text 是由待分类文本组成的列表,models 是训练时指定的文件夹名。
>>> res = cherry.classify(model='harmful', text=['她们对计算机很有热情,也希望学习到数据分析,网络爬虫,人工智能等方面的知识,从而运用在她们工作上'])
>>> res.word_list
[(2, '她们'), (1, '网络'), (1, '热情'), (1, '方面'), (1, '数据分析'), (1, '希望'), (1, '工作'), (1, '学习'), (1, '从而')]
>>> res.probability
# 返回结果分别对应 赌博,正常,政治,色情 4个 类别的概率
array([[4.43336608e-03, 9.95215198e-01, 3.51419231e-04, 1.68657851e-08]])
返回的 res 对象包含 word_list 以及 probability。其中 word_list 包含待分类文本中前 20个 词语(按出现频率降序排列),probability 包含对应类别索引下的概率(索引与每一条训练数据最后的类别一致)。
有两种方法使用自定义数据集。第一,你可以直接把数据以及对应参数直接传给 train() API,具体方式请参考训练。第二,通过文本文件进行训练。
数据集需要包含两个文件(参考 example/data_example 文件夹)
- 数据集
data.xxx(需命名为data开头,任意后缀的文件) - 停止词
stop_words.xxx(需命名为stop_words开头,任意后缀的文件,停止词可直接拷贝example文件夹中自带的stop_words.txt)
数据集中每一行代表一条数据,数据结束后需要添加 ',' 以及对应的分类类别(不需要空格),例如:
这是一条正常数据,0
这是赌博相关数据,1
cherry 会提取每一行数据最后的类别作为标签进行训练。
stop_words.xxx 文件每行包含一个停止词,例如
或者
不只
而且
还有
即使
接着
具体步骤
- 在 data 文件夹内新建
your_folder文件夹,你的模型所有数据以及生成的缓存都会存放在此文件夹中。 - 把
data.xxx以及stop_words.xxx放在文件夹中(可参考例子)。your_folder用作调用 APIs 时需要的model参数。
在开始训练前,你可以自定义分词函数,cherry 默认使用 jieba 进行中文分词,你也可以使用其他第三方库或者自行实现。此函数接受输入待分类文本,并返回分词后词语组成的列表。它位于 base.py 中的 tokenizer()
# base.py
def tokenizer(text):
'''
You can use your own tokenizer function here, by default,
this function only work for chinese
'''
# For English:
# from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
# return [t.lower() for t in word_tokenize(text) if len(t) > 1]
return [t for t in jieba.cut(text) if len(t) > 1]
>>> cherry.train(model='your_folder')
训练就是那么简单,你也可以把测试数据传到 train() 函数进行训练,这里以 sklearn 中的 iris 数据集为例
>>> from sklearn import datasets
>>> iris = datasets.load_iris()
>>> x_data, y_data = iris.data, iris.target
>>> cherry.train(model='your_data_name', x_data=x_data, y_data=y_data)
注意,你依然需要新建 your_folder 文件夹用来存放缓存文件,cherry 默认会使用 CountVectorizer 进行特征提取,使用 MultinomialNB 进行训练。如果你熟悉 sklearn,你也可以自定义特征函数以及分类函数
>>> from sklearn import datasets
>>> iris = datasets.load_iris()
>>> x_data, y_data = iris.data, iris.target
>>> cherry.train(model='your_folder_name', clf_method='SGD', vectorizer_method ='Tfidf ', x_data=x_data, y_data=y_data)
具体使用方法可以参考 API。非均衡数据集可以自定义先验概率:
>>> from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
>>> mnb = MultinomialNB(class_prior=[0.4, 0.15, 0.15, 0.15, 0.15, 0.1])
>>> cherry.train(model='your_data_name')
>>> res = cherry.classify(model='your_data_name', text=['your text'])
在大型数据集中,可以使用 HashingVectorizer 和 TfidfVectorizer 以节省内存。
训练完之后,cherry 会在 your_folder 下生成训练模型缓存,调用 classify() 就能直接使用模型进行分类了,
>>> res = cherry.classify(model='harmful', text=['她们对计算机很有热情,也希望学习到数据分析,网络爬虫,人工智能等方面的知识,从而运用在她们工作上'])
>>> res.word_list
[(2, '她们'), (1, '网络'), (1, '热情'), (1, '方面'), (1, '数据分析'), (1, '希望'), (1, '工作'), (1, '学习'), (1, '从而')]
>>> res.probability
# 返回结果分别对应 赌博,正常,政治,色情四个类别的概率
array([[4.43336608e-03, 9.95215198e-01, 3.51419231e-04, 1.68657851e-08]])
performance() 方法能够计算出输入模型分成 n_splits 份后交叉检验得出的分数
>>> cherry.performance(model='harmful', n_splits=5)
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.98 1.00 0.99 44
1 0.96 0.88 0.92 52
2 0.90 0.96 0.93 49
3 1.00 1.00 1.00 45
accuracy 0.96 190
macro avg 0.96 0.96 0.96 190
weighted avg 0.96 0.96 0.96 190
使用 display() API 可以得出不同特征函数以及分类器下的学习曲线,以下为使用默认 MNB, SGD, RandomForest 方法下的默认参数的学习曲线图像
>>> cherry.display(model='harmful', clf_method='SGD')
通过把传人需要搜索的参数范围,可以得出最佳参数。
>>> parameters = {
... 'clf__alpha': [0.1, 0.5, 1],
... 'clf__fit_prior': [True, False]
... }
>>> cherry.search(model='harmful', parameters)
score is 0.9199693815090905
clf__alpha: 0.1
clf__fit_prior: True
def train(model, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None)
-
model (string)
使用的训练模型,默认模型包括
harmful,news和spam -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
特征函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 特征函数,默认使用
CountVectorizer(),短文本建议使用
CountVectorizer(),长文本建议使用TfidfVectorizer(),大型数据集可以使用HashingVectorizer()节省内存。 -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置特征函数(仅当
vectorizer为None时会被调用),'Count' 会调用CountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizer对应base.py中定义的分词函数。Tfidf对应TfidfVectorizer,Hashing对应HashingVectorizer。 -
clf (sklearn object)
分类函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 分类函数,默认使用
MultinomialNB()。 -
clf_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置常用分类函数(包含常用参数)(仅当
