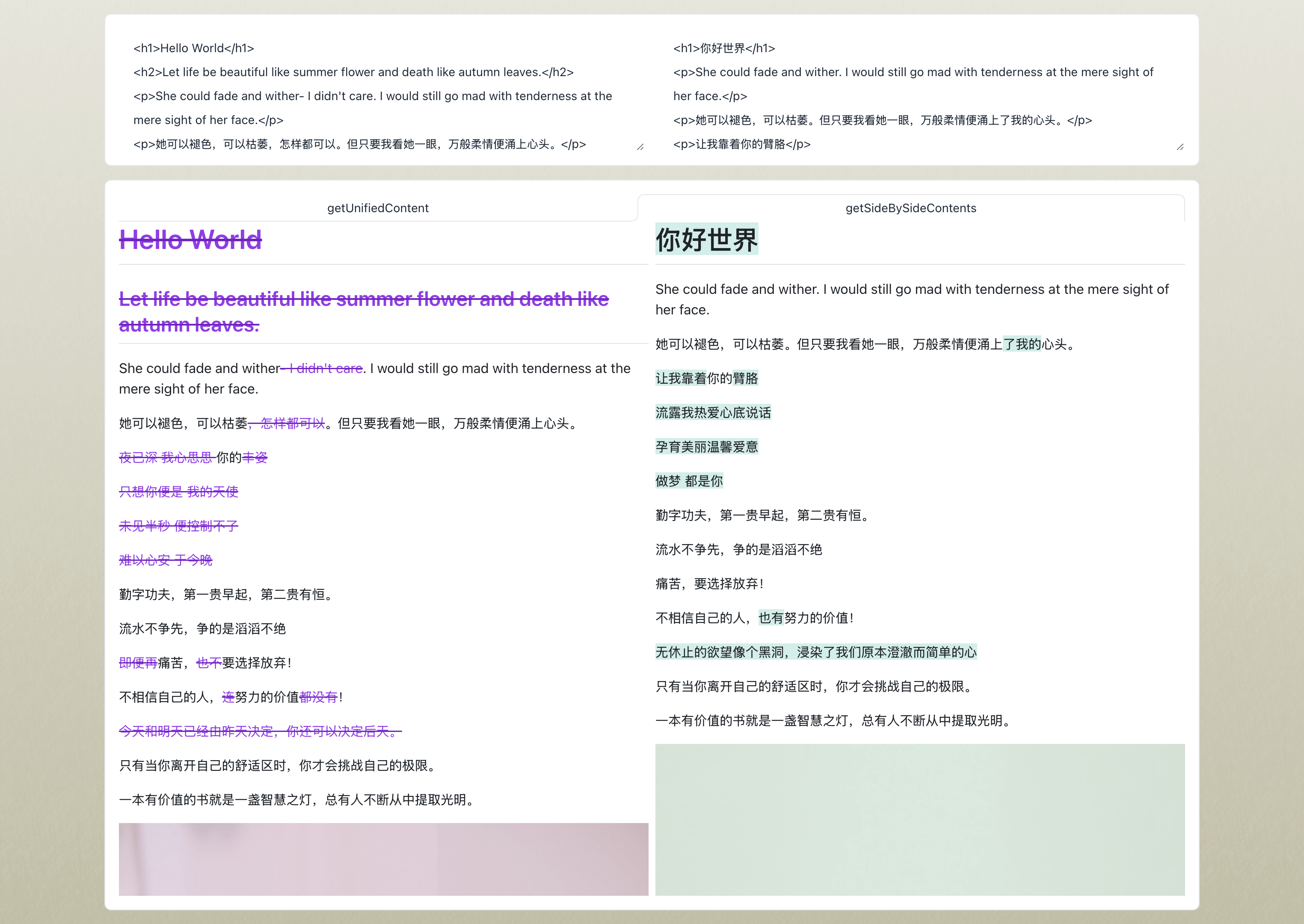
Compare HTML and generate the differences in either a unified view or a side-by-side comparison. See online demo...
pnpm add @armantang/html-diff
import '@armantang/html-diff/dist/index.css'
import HtmlDiff from '@armantang/html-diff'
const oldHtml = `<div>hello</div>`
const newHtml = `<div>hello world</div>`
const diff = new HtmlDiff(oldHtml, newHtml)
const unifiedContent = diff.getUnifiedContent()
const sideBySideContents = diff.getSideBySideContents()const diff = new HtmlDiff(oldHtml, newHtml, {
// options
})
interface HtmlDiffOptions {
/**
* Determine the minimum threshold for calculating common sub-tokens.
* You may adjust it to a value larger than 2, but not lower, due to the potential inclusion of HTML tags in the count.
* @defaultValue 2
*/
minMatchedSize?: number
/**
* When greedyMatch is enabled, if the length of the sub-tokens exceeds greedyBoundary,
* we will use the matched sub-tokens that are sufficiently good, even if they are not optimal, to enhance performance.
* @defaultValue true
*/
greedyMatch?: boolean
/**
* @defaultValue 1000
*/
greedyBoundary?: number
/**
* The classNames for wrapper DOM.
* Use this to configure your own styles without importing the built-in CSS file
*/
classNames?: Partial<{
createText?: string
deleteText?: string
createInline?: string
deleteInline?: string
createBlock?: string
deleteBlock?: string
}>
}In the sideBySideContents, some elements have the data-seq attribute. We can use this to implement synchronized scrolling. Click to see the demo.