clf为None时会被调用),MNB会调用MultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGD对应SGDClassifier,RandomForest对应RandomForestClassifier,AdaBoost对应AdaBoostClassifier。 -
x_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,x_data包含全部训练文本。 -
y_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,y_data包含全部训练文本对应的类别。
-
text (list)
需要训练的文本列表内容
-
model
使用的训练模型,默认模型包括
harmful,news和spam -
N
word_list属性 中 输出的词语数量,默认为 20
返回对象的属性
-
word_list
包含待分类文本中前 N个 词语
-
probability
输入文本的对应的每个类别的概率,例如
array([[4.43336608e-03, 9.95215198e-01, 3.51419231e-04, 1.68657851e-08]])
def performance(model, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None, n_splits=5, output='Stdout')
-
model (string)
使用的训练模型,默认模型包括
harmful,news和spam -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
特征函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 特征函数,默认使用
CountVectorizer(),短文本建议使用
CountVectorizer(),长文本建议使用TfidfVectorizer(),大型数据集可以使用HashingVectorizer()节省内存。 -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置特征函数(仅当
vectorizer为None时会被调用),'Count' 会调用CountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizer对应base.py中定义的分词函数。Tfidf对应TfidfVectorizer,Hashing对应HashingVectorizer。 -
clf (sklearn object)
分类函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 分类函数,默认使用
MultinomialNB()。 -
clf_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置常用分类函数(包含常用参数)(仅当
clf为None时会被调用),MNB会调用MultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGD对应SGDClassifier,RandomForest对应RandomForestClassifier,AdaBoost对应AdaBoostClassifier。 -
x_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,x_data包含全部训练文本。 -
y_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,y_data包含全部训练文本对应的类别。 -
n_splits (int)
使用 Kfold 进行交叉检验时,K 的值。
-
output (file path)
输出结果,默认输出到终端,这里可以指定输出的文件名。
def search(model, parameters, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None, method='RandomizedSearchCV', cv=3, iid=False, n_jobs=1)
-
model (string)
使用的训练模型,默认模型包括
harmful,news和spam -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
特征函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 特征函数,默认使用
CountVectorizer(),短文本建议使用
CountVectorizer(),长文本建议使用TfidfVectorizer(),大型数据集可以使用HashingVectorizer()节省内存。 -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置特征函数(仅当
vectorizer为None时会被调用),'Count' 会调用CountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizer对应base.py中定义的分词函数。Tfidf对应TfidfVectorizer,Hashing对应HashingVectorizer。 -
clf (sklearn object)
分类函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 分类函数,默认使用
MultinomialNB()。 -
clf_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置常用分类函数(包含常用参数)(仅当
clf为None时会被调用),MNB会调用MultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGD对应SGDClassifier,RandomForest对应RandomForestClassifier,AdaBoost对应AdaBoostClassifier。 -
x_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,x_data包含全部训练文本。 -
y_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,y_data包含全部训练文本对应的类别。 -
method (string)
可以选择 'RandomizedSearchCV' 或者 'GridSearchCV' 方法
-
cv (int)
使用 Kfold 进行交叉检验时,K 的值。
-
iid (boolean)
默认为 False,返回 Kfold 检验的平均分数,如果为 真,则在此基础上,按照不同类别样本数进行加权,详情可以参考[这里](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV.html
-
n_jobs (int)
运行
search()时使用的处理器数量
def display(model, vectorizer=None, vectorizer_method=None, clf=None, clf_method=None, x_data=None, y_data=None)
-
model (string)
使用的训练模型,默认模型包括
harmful,news和spam -
vectorizer (sklearn object)
特征函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 特征函数,默认使用
CountVectorizer(),短文本建议使用
CountVectorizer(),长文本建议使用TfidfVectorizer(),大型数据集可以使用HashingVectorizer()节省内存。 -
vectorizer_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置特征函数(仅当
vectorizer为None时会被调用),'Count' 会调用CountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenizer, stop_words=get_stop_words(model)),tokenizer对应base.py中定义的分词函数。Tfidf对应TfidfVectorizer,Hashing对应HashingVectorizer。 -
clf (sklearn object)
分类函数,可以直接传入 sklearn 的 分类函数,默认使用
MultinomialNB()。 -
clf_method (string)
cherry 支持使用缩写来设置常用分类函数(包含常用参数)(仅当
clf为None时会被调用),MNB会调用MultinomialNB(alpha=0.1),SGD对应SGDClassifier,RandomForest对应RandomForestClassifier,AdaBoost对应AdaBoostClassifier。 -
x_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,x_data包含全部训练文本。 -
y_data (numpy array)
train()支持直接传入文本数据进行训练,y_data包含全部训练文本对应的类别。